Subsistence Strategies: An Overview
advertisement

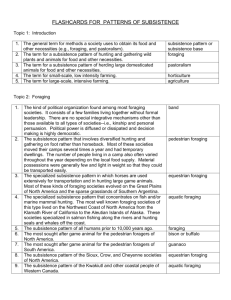
Subsistence Strategies Objectives 4/10 Describe the typologies for subsistence strategies and political organizations. Compare typologies. ____________________________________ Question Is Woody High a macro or micro culture? Why? Subsistence Strategies The way people in a society make a living Provide for their basic needs Subsistence strategies and political organizations are closely integrated Subsistence Strategies 2 different kinds Extensive Involves large areas of land and minimal labor input per acre Foraging 2. Horticulture 3. Pastoralism 1. Intensive Involves the cultivation of small amounts of land through the spending of great amounts of labor per acre 1. Agriculture 2. Industrialism Weekly Plan Pick subsistence strategy Provide notes for each section Use books and provided information Chapter 17 (p. 437-453) Write neatly Compile information for a master copy by Thursday Objectives 4/11 Understand foraging as a subsistence strategy. Describe specific aspects of foraging. _____________________________________ Which group of subsistence strategies uses the most amount of land? Foraging Oldest strategy Only form until 10-12,000 years ago Kin based bands made up of 100 people, no more! Leader is typically not special but has more responsibilities Speaks for the group Temporary encampments Men typically hunt large game Women gather and hunt small game close to camp Foraging Cont. Least complicated form of government Own dogs Herding, watch-animals, camp scavengers Controlled burns Burn off old vegetation to grow new fresh vegetation Social conflict controls the group number Misconceptions Short miserable lives Hard to find food Start work at a young age Objectives 4/12 Describe and identify horticulture and pastoralism as subsistence strategies Form a comparison between the subsistence strategies. _____________________________________ Name a misconception of foraging societies. Horticulture Small scale, low intensity farming Humid, tropical conditions Supplemented with hunting and gathering Higher densities 1-10 people/square mile Population size- 30 to several hundred Able to trade surplus Buy items that cannot be produced Horticulture Cont.… Shifting pattern Unfertile soil- move to new field Controlled burn Clear away dead brush to make way for new vegetation Ash acts as a fertilizer Labor intensive Pesticides are not used Harsh on the land Misunderstanding Unproductive Tangle of wild vegetation Better growing season Plant multiple seeds in same whole Pastoralism Tends heard of large animals Horses are preferred in Central Asia Open country where farming cannot be sustained Droughts Spread out herd Animals are rarely killed for family use alone Preserving meat Sharing amongst members Pastoralism Transhumance Nomadic Follow seasonal migratory pattern Not permanent Self-sufficient Follow a cyclical pattern of migration Warm highlands in summer /warm lowlands in winter Regular encampments Rely less on animals Personality/Social Life In East Africa, cattle herding societies also bleed their animals. The blood is mixed with fresh milk to make a protein rich drink. Men make important decisions and own animals Act on decisions easily Expanding territory at the expense of others Women perform domestic duties Military Conquests Agricultural societies Established important kingdoms Zulus defeated the Dutch in South Africa Operate in large societies Value extreme bravery Independent of lines of supply Objectives 4/13 Describe agriculture and industrialism as subsistence strategies. _____________________________________ What are “Use Rights”? Intensive Strategies Use least amount of land with the most amount being produced Two Strategies: Agriculture Industrialism Agriculture Primary strategy use in large-scale societies Formed 5,000 years ago Population growth= new strategy Made possible by domestication of large animals and irrigation systems Ancient vs. Modern Irrigation systems Agriculture Cont. Ancient Civilizations Egypt, Mesopotamia, India, Pakistan, North China, Mesoamerica, Western South America Current Civilizations Primary food production pattern in all developed nations Social Changes Permanent settlements that would last for generations Evolution to the complexity of labor Industrialism Involves production of goods through mass employment in business/commercial operations Income used to purchase food, shelter, and other products Complex social structures Nation states= Division of labor is varied Based on gender, age and intelligence Industrialism Dependence on fossil fuels Long work weeks Decreased family size