Chapter 4 - Dublin City Schools
advertisement

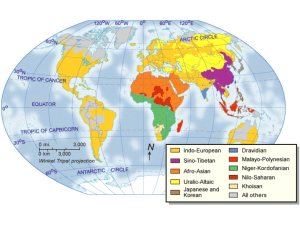
Introduction Section 1: World Population Section 2: Global Cultures Section 3: Political and Economical Systems Section 4: Resources, Trade, and the Environment Summary The characteristics and distribution of human populations affect human and physical systems. A study of the human world—population, culture, political and economic systems, and resources— will help you understand events in the world around you. Section 1: World Population What factors influence population growth in a given area or region? Section 2: Global Cultures How does the spatial interaction of cultures affect human systems? Section 3: Political and Economic Systems What types of human systems provide the power for groups of people to control Earth’s surface? Section 4: Resources, Trade, and the Environment How does the availability and use of natural resources affect economic activities and the environment? World Population What factors influence population growth in a given area or region? World Population • death rate • doubling time • birthrate • population distribution • natural increase • population density • migration • demographic transition World Population • trend • community • negative World Population A. Hungary B. Germany C. Canada D. Bangladesh E. Mexico City World Population Which continent contains most of the world’s people? A. Europe 0% C A C. Africa B A. A B. B 0% C.0%C B. Asia Population Growth Population growth varies from country to country and is influenced by cultural ideas, migration, and level of development. • More than 6.8 billion people now live on Earth, inhabiting about 30 percent of the planet’s land. • Global population is growing rapidly and is expected to reach 9 billion by the year 2050. Population Growth (cont.) • The Demographic Transition – The demographic transition model uses birthrates and death rates to show changes in the population trends of a country or region. – Most of the industrialized and technologically developed countries have reached zero population growth, in which the birthrate and death rate are equal. The Demographic Transition Model Population Growth (cont.) • Rapid population growth presents many challenges to the global community: – difficulty producing enough food to feed everyone – a shortage of resources – an uneven distribution of age Population Growth (cont.) • Countries, such as Hungary and Germany, have experienced negative population growth, in which the annual death rate exceeds the annual birthrate. Which of the following will help with problems due to rapid population growth? A. Fertilizers B. Irrigation systems C. New varieties of crops D. All of the above 0% A A. B. C. 0% D. B A B C 0% D C 0% D Population Distribution World population distribution is uneven and is influenced by migration and the Earth’s physical geography. • Almost everyone on Earth lives on a little less than one-third of the planet’s land. Population Distribution (cont.) • Population Density – To determine population density in a country, geographers divide the total population of the country by its total land area. – This does not account for uneven population distribution. World Population Density Population Distribution (cont.) • Population Movement – Many people are moving to urban areas. – The primary cause of urbanization is the desire of rural people to find jobs and a better life in more prosperous urban areas. – Population movement also occurs between countries. Urban Growth in Selected Cities Which country has one of the highest population densities in the world? A. Bangladesh B. Canada C. Sweden D. China 0% A A. B. C. 0% D. B A B C 0% D C 0% D Global Cultures How does the spatial interaction of cultures affect human systems? Global Cultures • culture • cultural diffusion • language family • culture hearth • ethnic group • culture region • similar • major Global Cultures A. Egypt B. Iraq C. Pakistan D. China E. Mexico Global Cultures When studying a culture, what areas are looked at? A. Language and religion 0% C A C. All of the above B A. A B. B 0%C. 0% C B. Daily life, history, and art Elements of Culture Geographers divide the Earth into culture regions, which are defined by the presence of common elements such as language and religion. • A particular culture can be understood by looking at the following elements: – Language – Religion World Language Families Elements of Culture (cont.) – Social Groups – Government and Economy – Culture Regions World Culture Regions Groups of people ranked according to ancestry, wealth, education, or other criteria fall under which term? A. Social group A C. Ethnic group B A. A B. B 0%C. 0% C 0% C B. Social class Cultural Change Internal and external forces change cultures over time. • The Agricultural Revolution – The shift from hunting and gathering food to producing food is known as the Agricultural Revolution. – Some of the farming villages evolved into civilizations. Cultural Change (cont.) – The world’s first civilizations arose in culture hearths. • The most influential culture hearths developed in areas that make up the modern countries of: – Egypt – Iraq – Pakistan – China – Mexico World Culture Hearths Cultural Change (cont.) • They have certain geographic features in common: – Mild climate – Fertile land – Located near a major river or source of water Cultural Change (cont.) • Cultural contact among different civilizations promoted cultural change as