The sanctity of human life (a PowerPoint presentation by Gary
advertisement
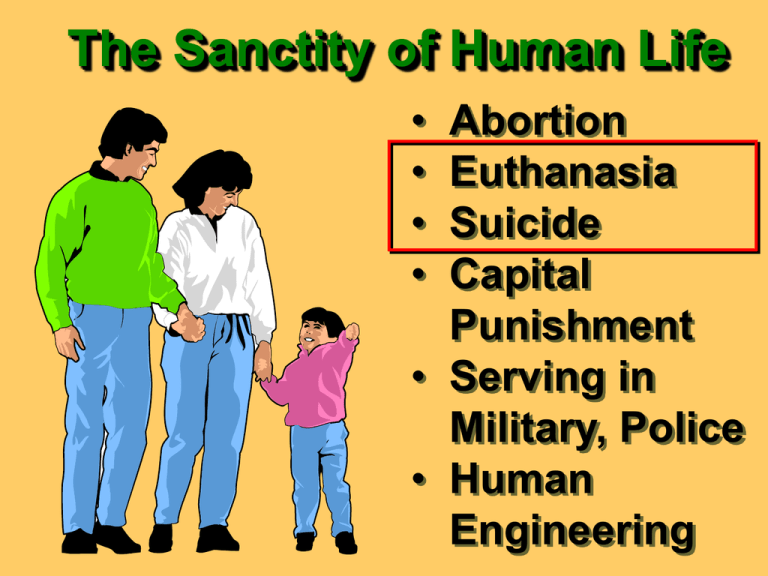
The Sanctity of Human Life • • • • Abortion Euthanasia Suicide Capital Punishment • Serving in Military, Police • Human Engineering The Sanctity of Human Life Is euthanasia a merciful way of preventing suffering? Is suicide an acceptable way to terminate one’s life? Is it morally wrong to execute a criminal? May a soldier or police officer to kill in the line of duty? What moral implications are related to human engineering? Foundation Principles Man: product of creation, not evolution • Gen. 2:7 • Acts 17:25 • 1 Tim. 6:13 Foundation Principles Only Creator has right to terminate the life of a human being Except when God • Gen. 9:6 delegates that • Ex. 20:13 right (e.g. capital • Ex. 21:12 punishment, war, • Lev. 24:21 etc. (Rm. 13:1-4) “When life is not good it deserves neither protection nor preservation” Euthanasia What is meant by a “good life”? “To be human is to be self-aware, consciously related to others, capable of rationality in a measure at least significant to support some initiative. When these things are absent, or cannot ever come to be, there is neither a potential nor an actual person.”Joseph Fletcher The Atlantic Monthly Vol. 22, No. 4, April 1968 Euthanasia’s Meaning From two Greek words: eu = well or good thanos = death It thus means to die well, easy, or without pain. In modern society it has come to refer to terminating human life [i.e. “mercy killing”] History of Euthanasia Greeks: respected aged, practiced infanticide Spartans: euthanized weak youth Plato, Aristotle – discouraged rearing deformed children South Sea Islands: abortion, infanticide Sardinia: old men killed with clubs 1938 – Euthanasia Society Euthanasia Has Many Supporters Many duped by emotional “merciful death” arguments Most vocal advocates are ruthless: Dr. William Duke George Paulson Joseph Fletcher Dr. Glanville Willams 4 KINDS OF EUTHANASIA • • • • Active Passive Voluntary Mandatory GENERAL ACCEPTANCE OF EUTHANASIA The general acceptance of euthanasia in modern America is evident in: • • • • “Dr. Death” • Dr. Robert “Infant Doe” Cooke Internists’ Survey • Abortion’s Newsweek report Acceptance Why Is Euthanasia Accepted? Value of life is less! Historical shock has dulled! God has been dismissed! Biblical Answers Active Euthanasia – murder, sinful (Ex. 20:13; Gen. 9:6) Biblical Answers Volunteer Euthanasia Biblical incidents, acts of ungodly men (1 Sam. 31:4-5; 2 Sam. 17:23; 1 Kings 16:18; Matt. 27:5) Wayne Jackson lists three biblical premises violated in suicide Sinfulness of Suicide 1.Asserts man is autonomous (Psalm 100:3; cf. Ezek 18:4) a.Only God has right to determine when life should end 2.Self-murder (Rev. 21:8; 22:15) 3.Robs God of service (Eccl. 12:13; cf. Phil. 1:20) 4.Act of supreme selfishness Biblical Answers Passive and Mandatory Euthanasia We have biblical guidance over life, death, and preservation of life Instances of euthanasia in Bible No specific teaching on intricacies of the natural and artificial means of preserving life Mindset of Society Concerning Euthanasia We live in a time where the average life span in American continues to increase each year. 1930 - average life expectancy for all gender and races in the U.S. was 59.7 years. In 2004 that number steadily climbed to 77.9 years. Many modern advances in the science and medical fields that correlate to our longer life spans. In 1947 the first person was saved by means of defibrillation. Since then millions of lives have been saved by this one devise. This allowed people to live years beyond what was