Supplier Selection
advertisement

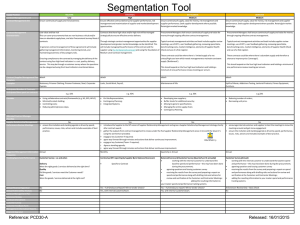
Supplier Selection RJ Whitehead BYU Undergraduate - Class of 2011 What will be covered • • • • • • • Supplier Selection Overview Brainstorming Exercise Supplier Selection in-depth Real World example Exercise Summary Reading List Supplier Selection • Supplier selection is the process by which firms identify, evaluate, and contract with suppliers Why is Supplier Selection Important? Average Percent of Revenue Use in COGS 50% 50% COGS Revenue after COGS Brainstorming Exercise • What is the role of strategy in supplier selection? • What are some of the difficulties with selecting suppliers? Nuts and Bolts Supplier Selection Process • Steps to Supplier Selection 1. 2. 3. 4. Determine the type of Relationships Find Potential Suppliers Evaluate Suppliers Select Suppliers Step 1- Determine type of Relationship • 3 Types of Relationships 1) Transactional • • • • • • • Not mission critical Commodity items Mostly focused on prices Minimal time and energy are required Less loyalty Inflexible Potential Communication problems Step 1- Determine type of Relationship 2) Collaboration • • • • • • • Non-commodity items and services Requirement of improvement of products (R&D) Long-term agreements Higher two-way communication Higher levels of trust Supply disruptions reduced considerably Lower total costs Step 1- Determine type of Relationship 3) Alliance • • • • • • • Relationship-specific capital investments Lower Total Cost Reduced time to market Improved quality Highest levels of trust High time commitment High switching costs Step 2 – Find Potential Suppliers • Finding a Supplier: o Internet o Supplier Records o Trade Registers o Trade Journals o Company Personnel o Trade Shows o Professional Organizations Step 3 – Evaluate Suppliers • Evaluate Suppliers: o o o o Supplier Survey Financial Analysis Facility Visits Quality Capability Analysis o Capacity Capability Analysis o Service Capability Analysis o Flexibility Capability Analysis o Information Technology Capability Analysis Step 3 – Evaluate Suppliers • Evaluate Suppliers: o Supplier Survey o Helps provided preliminary information about the company and whether they should be considered further for selection o Example information: Principal officers, bank references, credit references, history of sales and profit, number of employees, space currently occupied, Current defect rate, etc. Step 3 – Evaluate Suppliers • Evaluate Suppliers: o Financial Analysis o This is essential for a company to know if the supplier is financially stable enough to reliable o A member from the finance department generally does the analysis o The risk may be too great if they are financially unstable. Your supply may be disrupted at anytime without notice. Step 3 – Evaluate Suppliers • Evaluate Suppliers: o Facility Visits o Visiting a suppliers plant can be very educational. It allows you to decided if they are going to be able to do what they promised in their survey and other information they provided. o It helps you to survey their true technical capabilities. Step 3 – Evaluate Suppliers • Evaluate Suppliers: o Quality Capability Analysis o Quality is a critical factor for any supplier. It effects your product and your bottom line directly. They analysis should include a study of upper management’s philosophy on quality o Capacity Capability Analysis o This helps you assure if a supplier can meet the requested demand. It isn’t uncommon for suppliers to promise the sky and under delivery Step 3 – Evaluate Suppliers • Evaluate Suppliers: o Service Capability Analysis o This is an analysis of what levels of service they will offer. How they will react to special orders, rush orders, settling disputes, delivering on time, etc. o Flexibility Capability Analysis o This is an analysis of how lean they operate and how they will be able to react to changes in supply and demand, changes in regulation, etc. Step 3 – Evaluate Suppliers • Evaluate Suppliers: o Information Technology Capability Analysis o Information Technology is what has allowed to supply chain to become core competencies of companies. Their capability should fit in with your companies strategy. It should include information about integration through EDI and XML-SOAP services. Step 