What Are Tides?
advertisement

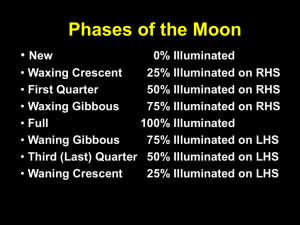
Moon FACTS • • • • • • The Moon is a natural Satellite that revolves around the Earth The Moon is made of rock The Moon is 382,400 kilometers 250,000miles from Earth The moon is about ¼ the size of Earth The moon’s gravity is about 1/6th that of Earth. The moon has craters, which are indents left by meteor impact. • The moon does not produce it’s own light; it reflects light from the sun. The moon has frozen water • The moon has a very very small atmosphere. • The moon doesn’t shine on its own, it reflects sunlight Motions of the moon • The moon orbits the Earth • The moon takes 28 days to revolve around the Earth • The moon takes 28 days to rotate once on its axis • The moon orbits at an angle compared to the Earth’s orbit around the sun. (See image) Sun Moon Earth connections • Phases • Eclipses • Tides PHASES OF THE MOON What causes the phases of the moon? The phases of the Moon depend on its position in relation to the Sun and Earth. As the Moon makes its way around the Earth, we see the bright parts of the Moon's surface at different angles. These are called "phases" of the Moon. Half of the moon is always lit by the sun. Only part of the lit half of the moon can be seen from Earth. We call the lit part that we can see phases. Each phase has a different name. -The cycle starts with the new moon and goes counter clockwise. -The cycle lasts 28 days, which is the time it takes for the moon to orbit the Earth one time. Try to name the phases of the moon in order starting with the New moon. Eclipses • The Sun and Moon occasionally line up so that we have an eclipse. 11 SOLAR ECLIPSE: When the Moon’s shadow covers part of the Earth • Three types: Annular, Partial, and Total • Only happens at New Moon Solar Eclipses 12 Solar Eclipse This animation shows that the moon creates a small shadow which Only allows certain areas of the earth to see a total solar eclipse. Here is an animation showing a total solar eclipse Remember that it is not safe to stare at a solar eclipse !!! Partial Solar Eclipse Animation View from Earth Lunar Eclipse That the moon is covered by the Earth’s shadow This Eclipse safe to look at. 2 Types of Lunar Eclipses: Total Lunar Eclipse- when the moon passes through the Umbra of Earth’s the shadow Partial Lunar Eclipse: the moon passes through the Penmbra of the Earth’s shadow Total Lunar Eclipse Animation Sometimes the moon turns red when totality occurs. Three types of Lunar Eclipses • Who on Earth will be able to see a lunar eclipse? Anyone who can see the Moon (anyone who is on the nighttime side of the Earth during the eclipse) 19 Which kind of eclipse is there during a • Full moon? • New moon? LUNAR ECLIPSE SOLAR ECLIPSE Tides • What causes the tides? • What is a spring tide? • What is a neap tide? What Are Tides? • Tides are the daily rise and fall of Earth’s waters on its coastlines. • As the tide comes in, the level of water on the beach rises, and as the tide goes out, the level of water on the beach goes down. • Tides occur in all bodies of water, but they are most noticeable in the ocean and large lakes. High Tides • High tides are when the water reaches its highest point. Low Tides • Low tides are when the water reaches its lowest point. What Causes Tides? • Tides are caused by the interaction of Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. • Gravity is the reason for tides. • Gravity is the force exerted by an object that pulls other objects toward it. Moon’s Gravity and Tides • The Moon’s gravity affects the water on Earth’s surface. • Since the Moon is close to the Earth, it has a strong gravitational pull on it (closer objects have stronger gravitational pull). Moon’s Gravity – Tidal Bulges • The Moon pulls on the water on the side nearest to it more strongly than it pulls on the center of the Earth. • This pull creates a bulge of water, called a tide bulge, on the side of Earth facing the the Moon. Moon’s Gravity – Tidal Bulges • The water on the side of Earth facing away from the Moon has a less strong pull. • This water is “left behind” and forms a second bulge. • As Earth rotates, different places on the planet’s surface pass through the areas of the tidal bulges and have the change in water levels. Tidal Bulges – High Tide • In places where there are tidal bulges, high tide is occurring along the coastlines. High Tide High Tide Tidal Bulges – Low Tide • In places between the bulges, low tide is occurring. LOW TIDE LOW TIDE Sun’s Gravity and Tides • The Sun is so large that its gravity also affects tides. • At times, the Sun and Moon pull together on Earth’s waters in the same direction. (SPRING TIDES) • At other times they pull in different directions. (NEAP TIDES) Daily Tide Cycle • Most seashores have four tides every day – two high tides and two low tides. Monthly Tide Cycle • Changes in the positions of Earth, the Moon, and Sun affect the height of tides during a month. Spring Tides • Spring tides occur 2 times a month, during a full and new moon when the Earth, Sun, and Moon are lined up. • Spring tides are higher and lower than normal tides. • “strong tides” Neap Tides • Neap tides occur in between spring tides, at the first and third quarters of the Moon when the Sun and Moon pull at right angles to each other. • Neap tides are not as high or low as normal tides. • “weak tides”