previously expected Various vaccinations used to stem the onset of various plagues • Smallpox eradicated in 1980 • Fewer than 500 with polio in world • Longer for many by additional medicinal breakthroughs • Advanced surgical procedures and medicines allow longer life [radiation, chemo therapy, dialysis, laser surgeries, etc] These factors produce a mindset concerning the quality of life The thought of a nice and peaceful death permeates into our societal belief system. Conversely, the thought of pain and suffering in dying is not at all desirable [it is natural to want to live our final years in peace] Thus, a more tolerant view of “mercy killing”/euthanasia (i.e. hastening death) of a person who is seriously or terminally ill or injured to bring relief to the individual. Two Types of Euthanasia Being Considered at This Time: Passive – a refusal to use life sustaining medical equipment to prolong life where there is no [medically] prospect of recovery Active – taking purposefully action to end a life, for some it is an aided suicide Pertinent Terms to Understand Medical Treatment Comatose Minimally Conscious State (MCS) Vegetative State (PS) Persistent Vegetative State (PVS) Purpose of Understanding These Terms A person might receive a feeding tube for an individual whose mouth, trachea or another area of the body which does not allow him to chew and/or swallow food Another might receive a feeding tube due to his being in a vegetative state Purpose of Understanding (cont.) These Terms This circumstance The intent for the first makes decisions difficult patient is to provide “life support” while he nurses back to health The intent for the second person is to provide life support with the sum hope that he regains consciousness Purpose of Understanding (cont.) These Terms • In both cases the intent is to save life • Reason for removing life support (respirator or feeding tube) is not to destroy life, but to realize there is no hope for life and thus discontinue artificial means of sustaining life Dilemmas Surrounding “Mercy Killing” Desire the ever improving means by which life can be prolonged or saved But, reached a point we can keep someone alive for years The means by which we keep a person alive creates our dilemma regarding euthanasia Dilemmas Surrounding “Mercy Killing” Ethical Dilemmas Extended comatose state with no perceived possibility of consciousness Vegetative state (or PVS) with no perceived possibility of recovery Someone terminal, but conscious and in severe pain Dilemmas Surrounding “Mercy Killing” Ethical Questions Is it wrong to “actively” end another person’s life? Who has authority to judge what is a “good cause” to end life? Are we to respect the desire of a patient desiring to be taken off life support when they are alive (alert)? Biblical Conclusions 1.Active Euthanasia is sin a.Even if patient is in pain or struggle b.Even if patient wished his life be ended 2.Passive Euthanasia is not sin a.Artificial means continues while there is hope – ends when hope is lost WHAT ARE CHRISTIANS TO DO? Do not be fooled (Eph. 4:14; Col. 2:8; Ps. 1:1) Respect All life! (Job 1:21; Gen. 1:26-27; Pr. 6:16-17; Acts 17:25, 28) Do good to all (Gal. 6:10; Ex. 23:7) Do not allow handicaps to devalue human life (Ex. 4:11) Become brother’s keeper (Pr. 24:11) THE TRAGIC FAILINGS! No knowledge of the inner man Confusion as to who would become a candidate Indecision as to the final judge • Patient – incompetent, drugged • Physician – trust ruined • Family – estate mongers rejoice • State – Nazi Germany reborn Job 1:21 Nations that fail to resist euthanasia are described in Deut. 28:49-50