Tibetan Worldview
advertisement

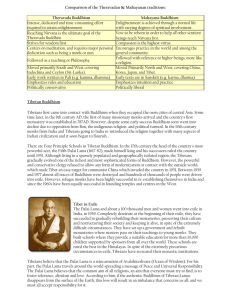
Tibetan Worldview Stacie Andrews, Richard Sweet, Glenni Rankin, Sarah Hollingsworth HCOM 301 04/29/13 The Dalai Lama... Those unrelentingly cruel ones, objects of compassion, Maddened by delusion's evils, wantonly destroy themselves and others; May they achieve the eye of wisdom, knowing what must be done and undone, And abide in the glory of friendship and love. Tibet: The Roof of the World China's Tibet Autonomous Region: 1965 Tibetan Settlements in India Tibetan-Government in Exile: Indian State of Himachal Predesh, a village known as Upper Dharamsala. This is where the Dalai Lama resides. Tibetan Refugees in Nepal Tibetans... Demographic Information - China’s grip makes this more difficult.. - Tibetan and Mandarin Chinese - The Han people - China’s Tibet Autonomous Region - Communities of faith Core Values - Individual expression of spirituality - Buddhism - The Dalai Lama: human happiness; interreligious harmony; survival of identity, culture, and religion - Faith Elements Necessary to Understand World View Tibetan philosophy engages in philosophical investigation not only to gain an understanding of the world but to also gain an understanding on how to eliminate suffering in the world. Religious or spiritual beliefs • • Indigenous Tibetan religion called Bon. Tibetan Buddhism (influenced from earlier Indian Buddhism and Bon). o Dalai Lama o Use of mantras and yogic techniques. o Preoccupation with the relationship between life and death o Gods and spirits taken from earlier Tibetan religions o Texts are separated into two sections Translated Words- the teaching of Buddha Translated Teachings- commentaries written by Indian and Tibetan authors o Four main sects of Tibetan Buddhism Ancient White Earth Oral Transmission Way of Virtue Ontological beliefs • Two different “schools” of ontological thinking that originated from Indian Mahayana Buddhism. o Mind Only School (Yogacara) Awareness and consciousness is the only thing with intrinsic essence. o Middle Way School (Madhyamaka) Denies that anything has an unchanging essence. Epistemological beliefs • • • Mysticism -meditation, Religious Faith- texts, dalai lama The Doctrine of Two Truths: o The Two Truths Conventional (Normal) truth Ultimate Truth ~Truth can mean “true” as well as “real”.~ Ethical Views/Teachings • • Utilitarian o • elimination of suffering Aristotelian Virtue o flourishing and freedom both function as a goal for good traits Education • • • Lower o Beginning in 1999, 200 schools were built and enrollment went from 85% to 98% in 2010. o Secondary education is taught in Mandarin and entrance exams to universities are in Chinese. o From primary school through college, tuition fees for ethnic Tibetans are completely subsidized by the central government Higher o In 1980, Tibetans were only 10% of higher education students o In 1984, Tibet University was est. o By 2006, had six institutions of higher learning. Medicine • • Ancient system based on Buddhist philosophy and psychology. The mind is considered to be the base because all existences and moments depend on its movements; it is the creator of every external and internal phenomena. Rural-Agrarian • • 90% work as herdsmen The other 10% live in towns earning living doing business and handicraft work, factory workers or government officials Clothing • • • • Cultural regions- home woven gowns Grasslands- sheepskin Men from Chamdo- red/black silk tassels Lhasa residents- more modern/stylish Rituals & Practices • • • • Buildings are blessed by a lama that circles it twice and throws handfuls of rice in each direction. The Hada is the most precious gift. Tibetan festivals such as Losar, Shoton, & the Bathing Festival are deeply rooted in indigenous religion. Tibetan music often involves chanting in Tibetan or Sanskrit, as an essential part of the religion. • • • Each house has altar tables for worshipping Buddha. o Most important part of the home is the prayer room. o Tend to be very colorful with scenes of Buddha’s life Do not eat horse, dog, or donkey meat, and some areas do not eat fish as well. Polyandry is practiced amongst nomadic Tibetans still today. Oppression • • • • • Nearly all the beggars in China are Tibetan. China has occupied Tibet for over 60 years Since 2009, about 100 Tibetan monks, nuns and others have set themselves on fire to protest the severe living conditions imposed on Tibetans More than 250,000 Tibetans die in prisons and labor camps. • • Since the 1960s, China has inflicted severe damage to Tibet’s environment: Toxic waste is dumped into rivers; forests are clear-cut; endangered species are hunted for sport; and nuclear-testing facilities are built. Hundreds of thousands of Tibetans die from famine and disease. Government-in-Exile • • • • Dharamsala, India Established after escape(CTA) Sino-Indian War Dalai Lama's policy of China owned Tibet Failure of Chinese Programs • "Great Leap Forward" (1958-1961) o o • Shift from Agrarian to Modern Communist Massive failure of the program Commune system Industrialization Economic Loss "Cultural Revolution" (1966-1976) Another attempt to modernize o To fix the mistakes of "Great Leap Forward" o Led to the destruction of 6,000 Tibetan monasteries o Protests • 3•14 Riots o o o o o Meant to bring attention 44 monks since 2009 Arrests and Deaths Censorship United States Reaction What Can You Do? • • Read more about the issues... Internet Websites o • o http://www.savetibet.org/support-tibet http://www.helptibet.org.uk/ Spread awareness! For More Information: • • • • • For more on Tibet: http://www.tibet.org/ Free Tibet: http://www.freetibet.org/ For more information on Tibetan Buddhism: http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/buddhism/subdivisions/tibetan_1 http://www.religionfacts.com/buddhism/sects/tibetan.htm Tibetan Epistemology and Philosophy of Language: http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/epistemology-language-tibetan/#Epi/ Tibetan Philosphy: http://www.iep.utm.edu/tibetan/