Four Basic Period of Computer History
advertisement

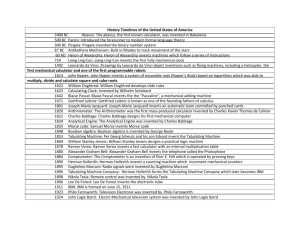
Four Basic Period of Computer History • Pre-mechanical Age • Mechanical Age • Electromechanical Age • Electronic Age Pre-Mechanical Age (3000B.C. - 1450 A.D.) Writing and Alphabets • Petroglyths (signs or simple figures carved in rock) Petroglyths Cave painting from Lascaux, France (15,000-10,000 B.C.) • Ideographs (symbols to represent ideas and concept) Mayan Ideograph • Cuneiform – the first true written language and the first real information system. (coonay-eh-form) • Star – heaven or God Cuneiform • At around 2000 BC the Phoenicians created symbols that expressed single syllables and consonants (the first true alphabet) • Greek adopted the Phoenician alphabet and added vowels • Romans gave the letters Latin name to create the alphabet we use today. Papers and pens • Sumerians – stylus and wet clay • Egyptians – papyrus plants (2600 BC) • Chinese – made paper from rags (100 AD) Stylus and wet clay Papyrus Plant Chinese Books and Libraries (permanent storage device) • Mesopotamia – religious leaders kept the earliest book • Egyptians – kept scrolls • Greeks – (600 BC) fold sheets of Papyrus vertically into leaves and bind them together. First Numbering System • Egyptian – Vertical lines (|)for numbers 1 – 9 - U or O – 10 - coiled rope – 100 - lotus blossom for 1000 • Hindus – (100 – 200 AD) 9 digit numbering • 875 AD the concept of zero was developed. The First Calculator • Abacus – was man’s first recorded adding machine. Invented in Babylonia and popularized in China. Mechanical Age (1450 – 1840) First Information Explosion • Johann Guttenberg – Movable metaltype printing process in 1450. The first general purpose computers • John Napier – (1614) a Baron of Merchiston, Scotland invented LOGS (Logarithm). • LOGS – allows multiplication and division to be reduce in addition and subtraction. • 1614 – Arabian Lattice – lays out a special version of the multiplication tables on a set of four-sided wooden rods.(multiply, divide large numbers and find square and cube root) Napier’s Bone John Napier • Wilhelm Shickard – 1623 - (Professor at University of Tubingen, Germany) – invented the first mechanical calculator that can work with six digits and can carries digits across columns. • William Oughtred – (1575 – 1660) invented the slide rule. • Blaise Pascal (1642) – invented the Pascaline. (made of clock gears and levers) that could solve mathematical problems like addition and subtraction. • Gottfried Leibniz – (1617) invented Stepped Reckoner that could multiply 5 digit and 12 digit numbers yielding up to 16 digit numbers. Stepped Reckoner • Joseph-Marie Jacquard (1801) developed the automatic loom (weaving loom) that was controlled by punched cards. • Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar -1820 – developed Arithmometer (the first mass produced calculator) • Charles Babbage – invented the difference engine (1821) and analytical engine (1832). - Father of modern computer. Difference Engine Analytical Engine • Lady Ada Augusta Lovelace Byron – 1842 – the first computer programmer. Electromechanical Age (18-40 1940) The Beginning of Telecommunications • Voltaic Battery – first electric battery known as voltaic pile - invented by Alessandro Volta • Telegraph Samuel F.B. Morse – conceived of his version of an Electromagnetic Telegraph (1832) Morse Code • Telephone and Radio Alexander Graham Bell – 1879 - developed the first working telephone. Guglielmo Marconi – 1894 – (RADIO) discovered that electrical waves travel through space and can produce and effect far from the point at which it originated. • George Boole – 1852 – developed the binary algebra known as Boolean Algebra Electromechanical Computing • Pehr and Edward Scheutz – 1853 completed a Tabulating Machine, capable of processing fifteen digit numbers, printing out result and rounding off to eight digits. Dorr Felt – 1885 – devises the comptometer, a key driven adding and subtracting calculator. Comptograph containing a built in printer Comptometer Comptograph Herman Hollerith – father of information processing. Punched Card – provided computer programmers with a new way to put information into their machines. He founded the Tabulating Machine Company , later became the Computer Tabulating Recording Company and International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) Herman Hollerith Tabulating Machine Otto Shweiger – 1893 – invented the first efficient four function calculator called Millionaire. Lee de Forest – 1906 – developed vacuum tubes This is important for it provided electrically controlled switch. Electronic Age (1941 – present) Konrad Zuse – 1941 – built the first programmable computer called Z3. Howard Aiken – 1942 – developed Mark I the first stored program computer. John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry – 1942 – completed the first all electronic computer called ABC or Atanasoff-Berry Computer John Atanasoff Clifford Berry