SCLOA_files/SLO5 Explain Social Learning Theory
advertisement

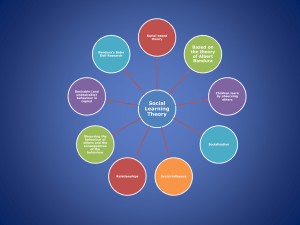
Sociocultural Level of Analysis Social Norms Learning Outcomes: Explain Social Learning Theory, making reference to two relevant studies Three Strands of SCLOA and Specific Learning Outcomes Socio-cultural Cognition (4.1) 1. Describe the role of situational and dispositional factors in explaining behaviour. 2. Discuss two errors in attributions. (for example, fundamental attribution error, illusory correlation, self-serving bias). 3. Evaluate social identity theory, making reference to relevant studies. 4. Explain the formation of stereotypes and their effect on behaviour. Social Norms (4.2) 1. Explain social learning theory, making reference to two relevant studies. 2. Discuss the use of compliance techniques.(for example, lowballing, foot-in-the-door, reciprocity) 3. Evaluate research on conformity to group norms. 4. Discuss factors influencing conformity. (for example, culture, groupthink, risky shift, minority influence). Cultural Norms (4.2) 5. Define the terms culture and cultural norms. 6. Examine the role of two cultural dimensions on behaviour. (for example, individualism/collec tivism,power distance, uncertainty avoidance, Confucian dynamism, masculinity/feminin ity). 7. Using one or more examples, explain emic and etic concepts. SLO.1: Explain social learning theory, making reference to two relevant studies. Norm: is a set of rules based on socially or culturally shared beliefs of how an individual should behave. Question: How does a society or culture pass on its norms to individuals with the group? SLT is the predominant theory. Social Learning Theory: People learn behaviour through observational learning. Observational learning: Learning by watching models and imitating their behaviour Social Learning Theory: Sometimes the model is trying to have a direct effect on the learner. Ex. Teacher Often models serve as indirect models – they are not trying to influence behaviour Social Learning Theory Social learning involves the following factors: ARMM 1. 2. 3. 4. Attention Retention Motor Reproduction Motivation Attention You have to pay attention to the model in order for learning to occur. Likewise, anything that reduces/distracts attention is going to decrease learning. Calvin’s not paying attention!! More on Attention Bandura also found that characteristics of the model affected attention. Example: Dramatic models were paid more attention. Attractive or prestigious models and models that seem more like the subject were also paid more attention. Retention You must be able to remember the behaviour that has been observed. Motor Reproduction The observer must be able to replicate the action. Just because you watch someone do this doesn’t mean you can do it! Motivation You must want to demonstrate what you have learned. What influences us to be motivated to learn a behaviour? Consistency- Model behaves consistently across situations. Ex. Always being brave. Identification with the model- A tendency to imitate models who are like ourselves Ex. Age, gender Rewards/punishments: Vicarious reinforcement – learn from others Liking the model – Warm and friendly models are more likely to be imitated than cold and uncaring models. Evaluation of Social Learning Theory Helps explain why behaviours may be passed down in a family or within a culture Explains why children can acquire some behaviours without trial-and-error learning However, though a behaviour may be acquired it is not always demonstrated (some see this as a criticism of the theory) – gap between when one observes the model and when one may demonstrate the behaviour It also doesn’t explain why some people never learn a behaviour, in spite of the above criteria being met Social Learning Theory has developed into social cognitive theory and selfefficacy theory Both are based on SLT but the focus is on beliefs and how self-beliefs influence behaviour This is an important elaboration of SLT to include how people are motivated not only by role models but also their own beliefs and experiences. Sabido Method Method for designing and producing radio and television drama that aims to change people’s behaviour Albert Bandura "Of the many cues that influence behavior, at any point in time, none is more common than the actions of others" Key Study: 'Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models' Bandura, Ross, and Ross (1961) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zerC K0lRjp8 (5-ish minutes) Aim, Method, Findings, and Evaluation (GMEC) of Bandura (1961) Work with a group of 3 to create a Google Doc in which you summarize the AMF and use critical thinking skills to EVALUATE Bandura’s study. The study is found on the OneNote document. Class Discussion – taking up the study So what happened in this study? What are some of its strengths and limitations? With an ‘elbow partner’… Read about Gergely et al. (2002) in your Pearson (green) text on pg. 123. As well, consult the full article on this site: http://webhost.ua.ac.be/funmorph/publications/Van%20Damme%20et%20al% 202002%20Nature.pdf How does this study relate to, or support social learning theory? What strengths or weaknesses can you identify regarding the study?