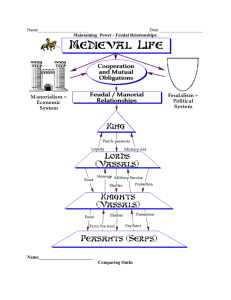
Feudalism
advertisement
THE FEUDAL SYSTEM A social, economic, and political system of organization. FEUDALISM William the Conqueror from Normandy, France introduced the Feudal System to England in 1066 when he became the King of England. FEUDALISM Was based on the 3 F’s Fief – land Fealty – loyalty Faith – religion (Christianity) Feudal Contract Between the lord and his vassal Was an oath of allegiance (homage) in a formal ceremony Everyone in the feudal society was involved in an oath of allegiance Feudal Pyramid Obligations and Responsibilities MONARCH Gives land to nobles in exchange for loyalty Defends nobles from attack and settles disputes between two or more nobles Protects nobles and administers justice Nobles Promises king fealty (loyalty) in exchange for land Serves in king’s army for a certain amount of days per year Supply king with extra knights in time of war Serve in king’s court and give him advice Lesser Nobles/Minor Nobles Involved in an oath of allegiance/feudal contract with greater nobles Serve as knights in times of war Have some land Noble – has land Commoners/Peasants Freeholder - Own the land they farm, pay a yearly fee (rent) to the lords Craftsmen and Merchants – Make and sell products on the manor: tanners, blacksmiths, bakers Serfs – No power, considered part of the property Work the land as farmers and live on the manor Not slaves – nobles could not remove their right to work and live on the land. The Manor All classes live together, with the exception of the pope and king. The manor is a large farm with a village. Manor