4 – Select Supplier • Selection Methods: o Bidding o Negotiation o Reverse Auctions o Two-Step Bidding/Negotiation o Solicitation o Weighted-Factor Analysis Step 4 – Select Supplier o Bidding o Bidding is the process of sending out request for bids to a few suppliers and the lowest price wins o Good when contract is large enough to justify the bidding expense o Specification are explicit o Must have sufficient number of qualified suppliers o Suppliers must want the contracts o There must be sufficient to for suppliers to send bids Step 4 – Select Supplier o Negotiation o Negotiation is the process where there is deliberation between supplier and purchase over price and terms o Good technique when difficult to estimate costs o Used when prices aren’t the only determining factor o Used when there are possibilities to specifications changes o Used when there is required tooling and setup costs Step 4 – Select Supplier o Reverse Auction o Reverse auctions allow a company to get as close as possible to the true market price o All bidders must already meet all requirements o Must be used with caution. It can often damage longterm relationships. It shows that you are more concerned with the lowest price than relationships Step 4 – Select Supplier o Reverse Auction o Reverse auctions allow a company to get as close as possible to the true market price o All bidders must already meet all requirements o Must be used with caution. It can often damage longterm relationships. It shows that you are more concerned with the lowest price than relationships Step 4 – Select Supplier o Weighted-Factor Analysis o Weighted-Factor Analysis allows you to quantify different factors and attribute of suppliers to easily compare them o Best used when the best supplier isn’t easily identifiable o 4 Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. Determine Factors and Weights Determine Sub-factors and Weights Determine Scoring point scale (1-5, 1-10, etc) Score and Evaluate suppliers Weighted Factor Analysis Factors Weight Sub Weight Score (1-10) Supplier -1 Weighted Score Supplier -2 Weighted Technical 25 Design 10 7 7 6 6 Experience 15 8 12 10 15 References 15 10 15 7 10.5 Liquidity 10 5 5 10 10 Defect Rate 20 7 14 6 12 Practices 5 8 4 4 2 6 15 10 6 Finance Quality Price Total 25 25 25 72 61.5 Real World Example • In 1997 Quaker Oats realized that their supplier was charging them a 40% mark up on the plastic bottles for Gatorade. • They explored new options supplier options. They decided that an alliance would prove to be the most lucrative. They came up with requirement and visited 8 different bottling companies. After negotiation they found one supplier that best fit with their strategic plans. Exercise • On the following slides take each exercise and determine the following things: – What is the optimal type of relationship? – What would be the best way to find the supplier? – What factors would you focus on for your weighted-factor analysis? Exercise • #1 - You are a producer of silicon memory chips. You have been working with a longtime supplier for silicon but you are trying to lower your costs. Silicon is a commodity and there are many suppliers Exercise • #2 – You are a manufacturer of medical equipment and are considering outsourcing major mechanical assemblies. You have long produced them yourself. You are hoping to gain design insights from your new supplier. Exercise • #3 – You are a small niche market company. You provide consulting for reverse logistics providers. You have identified the need for web based tracking program for the industry. Summary • Supplier selection is a integral part of any company. • If ignored there is a gold mine of savings waiting to be found. • Supplier selection should always work within the bounds of company goals Reading List • • • • • Beil Damian Supplier Selection [Online]. - July 2009. - April 11, 2010. http://www-personal.umich.edu/~dbeil/Supplier_Selection_Beil-EORMS.pdf. Burt David, Petcavage Sheila and Pinkerton Richard Supply Management [Book]. - New York : McGraw-Hill Irwin, 2010. - Eighth. http://www.businesslink.gov.uk/bdotg/action/layer?topicId=1073920782 http://www.asq.org/learn-about-quality/supplier-quality/overview/tutorial.html http://www.ism.ws/education/PastConfDetail.cfm?ItemNumber=19340