WWIAftermath
advertisement

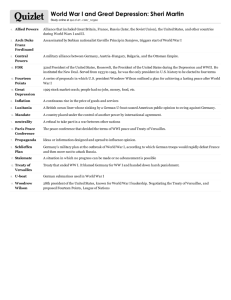
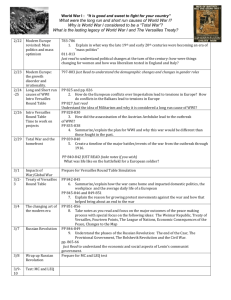
A World at War…World War I: 1914-1918 SEs: 2D,4C,4D,4E,4F, 4G, 15D, 19B, and 26F: Explain the significance of the following years as turning points: World War I; Identify the causes of world war I and reasons for U.S. entry; analyze the impact of significant technological innovations in World War I such as machine guns, airplanes, tanks, poison gas, and trench warfare that resulted in the stalemate on the Western Front. Analyze major issues such as isolationism and neutrality raised by U.S. involvement in WWI, Woodrow Wilson’s fourteen points, and the Treaty of Versailles. Analyze significant events such as the Battle of Argonne Forest. Describe the economic effects of international military conflicts, WWI, Explain constitutional issues raised by federal government policy changes during times of significant events including WWI. Discuss the importance of congressional medal of honor recipients, including individuals of all races and genders such as Vernon J. Baker, Alvin York, and Roy Benavidez. WW I: Aftermath: Things that followed after the war was over. Homefront and Aftermath of World War I: The Treaty of Versailles The Treaty of Versailles was the peace settlement signed after WWI had ended in 1918. The treaty was signed at the vast Versailles Palace near Paris; between Germany and the Allies. Germany admits fault through the Guilt Clause. Why was Germany upset over the terms of the Treaty of Versaille? 1. Germany was blamed for the war; therefore should pay for it (reparations) $33 Billion in 1921 dollars. 2. Severe restrictions on the German Military: army limited to 100,000 men; No air force at all. Limits on the number and types of naval vessels. No conscription. 3. loss of vital territory = 10 percent of German lands confiscated resulting in almost 13% of German population staying in foreign territory. 4. Prohibition of union of Germany and Austria Homefront and Aftermath of World War I : Treaty of Versailles, Reparations Reparations = how Germany was to be made to pay for the damage world war one had caused. The figure of 396.6 billion dollars was set some time after the signing of the treaty. Homefront and Aftermath of World War I: League of Nations League of Nations = was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of The Treaty of Versailles in 1919–1920. The League's goals included upholding the new found Rights of Man, disarmament, preventing war through collective security, settling disputes between countries through negotiation, diplomacy and improving global quality of life. Similar to today’s United Nations. Homefront and Aftermath of World War I: Domestic Policy changes Isolationism = The policy of noninterference in foreign conflicts. The United States wanted to stay clear of conflicts through this policy. It isolated us by staying neutral and at the same time it protected us. Homefront and Aftermath of World War I: Wilson’s Fourteen Points. The Fourteen Points = was a speech delivered by President Woodrow Wilson to a joint session of congress on January 8, 1918. The Fourteen Points became the basis for Wilson’s terms for German surrender. The main points were: no more secret treaties, countries must reduce weapons, no country could govern another and that all countries should belong to the League of Nations. Fourteen Points was never ratified by the U.S. Senate. Famous people during time periods of WWI Alvin York = One of the most decorated Americans during WWI. He received the Medal of Honor for leading an attack on a German machine gun nest, taking 32 machine guns, killing 28 German soldiers and capturing 132 others.