Unit 4: Foundations of Government in Georgia
advertisement

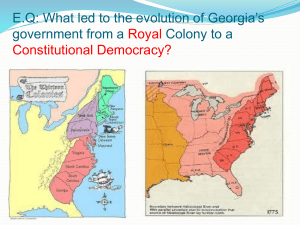
Unit 4: Foundations of Government in Georgia SS8CG1: The student will describe the role of citizens under Georgia’s constitution. Georgia’s Constitution GA was one of the original 13 colonies and became a state after the American Revolution. Georgia adopted its first constitution in 1777. In 1983, Georgians approved the state’s tenth constitution. Georgia’s constitution states: 1) Any power the government has is given to it by the citizens and is for the good of everyone. 2) Georgia’s gov’t is meant to serve people and the constitution allows the people to change the gov’t when it fails to serve their needs. GA’s constitution continued: There are 11 articles in the 1983 constitution. The first article consists of a bill of rights, twenty-eight paragraphs that set out the rights of Georgia citizens. Separation of Powers The Georgia constitution, like the U.S. constitution, divides the responsibilities of government among the three branches in what is known as a separation of powers. Separating government powers creates a “limited government.” 3 Branches of Government 3 branches of gov’t continued: The executive branch can veto bills passed by the legislative branch and can call special sessions of the legislature. The legislative branch can impeach officials in the executive or judicial branches. It can override a governor’s veto of bills to make them into laws. It can propose a constitutional change. It must also confirm appointments made by the governor. 3 branches continued… The judicial branch determines whether or not laws are constitutional. Each branch of government is responsive to the citizens of Georgia because most officials in each branch are directly elected by the voters. Checks and Balances Each branch of government was given some power to control or prevent some actions of the other two branches. This process is known as a system of checks and balances. The checks and balances ensure that no one branch becomes too powerful. Rights and Responsibilities of Citizens -Sovereignty- the concept that power and authority rest with the citizens. -Federalism- a system where the national, state, and local governments share authority over the same land and the same people The status of citizenship If your parents are U.S. citizens or if you were born in the United States, then you are a U.S. citizen. You are entitled to all of the protections and rights afforded by the federal and state constitutions. These rights include free speech, the right to bear arms, freedom of religion, and the right to a speedy and fair trial. The status of citizenship continued… Naturalized citizens are foreign nationals (those who were born in other countries) who chose to become American citizens and give up their citizenship in those other countries. The status of citizenship continued… People who are 18 years of age who have lived in this country for at least five years, and who entered the country legally can apply for citizenship They must meet certain requirements- an ability to read and speak English; a knowledge and understanding of U.S. history; good moral character; & a belief of the principles of the U.S. Constitution Rights and Responsibilities of Citizens Voting, while a right, is also the most basic responsibility of citizens, enabling them to participate in government. Another responsibility of citizens is to pay federal, state, and local taxes to fund the services those governments provide. Rights and Responsibilities of Citizens continued… Another responsibility is upholding the laws of the nation. Also, defending the nation against its enemies. (All young men are required to register with the Selective Service Board when they turn eighteen). Voting Qualifications To register to vote in Georgia, a person must be at least 18 years old and a citizen of the United States. An individual must also be a legal resident of Georgia and the county in which he or she registers. Elections A general election is held in November in at least every evennumbered year. This is when major federal and state officials are selected. Other elections are held as needed to select public officials. Elections continued Voters select the most important state officials. These officials, in turn, appoint others who work for and with them. Political Parties Political Parties are organized groups of people who share common ideals and who seek to influence government policies and decisions by electing members of their party to government offices. Political Parties continued.. Today, America has two major political parties: The Republican Party and the Democratic Party Members of these groups share common beliefs about government’s role in American life Political Parties continued.. People who are not members of these two major parties are usually referred to as independents. The General Assembly There are 180 members of the house of representatives and 56 members of the senate. Members of the legislature are elected by popular vote to two-year terms of office. There is no limit to the number of terms a representative or senator can serve. The General Assembly continued… Members of the Senate must be: 25 years of age Citizens of the U.S. Citizens of Georgia for at least two years They must have been legal residents of the district from which they were elected for at least one year Members of the House must be: 21 years of age Citizens of the U.S. Citizens of Georgia for at least two years They must have been legal residents of the district from which they were elected for at least one year The General Assembly continued… The General Assembly is bicameral: (has two houses/chambers). One is the house of representatives and the second is the senate. The lieutenant governor presides over the senate. Members of the House elect a speaker. Casey Cagle- GA’s lieutenant governor The lieutenant governor does not have a vote in the senate, but the speaker of the house votes when it is necessary to break a tie. Committee System Members of the Georgia house and senate are organized into committees. All bills must be reviewed by a house or senate committee before they can be brought to either the whole house or sent for a vote. Committee System continued.. Some committees are permanent, lasting from one session to the next. They are called standing committees. Some of the standing committees include: The Ways and Means Committee which handles bills involving taxes The Appropriations Committee which works on the budget The Judiciary Committee which deals with bills concerning the state’s laws and court system. (Other committees are organized for a special task and last only until their work is complete).