Lecture8
advertisement

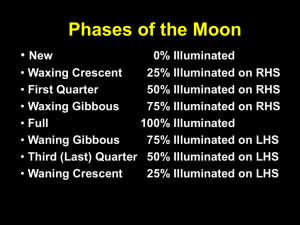
Astronomy 1 – Fall 2014 Lecture 8: October 30, 2014 A Job Offer (Apply only if you scored > 60% on midterm 1.) You Are Invited! • Astro 1 Observing Session (Optional, Just for Fun) • WHEN: November 13th at 7-9pm • • • Same time Nov. 20th if the 13th is cloudy WHERE: Broida rooftoop; take elevator to 6th floor. Turn right as you exit the elevator. Go up the stairs. A TA will great you. WHAT: 3 Celestron C8 Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes and one C11. • • • Andromeda Galaxy, Uranus, Mars, Crab Nebula, Pleides, etc. Help identifying the Celestial Equator, NCP (& Polaris), and the Ecliptic Constellations: Pegasus, Taurus, Summer Triangle, Orion, etc. • Will you be able to see the moon? Previously on Astro 1 Solar System Formation: the nebular hypothesis. The Sun: formed by gravitational contraction of the center of the nebula. Terrestrial planets: formed through accretion of dust particles into planetesimals, then into larger protoplanets. Jovian planets: Began as rocky protoplanetary cores, similar in character to the terrestrial planets. Gas then accreted onto these cores. Alternatively, they formed directly from the gases of the solar nebula. In this model the cores formed from planetesimals falling into the planets. Today on Astro 1 • • • • What does the Moon look like? What is the Moon made of? How did the Moon form? Tidal forces • What they are • Affect on Earth • Affect on Moon The Moon’s Rotation and Libration • Wobbles back and forth due to the elliptical shape of its orbit. • Nods up and down because rotation axis is not exactly perpendicular to its orbit. The Moon Appears to Wobble & Nod How Well Do You Know the Moon? You are living at a moon base and watch the motions of the Earth and Sun in the lunar sky. What would you see? A. The Earth and the Sun would rise and set once a lunar month. B. The Earth would rise and set once a lunar month, but the Sun would not appear to move significantly in the lunar sky. C. The Earth would not appear to move significantly in the lunar sky, and the Sun would rise and set once a lunar month. D. The Earth and Sun would not appear to move significantly in the lunar sky. E. Q10.2 None of these answers are correct. The astronaut footprint on the Moon shown in this photograph will probably A. exist for >10,000 years because there is very little weathering on the Moon. B. exist for >10,000 years because the Moon’s surface is hard and durable. C. exist for <10,000 years due to erosion from wind in the tenuous lunar atmosphere. D. exist for <10,000 years due to bombardment by large numbers of meteors. E. Both C and D are correct. Q10.1 The large flat plains on the Moon are called maria. The maria were formed A. in old sea beds. B. when large meteors hit the Moon and flattened its surface. C. when ancient lava flows solidified, sometimes in a very large crater. D. when the surface of the Moon was eroded and flattened over millions of years by its tenuous atmosphere. E. by tidal interactions between the Earth and Moon. Q10.3 Some areas of the Moon are relatively smooth, whereas other areas are heavily cratered. This is because A. meteors did not strike the flat areas because they are in the Earth’s shadow. B. weathering has smoothed parts of the Moon. C. plate tectonics has recycled parts of the lunar crust. D. in some places lava flows have covered over older craters, leaving a smoother surface. E. tidal forces between the Earth and Moon smoothed parts of the Moon. Q10.4 The narrow snaking channels on the Moon are A. due to water flowing on the Moon in the past. B. due to lava flowing on the Moon in the past. C. skid marks where meteors landed in the past. D. due to tidal forces between the Earth and the Moon. E. due to plate tectonic activity. Q10.5 The Moon’s Surface Lunar Craters Crater Clavius Moon’s Impact History Near/Far Sides of the Moon Some Scarps are Less Than 1 Billion Years Old • As the moon cools it shrinks and wrinkles • This scarp is younger than the craters which cut across it. How Did the Moon Form? Tidal Forces The lunar mountains were created by A. colliding plates. B. meteor collisions that uplifted the surface of the Moon. C. tidal interactions with the Earth. D. volcanic hotspots. E. erosional forces. Q10.6 Is there evidence for water in any form on the Moon? A. No. B. Yes, water vapor has been detected in the tenuous lunar atmosphere. C. Yes, there must be liquid water below the surface because it once formed seas. D. Yes, there is evidence for solid water (ice) frozen in craters at the north and south lunar poles. E. The existence of water on the Moon remains an unanswerable question. Q10.8 The Moon is geologically A. totally inactive. B. active, with many minor moonquakes occurring per day. C. active, with minor moonquakes occurring only when the Moon is full. D. active, with occasional (approximately every 100 years) small volcanic eruptions. E. active, with slow movement of various lunar crust plates. Q10.9 Tidal interactions between the Earth and the Moon are causing A. the Earth's rotation to slow down and the Moon to move toward the Earth. B. the Earth's rotation to slow down and the Moon to move away from the Earth. C. the Earth's rotation to speed up and the Moon to move toward the Earth. D. the