Attitudes to Poverty - Coatbridge High School
advertisement

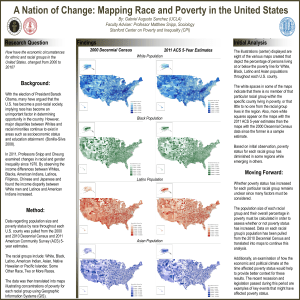
Changing Attitudes Towards Poverty: Gustave Dore, Houndsditch (1872) Wentworth Street, Whitechapel (1872) Investigators • Booth: founder of Salvation army • Andrew Mearns: ‘The bitter Cry of Outcast London • http://www.attackingthedevil.co.u k/related/outcast.php • GR Sims: report on the poor in London Charles Booth • Wealthy Liverpool ship owner • Began investigation to disprove the claim that a quarter of Londoners lived in poverty • Over 1 million families investigated 'Map Showing Degrees of Poverty in London for 1889-1890', Booth’s classification of the people he interviewed: A (0.9% in poverty) The Lowest class-occasional labourers,loafers and semi-criminals B (7.5% in poverty) C and D (22.3% In poverty) E and F (51.5% In comfort) The very poor-casual labour, hand to mouth existence, chronic want The poor-including those who have small earnings because of irregular employment or poor pay The regularly employed and fair paid working class Charles Booth • Shocked to discover that figures were actually underestimated • 30% living below ‘poverty line’ • But only 10% been helped by Poor law Bluegate Fields (1872) Seebohm Rowntree • Wealthy York manufacturing family • Aim: to see if the level of poverty in York was different to london • 1901 published Poverty, A study of Town Life Nestle Rowntree Key findings • Identified two types of poverty: • Primary poverty, those people whose earnings were so low they could not survive on them alone • Secondary Poverty: those who had enough to live on but spent money Key findings • Determined poverty line at 21s 8d (£1.08) • Found York had 27.8% of its population living in poverty • Poverty was not always the fault of the person e.g. low wages, sick, elderly Significance • Both investigators used new methods to study poverty • Charity was not enough, the government would have to provide help • Greater awareness of poverty Pressures • Employers e.g Rowntree, Lever, Brunner believed there was a need for action • Politicians: increasing number ready to support state action • Extension of the franchise to working class men (1867 and 1884) Pressures • Growth of the labour and socialist societies • E.g. Fabian society: Sidney and Beatrice webb First Boer War (1880–1881) Boer war: the Second Boer War (1899–1902) • The British consolidated their power over most of the colonies of South Africa in 1879 after the Anglo-Zulu War. • The Boers protested and in December 1880 they revolted. • Boer: is the Dutch word for farmer Boer women and children in a concentration camp Boer war: • many men unfit to fight • In Manchester 8,000 volunteered but only 1200 were accepted • up to 40% of recruits were unfit for military service, suffering from medical problems such as rickets and other poverty-related illnesses. Overall • For all these reasons there was a gradual shift from self help and hard work attitude towards a ‘collectivist’ belief in social reform • Activity • What were the main causes of Poverty in the late nineteenth century • Describe the work of Charles Booth and Seebohm Rowntree in changing attitudes to poverty in the early twentieth century