ideas and practices spread through trade and travel. Cultural Change (cont.) • Industrial and Information Revolutions – In the late 1700s and 1800s some countries experienced the Industrial Revolution, which led to social changes. – At the end of the 1900s, the information revolution opened doors for experiencing new cultures. Which of the following “set the stage for the rise of cities and civilizations”? A. Nomadic hunting B. Housing C. Surplus food 0% D. Military power A A. B. C. 0% D. B A B C 0% D C 0% D Political and Economical Systems What types of human systems provide the power for groups of people to control Earth’s surface? Political and Economical Systems • unitary system • democracy • federal system • traditional economy • autocracy • market economy • monarchy • mixed economy • oligarchy • command economy Political and Economical Systems • unique • authority • assembly Political and Economical Systems A. United States B. Saudi Arabia C. United Kingdom D. China E. Vietnam Political and Economic Systems An oligarchy is a government ruled by what? 0% C C. Many individuals B B. A single individual A. A B. B C.0% C0% A A. A few individuals Features of Government Territory, population, and sovereignty influence levels and types of governments in countries around the world. • Levels of government – Most countries have several levels of government, ranging from the national level to the village level. Features of Government (cont.) • Two types of government systems are: – Unitary—the United Kingdom and France use this system. – Federal—the United States, Canada and Switzerland are three of many countries that use this system. Features of Government (cont.) • All governments belong to one of three major groups: – Autocracy—rule by one person – A monarchy is another form of autocratic government. – Oligarchy—rule by a few people – Democracy—rule by many people Which form of government do you feel works best and why? A. Autocracy A 0% 0% C C. Democracy A. A B. B C.0%C B B. Oligarchy Economic Systems The three major economic systems are traditional economy, market economy, and command economy. • All economic systems must make three basic economic decisions: – What and how many goods and services should be produced Economic Systems (cont.) – How should they be produced – Who gets the goods and services that are produced • These decisions are made differently in the three major economic systems: – Traditional—habit and custom determine the rules. – Market—this economy is based on free enterprise, the idea that private individuals or groups have the right to own property or businesses and make a profit with only limited government interference. Economic Systems (cont.) – Most market economies are actually mixed economies. – Command—the government controls the economy is this system. Economic Systems (cont.) • Two types of command economies: – Communist—strict government control of the entire society – Socialist—three main goals of this type of economy: • An equitable distribution of wealth and economic opportunity • Society’s control, through its government, makes decisions about public goods. • Public ownership of services and factories that are essential. Capitalism is another term for which type of economy? A. Traditional B. Market 0% C A 0% A. A B. B C.0%C B C. Command Resources, Trade, and the Environment How does the availability and use of natural resources affect economic activities and the environment? Resources, Trade, and the Environment • natural resource • developing country • industrialization • free trade • developed country • pollution • newly industrialized country Resources, Trade, and the Environment • ensure • benefit • conduct Resources, Trade, and the Environment A. Malaysia B. European Union Resources, Trade, and the Environment Geographers and economists classify the world’s economic activities into how many types? 0% 0% C C. Four 0% B B. Two A A. Eight A. A B. B C. C Resource Management Natural resources must be managed to ensure future needs. • Because fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, and other nonrenewable resources cannot be replaced, they must be conserved. Resource Management (cont.) • Alternative energy sources: – Hydroelectric power – Solar energy – Nuclear energy The Global Economy Which is a renewable resource? A. Oil B. Minerals C. Coal D. Sun 0% A A. B. 0% C. D. B A B 0% C D C 0% D Economies and World Trade Countries with varying levels of economic development have become increasingly interdependent through world trade. • Geographers and economists classify all of the world’s economic activities into four types: – Primary economic activities—taking or using natural resources directly from the Earth Economies and World Trade (cont.) – Secondary economic activities—raw materials are used to produce something new and more valuable. – Tertiary economic activities—provide services to people and businesses – Quaternary economic activities—the processing, management, and distribution of information The Global Economy Economies and World Trade (cont.) • Factors affecting trade: – The unequal distribution of natural resources – Differences in labor costs – Differences in education levels Economies and World Trade (cont.) • Barriers to trade: – Tariffs – Embargos – A quota on the quantity of a product that can be imported from a country • Many governments around the world have moved toward free trade. World Economic Trends Manufacturing automobiles would fall