Infant Reflexes
advertisement

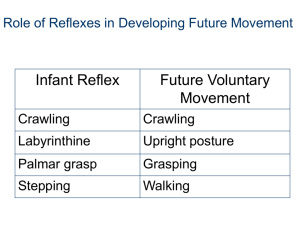
Infant Reflexes Prepared by : Emad al Khatib Objectives • Explain the infant reflexes and their importance. • Pinpoint and explain the number of infant reflexes. What are Infant Reflexes? • Involuntary stereotyped movement responses to a particular stimuli. • Dominant movement form during the first 4 months after birth. Infant Reflexes • Most “infant” reflexes do not last beyond the first year. • Infant reflexes may not completely disappear. – May be inhibited by maturing CNS. Infant reflexes are very important in the process of development. Role of Reflexes in Developing Future Movement Infant Reflex Future Voluntary Movement Crawling Crawling Palmar grasp Grasping Stepping Walking Reflexes as Diagnostic Tools • Reflexes can determine level of neurological maturation. – Reflexes are age-specific in normal, healthy infants – Severe deviations from normal time frame may indicate neurological immaturity or dysfunction. • Reflexes should be tested carefully and only by trained professionals. – Need state of quiet. – If baby restless, crying, sleepy, or distracted, may not respond to applied stimulus. Reflexes • • • • • • • Palmar Grasp Sucking Moro Symmetric Tonic Neck Plantar Grasp Babinski Stepping Reflexes ~ Palmar Grasp Stimulus / Response S: Palm stimulated R: 4 fingers (not thumb) close Duration 5 months gestation - 4 months postpartum Concerns No palmer grasp may indicate neurological problems (spasticity) Reflexes ~ Sucking Stimulus / Response Duration S: touch of lips R: sucking action 3 months postpartum Concerns No reflex problematic for nutrition Reflexes ~ Rooting Stimulus / Response S: touch cheek R: head moves toward stimuli Duration 3 months postpartum Concerns No reflex problematic for nutrition No reflex or lack of persistence may be sign of CNS dysfunction. Reflexes ~ Moro Stimulus / Response Duration S: Suddenly but gently lower baby’s head R: Arms and legs extend ( C – shape ) 4-6 months postpartum Concerns May signify CNS dysfunction if lacking. May delay sitting & head control if persists. May indicate injury to one side of brain if asymmetical. Reflexes ~ Moro Reflexes ~ Symmetric Tonic Neck Stimulus / Response Duration S: Baby sitting up and tip forward R: Neck and arms flex, legs extend 3 months Concerns Persistence may impede many motor skills and cause spinal flexion deformities Reflexes ~ Plantar Grasp Stimulus / Response Duration S: Touching the ball of foot R: Toes grasp 1 year Other Must disappear before the baby can stand or walk. Reflexes ~ Babinski Stimulus / Response Duration S: Stroke bottom or lateral portion of foot R: Great toe turns as a fan 4 months Concern Test of the pyramidal tract (i.e. ability to perform conscious / voluntary movement) Reflexes ~ Stepping Stimulus / Response Duration S: Infant upright with feet touching surface R: Legs lift and descend After birth – 5-6 months Concerns Essential for walking








![2.2 Reflex Actions [Recovered]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005391273_1-054579405a11249686dc3e18a88c3962-300x300.png)

