Equality
advertisement
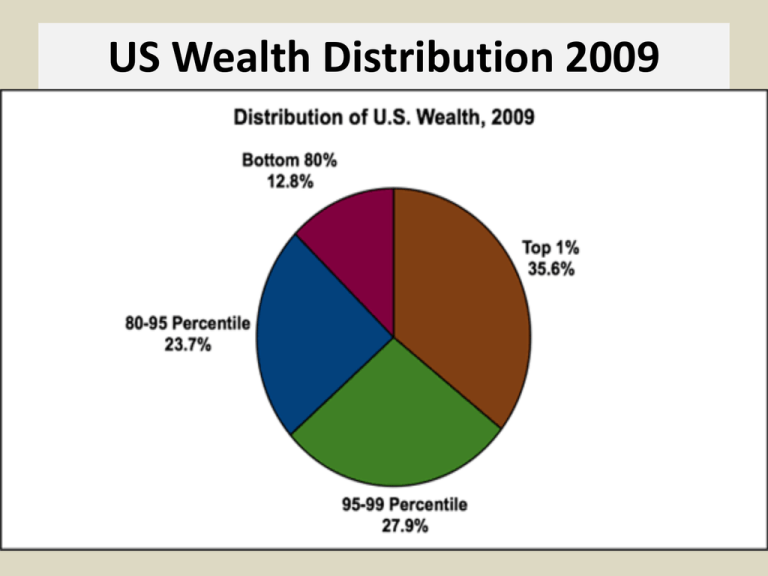
US Wealth Distribution 2009 Economic Inequality – GINI Coefficients (CIA 2009) Social Mobility/Income Inequality Homicide and Income Inequality Fishkin's Trilemma Three ideals –Equality of life chances –Merit –Family autonomy People in unequal family conditions have unequal resources/abilities Thus we can satisfy two, but not all three, of these principles Equality of life chances The prospects of children for eventual social positions should not significantly vary because of arbitrary native characteristics. Alternative to equality of results, still may require some “affirmative action” to provide basic resources for children of poor families. Merit Insistence on procedural fairness in the evaluation of qualifications for positions and access to benefits Assumes possibility of measuring qualifications in reasonably equitable and uniform manner Autonomy of the Family Parents have autonomy in raising their children, unless parents harm or hamper them for adult participation in society State cannot insist that parents follow best practices for children’s education or socialization Possible Resolutions of Trilemma Reduce family autonomy – greater social/state role in child rearing Adopt affirmative action – reduce role of merit in admissions, hiring, promotion Accept greater inequality disadvantaged children will be penalized for their bad luck Compromises Encourage family autonomy, but supplement with universal education Implement affirmative action, but do so in early development, e.g., head start programs Black Codes Former slaves were “forbidden to appear in the towns in any other character than menial servants. They were required to reside on and cultivate the soil without the right to purchase or own it. There were excluded from many occupations of gain, and were not permitted to give testimony in the courts in any case where a white man was a party.” Slaughterhouse Cases (1872) Barriers to Voting for African-Americans literacy requirements poll taxes discretionary registration rules “grandfather” waivers single race primary elections Economic Barriers for African-Americans lack of access to capital or land limited skills and literacy significant intimidation, including vagrancy laws licensing procedures excluding blacks Social Discrimination against African-Americans Laws Prohibiting Intermarriage Use of Separate Facilities Residential Segregation School Segregation Griggs v. Duke Power (1971) Discrimination by Design v. Disparate Impact Duke had segregated plant until 1964 Civil Rights Act, African-Americans only worked in labor dept Following CRA, Duke requires HS degree or passage of aptitude test for any position, including truck driving, outside Labor Dept. Griggs v. Duke Power (1971) Results of Segregated Education % of NC male high school grads, 1966 Black Men: 12% White Men: 34% Applicants who passed aptitude test Black Men: 6 % White Men: 58% Do African-Americans have an equal chance as whites in being hired for a job for which they are qualified? Whites 1963 2011 41% 78% African Americans 23% 39% USA Today/Gallup Poll, 8/17/2011 Are new civil rights laws needed to reduce discrimination against blacks? 1993 2011 Total (all races) 38% 21% Whites 33% 15% Blacks 70% 52% USA Today/Gallup Poll, 8/17/2011 Should the government have a ____ in improving the social/economic position of blacks and other minority groups? Major Minor No Role Role role Total Whites Blacks 27% 19% 59% USA Today/Gallup Poll, 8/17/2011 46% 26% 50% 30% 32% 8%