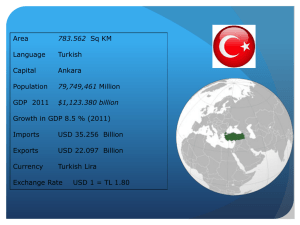
Network Switch
AGENDA
I.
Product Introduction
•
Network Switch
•
Smart Network Switch
•
L2 Manage Network Switch
•
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
II. Product Specification
•
Hardware Specification
•
Software Specification
III.WEB Interface
•
Software Features
I. Product Introduction
Product Introduction
Network Switch
A switch connects to devices (computers, access points, cameras, VoIP
phones, NAS, servers, etc. — or other switches) via Ethernet cables to
establish a network or to expand a network.
Product Introduction
Smart Network Switch
Smart switches have capabilities that lie between unmanaged
and managed switches and normally provide the configuration
of basic settings.
Product Introduction
Manageability — typically provided using a Web Interface which
allows performance monitoring (port activity), the ability to configure
network trunks (bandwidth control), and supports Port Mirroring.
QoS (Quality of Service) — which prioritizes
network traffic to support delay sensitive
applications such as VoIP (Voice over Internet
Protocol) and Streaming Video and enhanced
security which offers support for VLANs (Virtual
LANs).
Product Introduction
Smart Network Switch
Like a bridge, a Layer 2 switch connects segments of a network and makes
filtering decisions about which data is allowed to travel between the segments
and which data stays on a single segment. But while a bridge may connect
only two segments, a Layer 2 switch can connect many segments.
Product Introduction
Basically a layer 2 switch operates utilizing Mac addresses in it's caching table
to quickly pass information from port to port.
A layer 2 switch is essentially a multiport transparent bridge. A layer 2 switch
will learn about MAC addresses connected to each port and passes frames
marked for those ports. It also knows that if a frame is sent out a port but is
looking for the MAC address of the port it is connected to and drop that frame.
Layer 2 switches use the MAC address of data packets to determine where
those packets should go.
When you connect a Layer 2 switch to a network, it immediately “listens” for
all the devices on all the segments that are connected to the switch's ports.
Product Introduction
It learns the MAC addresses of all of those
devices and creates a segment table or
forwarding table. Because a switch can discover
all this for itself, it is relatively easy to connect a
switch to a network.
This self-learning ability is one of the important
features of Layer 2 switches. The IEEE 802.1D
standard defines this bridge and switching
function.
Product Introduction
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
A PoE device can send or receive power via Ethernet, but not send and receive
power at the same time. The maximum cable length recommended were up to
100 meters.
The sender is a Power Sourcing device (PSE) like a PoE switch, while a device
(like an access point,
IP Camera or VoIP phone) that is powered
via PoE is a Powered Device (PD).
The PSE supplies power, which can
be divided between several PDs.
Product Introduction
Product Introduction
IEEE Standard Power Classes
Product Introduction
Standard PoE Parameters and Comparison
Notes :
1.
Most Switched power supplies within the devices will lose up to 10 to 20% of the available power.
2.
Most cable specification allow assumption of more current carrying capacity and lower resistance (20 Ohms for Cat 3 vs Cat 5)
3.
The standard of IEEE 802.3at and IEEE 802.3af is classified Class 4.
4.
All our Indoor AP is Class, mode B, End-Span.
Product Introduction
Standard PoE Current flow
The powered device completes the current loop. DC current within specific
minimum and maximum thresholds means that a PoE-powered device is
connected and requires continued PoE
Product Introduction
Standard PoE flow chart
The flow chart is a guide that PoE support different types of hardware.
II. Product Specification
• Hardware Specification
• Software Specification
Product Specification
Hardware Specification
Model Name
EGS2108P
EGS2110P
EGS5110P
Switch Capacity
16Gbps
16Gbps
20Gbps
Forwarding Rate
14.88Mpps
14.88Mpps
14.88Mpps
Forwarding Mode
Store and
Forward
Store and
Forward
Store and
Forward
Packet Buffer
512Kb
512Kb
512Kb
Flash Memory
4Mb
4Mb
4Mb
Jumbo Frame
9.6K
9.6K
9.6K
45,418hrs
44,689hrs
38,455hrs
RJ45
8
8
8
SFP
0
2 (additional)
2 (additional)
RJ45 Console
-
-
-
Hardware Specifications
Descriptions
Performance
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
Port Functions
Product Specification
Power Spec
External (48v
1.87a)
External (48v
1.87a)
Internal
802.3af
802.3af
802.3at/af
PoE Capable Ports
port1-4
port1-8
port1-8
Power budget
61.6w
61.6w
130w
(Desktop Type)
(Desktop Type)
Metal
Metal
Metal
Dark Blue
Dark Blue
Dark Blue
Power Type
PoE Capability
PoE standard
IEEE802.3at/af
Mechanical & ID
Dimension
Material
Color
(1U 13”
230mm
depth)
Functional Buttons
Mode Selector
Control Mode LED to indicate the status
of opertaion modes.