under with type of economic activity? A. Primary B. Secondary C. Tertiary 0% D. Quaternary A A. B. 0% C. D. B A B 0% C D C 0% D People and the Environment Economic activities have led to environmental pollution. • The water, land, and air have all been polluted due to human activity. • When humans harm natural ecosystems, they are also hurting themselves. What is a solution to our pollution problems? A. Plant more trees B. Reduce chemical spills C. Alternative fueled cars D. All of the above 0% A A. B. 0% C. D. B A B 0% C D C 0% D World Population • Population growth increased rapidly, but unevenly throughout the twentieth century and into the twentyfirst century. • The world’s population is unevenly distributed. Large numbers of people are migrating from rural areas to cities for jobs or to escape famine and war. • As people become more mobile, so do goods. Countries trade to gain access to resources they lack. World Culture • Language, religion, social groups, government, and economic activities define cultures. • Geographers divide the Earth into specific culture regions. • Trade, migration, war, and technology can change cultures. • The world’s first civilizations arose in culture hearths in Central America, Africa, and Asia. Government and Economic Systems • Governments may be organized as a unitary system, a federal system, or a confederation. • An autocracy, an oligarchy, and a democracy differ in the way they exercise authority. • The three major economic systems are traditional economy, market economy, and command economy. • The type of economic system helps determine how a country will view international trade. Market economies are more open to free trade, while command economies are likely to put up trade barriers. death rate the number of deaths per year for every 1,000 people birthrate the number of births per year for every 1,000 people natural increase the growth rate of a population; the difference between birthrate and death rate migration the movement of people from place to place demographic transition the model that uses birthrates and death rates to show changes in the population trends of a country or region doubling time the number of years it takes a population to double in size population distribution the pattern of population in a country, a continent, or the world population density the average number of people in a square mile or square kilometer culture way of life of a group of people who share beliefs and similar customs language family group of related languages that have all developed from one earlier language ethnic group group of people who share common ancestry, language, religion, customs, or combination of such characteristics culture region division of the Earth based on a variety of factors, including government, social groups, economic systems, language, or religion cultural diffusion the spread of new knowledge and skills from one culture to another culture hearth a center where cultures developed and from which ideas and traditions spread outward unitary system a government in which all key powers are given to the national or central government federal system form of government in which powers are divided between the national government and the state or provincial government autocracy government in which one person rules with unlimited power and authority monarchy a form of autocracy with a hereditary king or queen exercising supreme power oligarchy system of government in which a small group holds power democracy any system of government in which leaders rule with consent of the citizens traditional economy a system in which tradition and custom control all economic activity; exists in only a few parts of the world today market economy an economic system based on free enterprise, in which businesses are privately owned, and production and prices are determined by supply and demand mixed economy a system of resource management in which the government supports and regulates enterprise through decisions that affect the marketplace command economy system of resource management in which decisions about production and distribution of goods and services are made by a central authority natural resource substance from the earth that is not made by people but can be used by them industrialization transition from an agricultural society to one based on industry developed country country that has a great deal of technology and manufacturing newly industrialized country a country that has begun transitioning from primarily agricultural to primarily manufacturing and industry activity developing country country in the process of becoming industrialized free trade the removal of trade barriers so that goods can flow freely between countries pollution the existence of impure, unclean, or poisonous substances in the air, water, or land To navigate within this Presentation Plus! product: Click the Forward button to go to the next slide. Click the Previous button to return to the previous slide. Click the Return button to return to the main presentation. Click the Home button to return to the Chapter Menu. Click the Help button to access this screen. Click the Exit button or press the Escape key [Esc] to end the chapter slide show. Links to Maps in Motion, static maps and charts, and transparencies appear near the bottom of slides as they are relevant. Links to the Reference Atlas and Geography Online are located on the navigation bar of most screens. This slide is intentionally blank.