Earth's rotation to speed up and the Moon to move away from the Earth. E. no measurable effects. Q10.10 Which of the following is most likely responsible for the Moon’s formation? A. Asteroid debris from space was collected in Earth’s orbit, and this material slowly coalesced to form the Moon. B. A large body impacted the Earth during its early formation. The impact ejected material into space that later formed the Moon. C. The Moon formed elsewhere in the solar system and was later captured by the Earth. D. The Moon is merely a large captured asteroid. E. Q10.11 The Moon split off from the Earth, leaving the Pacific Ocean basin behind. Summary • The moon’s surface has very old rocks in the highlands and much younger rock in the maria. • • • The far side of the moon has a thicker crust & few maria. Heavily cratered surface indicates no plate tectonics Late Heavy Bombardment formed the maria basins 4.1 to 3.8 Gyr ago which were later filled by lava. • Meteoroids and solar wind ‘weather’ the surface. • Collisional ejection theory for the Moon’s origin • • Early moon was molten Formed from debris of proto-planet & Earth collision • Tidal interactions of Earth and the Moon • • Slow Earth’s rotation Push the Moon further away Homework • Do all Review Questions for ch. 10 on your own. • For TA’s, do 10.26, 10.32, 10.36, 10.38 Midterm 1 Results Answers to iClicker Questions The astronaut footprint on the Moon shown in this photograph will probably A. exist for >10,000 years because there is very little weathering on the Moon. B. exist for >10,000 years because the Moon’s surface is hard and durable. C. exist for <10,000 years due to erosion from wind in the tenuous lunar atmosphere. D. exist for <10,000 years due to bombardment by large numbers of meteors. E. Both C and D are correct. A10.1 You are living at a moon base and watch the motions of the Earth and Sun in the lunar sky. What would you see? A. The Earth and the Sun would rise and set once a lunar month. B. The Earth would rise and set once a lunar month, but the Sun would not appear to move significantly in the lunar sky. C. The Earth would not appear to move significantly in the lunar sky, and the Sun would rise and set once a lunar month. D. The Earth and Sun would not appear to move significantly in the lunar sky. E. A10.2 None of these answers are correct. The large flat plains on the Moon are called maria. The maria were formed A. in old sea beds. B. when large meteors hit the Moon and flattened its surface. C. when ancient lava flows solidified, sometimes in a very large crater. D. when the surface of the Moon was eroded and flattened over millions of years by its tenuous atmosphere. E. by tidal interactions between the Earth and Moon. A10.3 Some areas of the Moon are relatively smooth, whereas other areas are heavily cratered. This is because A. meteors did not strike the flat areas because they are in the Earth’s shadow. B. weathering has smoothed parts of the Moon. C. plate tectonics has recycled parts of the lunar crust. D. in some places lava flows have covered over older craters, leaving a smoother surface. E. tidal forces between the Earth and Moon smoothed parts of the Moon. A10.4 The narrow snaking channels on the Moon are A. due to water flowing on the Moon in the past. B. due to lava flowing on the Moon in the past. C. skid marks where meteors landed in the past. D. due to tidal forces between the Earth and the Moon. E. due to plate tectonic activity. A10.5 The lunar mountains were created by A. colliding plates. B. meteor collisions that uplifted the surface of the Moon. C. tidal interactions with the Earth. D. volcanic hotspots. E. erosional forces. A10.6 Is there evidence for water in any form on the Moon? A. No. B. Yes, water vapor has been detected in the tenuous lunar atmosphere. C. Yes, there must be liquid water below the surface because it once formed seas. D. Yes, there is evidence for solid water (ice) frozen in craters at the north and south lunar poles. E. The existence of water on the Moon remains an unanswerable question. A10.8 The Moon is geologically A. totally inactive. B. active, with many minor moonquakes occurring per day. C. active, with minor moonquakes occurring only when the Moon is full. D. active, with occasional (approximately every 100 years) small volcanic eruptions. E. active, with slow movement of various lunar crust plates. A10.9 Tidal interactions between the Earth and the Moon are causing A. the Earth's rotation to slow down and the Moon to move toward the Earth. B. the Earth's rotation to slow down and the Moon to move away from the Earth. C. the Earth's rotation to speed up and the Moon to move toward the Earth. D. the Earth's rotation to speed up and the Moon to move away from the Earth. E. no measurable effects. A10.10 Which of the following is most likely responsible for the Moon’s formation? A. Asteroid debris from space was collected in Earth’s orbit, and this material slowly coalesced to form the Moon. B. A large body impacted the Earth during its early formation. The impact ejected material into space that later formed the Moon. C. The Moon formed elsewhere in the solar system and was later captured by the Earth. D. The Moon is merely a large captured asteroid. E. A10.11 The Moon split off from the Earth, leaving the Pacific Ocean basin behind.