●
●
●
Reset Button
Reboot or Reset to default
●
●
●
Product Specification
Software Specifications
L2 Feature
Loopback detection
STP independent + port base
shutdown only
●
●
●
IGMP Snooping
Support v1,v2
●
●
●
Port Mirroring
Support one to one and many to one
●
●
●
●
●
●
Port Trunking
Packet Suppression Control / Storm
Control
Broadcast/Multicast/Unknownmulticast, and unknown-unicast
●
●
●
Static MAC Address
Support 16 entries
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Dynamic MAC List
Bandwidth control
Rate limit according to network speed:
- 64kbps ~ 1000Mbps: in step of
64Kb
Product Specification
VLAN
●
●
●
VLAN Group
Number of VLANs supported per
device
Max. Static VLAN #: 64
Be able to configure VID from 14094
●
●
●
Port-base VLAN
Max. VLAN Group: equivalent to
switch's port number
●
●
●
Number of priority queues supported:
4
●
●
●
CoS based on 802.1p priority
●
●
●
CoS based on physical port
●
●
●
●
●
●
802.1Q support
CoS
Queue
Security
Storm control
Support Broadcast/Muticast/Unknow
unicast. Min. granularity:
1~1953125 pps
Product Specification
Management
Power on/off per port
●
●
●
Power class configuration
(autoclass/userdefine)
●
●
●
Power feeding with priority
●
●
●
User define power limit
●
●
●
BootP/DHCP Client
●
●
●
Web-based support
●
●
●
Firmware Burn-Proof
Proprietary technology for firmware
upgrade protection to ensure
firmware can be upgraded
successful when burning
damage.
●
●
●
Web UI supports non-IE browser
Chrome, Firefox, Safari
●
●
●
●
●
●
PoE management
Cable Diagnostic
III. WEB Interface
• Software Specification
WEB Interface
Software Specifications
The layout display the main manual of the Network Switch.
The layout consists of System, L2 Feature, VLAN and QoS.
System
L2 Feature
VLAN
QoS
Summary
Port Trunking
802.1Q
802.1p Default
Priority
IP Setting
IGMP Snooping
PVID
Cos Priority Class
Port Setting
Multicast Group
List
Port-base
VLAN
Storm Control
PoE Management
Port Mirroring
PoE Port
Configuration
Loopback Detection
Cable Diagnostics
Static MAC Address
Password
Dynamic Address
List
Zero Configuration
Bandwidth Control
WEB Interface
Login Page
The web interface default IP address http://192.168.0.239 and
default password is password.
WEB Interface
WEB Interface Layout
The layout display the main manual of the Network Switch.
WEB Interface
System
Port Setting
In Port Setting, user can view and configure the individual port speed.
WEB Interface
System
PoE Management
It is capable of delivering up to 15.4W of power to devices such as wireless
access points, IP phones and IP Cameras, provide flexibility and ease of
deployment to your network. To help you better control and monitor your
power resource. It will show the total power consumption of the device
connected.
WEB Interface
Web Interfaces
System
PoE Port Configuration
In Port Configuration, you can configure and view the operation mode for each
port. If priority is set all “low”, it will auto allocate power resource.
WEB Interface
Web Interfaces
L2 Feature
Port Trunking
In Computer Networking, Port Trunking refers to the use of multiple network
connections in parallel to increase the link speed beyond the limits of any one
single cable or port. This is called link aggregation. These aggregated links may
be used to interconnect switches or to connect high-capacity servers to a
network.
WEB Interface
Web Interfaces
L2 Feature
Port Trunking Topology
•Port Trunking need to enable in both switches.
•Trunks carry traffic from all VLANs to and from the switch by default but can
be configured to carry only specified VLAN traffic.
Port Trunking
WEB Interface
Web Interfaces
L2 Feature
IGMP Snooping
IGMP snooping is the process of listening to Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP) network traffic. The feature allows a network switch to listen in
on the IGMP conversation between hosts and routers. By listening to these
conversations the switch maintains a map of which links need which IP
multicast streams. Multicasts may be filtered from the links which do not need
them and thus controls which ports receive specific multicast traffic.
WEB Interface
Web Interfaces
L2 Feature
Port Mirroring
Port mirroring is used on a network switch to send a copy of network packets
seen on one switch port (or an entire VLAN) to a network monitoring connection
on another switch port. This is commonly used for network appliances that
require monitoring of network traffic
WEB Interface
VLAN – Virtual LAN
PVID (Port VLAN ID)
A Port VLAN ID (pvid) is a default VLAN ID that is assigned to an access port to
designate the virtual LAN segment to which this port is connected.
WEB Interface
Web Interfaces
VLAN – Virtual LAN
802.1Q – VLAN Tagging
802.1Q allow the user to configure the network port to be tag or untag to the
VID.
Port 1 configure VID10 and
VID20
SSID 1 tag VID10
SSID 2 tag VID10
WEB Interface
VLAN – Virtual LAN
Port-based VLAN
To provide priority to identified network traffic including dedicated
bandwidth, controlled jitter and latency that is required by real time
applications while improving quality by reducing packet loss.
WEB Interface
QoS – Quality of Service
Cos (Class of Services)
Priority queuing ensures high-priority traffic gets delivered efficiently, even
during congestion from high-traffic bursts. For example, certain types of traffic
that require minimal delay, such as Voice, Video, and real-time traffic can be
assigned to a high priority queue, while other traffic can be assigned to a lower
priority queue.
WEB Interface
QoS – Quality of Service
Storm Control
Storm control prevents traffic on a LAN from being disrupted by a broadcast,
multicast, or unicast storm on a port. This occupies bandwidth and loads all
nodes on all ports.
WEB Interface
QoS – Quality of Service
Bandwidth Control
To provide priority to identified network traffic including dedicated bandwidth,
controlled jitter and latency that is required by real time applications while
improving quality by reducing packet loss.
Troubleshooting EnGenius WLAN Products
www.engeniustech.com.sg
@ 2013 EnGenius Networks Singapore Pte Ltd. All rights reserved.