11-4 Making the Peace
advertisement

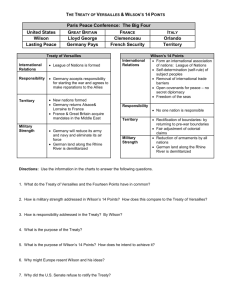
Today’s Standard 10.6 Students analyze the effects of the First World War. Analyze the aims and negotiating roles of world leaders, the terms and influence of the Treaty of Versailles and Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points, and the causes and effects of the United States's rejection of the League of Nations on world politics. Today’s Objectives 1. Discuss and evaluate the conditions of the Treaty of Versailles and how it could lead to WWI. 2. Evaluate the human and financial cost of war. Chapter 11 Section 4 Making the Peace 3 Essential Question What factors influenced the peace treaties that ended World War I, and how did people react to the treaties? Costs of War Human Costs Millions of soldiers dead and more wounded 8.5 million in battle Est. 21 million as a result of starvation and disease. 1918 – deadly influenza pandemic Killed more than 20 million people Aftermath Financial of the Battle Toll of Verdun Mass destruction of property from France to Russia Homes, farms, factories, roads and churches – shelled to rubble People felt bitter and wanted losers to pay reparations Payments for war damage Original caption: Aftermath Of Great War - Scenes In Berlin. The original German caption says 'A great friend of children distributing money & food gifts to Berlin schoolchildren.' French War Losses • No other nation suffered a greater percentage of its population dead or wounded. • Of Frenchmen between 20 and 32 at the start of the war, more than 50% were killed. • Property damage in northern France • • 300,000 houses destroyed 20,000 factories ruined • 1,360,000 head of livestock killed or confiscated • Bombing ravaged thousands of acres of forest and farmland. The Allies Meet at Versailles January 18, 1919 - Paris Peace Conference at the Palace of Versailles begins Delegates from 32 countries meet Russia and Germany & its allies are NOT represented The Big Four Major decisions at Peace Conference were made by the Big Four: Woodrow Wilson: United States David Lloyd George: Great Britain Georges Clemenceau: France Vittorio Orlando: Italy The Big Four Allies Dictate A Harsh Peace Britain & France concerned w/ national security Determined to punish Germany Compromises are made: Treaty of Versailles signed June 28, 1919 Major Provisions of Treaty League of Nations: 5 Allied Powers and 32 allied and neutral nations; Germany & Russia excluded; goal is everlasting peace 1648-1871 Territorial Losses: Treaty of Frankfurt 1871 Franco-Prussian War Alsace-Lorraine & 1871-1918 colonies in Africa & of Versailles 1919 Treaty Pacific 1919-1940 1940-1944 1945-present ruled by France ceded to Germany ruled by German Empire restored to France ruled by France ruled by Third Reich ruled by France Military Restrictions: reduced size of Germany’s army; restricted importing & manufacturing of weapons War Guilt: Article 231; Germany was held solely responsible; had to pay allies $33 Billion Creation of New Nations Many new Independent nations were created – Germany divide Austria-Hungary Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, & Yugoslavia Many nations created from former lands of Russia Poland, Romania Estonia, Latvia, etc… Peace Built on Quicksand Many in US wanted to stay out of European affairs Many in US rejected Treaty of Versailles War Guilt = Bitter Germans Many countries felt cheated b/c wanted independence or more land A League of Nations One of Wilson’s 14 points collective security Keep world peace 40 Nations joined Agreed to negotiate disputes U.S. Refused to enter in the end – weakened the league Very weak, no way to enforce decisions Legacy of the War War on a global scale About 8.5 million soldiers died; 21 million more wounded Economic drain on Europe; total cost $338 billion Countless homes, farms, & towns destroyed Laid foundation for WWII Wilson’s League of Nations “Touch Not a Single Bough” from Literary Digest 8/9/1919 Wilson’s League of Nations “Muzzled” from Literary Digest 9/13/1919 Wilson’s League of Nations “The Rainbow” from Literary Digest 9/13/1919 Wilson’s League of Nations “Blowing Bubbles” from Literary Digest 9/20/1919