MR. LIPMAN’S APUS
POWERPOINT
CHAPTER 38
The Stormy 1960s
Keys to the Chapter
Focus
on four (4) key major issues:
Civil Rights
War on Poverty and the expansion of the
welfare state
Vietnam and the Anti-War Movement
Counter Culture Movement
Key Figures: JFK, LBJ, MLK, Malcolm X
Inauguration Jan. 1960- “The Best and
the Brightest” begins
THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT JFK
Ivy
League (best and the brightest)
RFK and McNamara
Peace Corps
Tax Cuts
Race to the Moon
Reduced Tariffs to increase trade
Civil Rights
Kennedy and Foreign Affairs
Bay
of Pigs (April 1961)
Meeting with Khrushchev in ( June 1961)
The Berlin Wall (August 1961)
Cuban Missile Crisis (October 1962)
Increase in Military Advisors and troops to
Vietnam (15,000 by November 1963)
American University Speech and the call
for peace with Russia (June 1963)
Kennedy
and
Khrushchev,
Vienna,
1961
------------Khrushchev
feels he is
“young and
weak”
Protest by a Buddhist Monk
Against Diem’s Repression as Vietnam
“heats up”
The Cuban Missile Crisis
How
close
did we
get?
JFK and Civil Rights
Freedom
Riders (1961)
James Meredith (“Ole Miss-Sept. 1962)
Birmingham (1963)
Medgar Evers (June 1963)
Washington and MLK (August 1963)
Birmingham Church Bombing (Sept. 1963)
Southern Democrats block Congressional
bills from passing
Greyhound Bus Burning After White
Attack on Freedom Rides Bus,
Alabama, May 1961
US Army Convoy at the University of Mississippi
to Enforce James Meredith’s Admission
Civil Rights Protestors Sprayed
with Fire Hoses in Birmingham
Civil Rights Segregation Protesters Flee from in
Birmingham, Alabama---T.V. Changes everything
The “ I Have a Dream ”
Speech in Front of the Lincoln
Memorial
Thousands of
Marchers
Gather at the
Lincoln
Memorial for
the March on
Washington
and Dr. King’s
“ I Have A
Dream ”
Speech
The 16th
Street
Baptist
Church
After the
Bombing
Kennedy’s Limousine Immediately Before the
Assassination
The Killing of Kennedy- November 22, 1963
The importance of Kennedy
Later revelations tarnished Kennedy’s reputation
Nation mourned young president
Remember more for the spirit than accomplishments
Womanizing and Involvement with organized crime
President Lyndon Johnson
Sworn in on plane in Dallas before leaving (with
Kennedy’s body) for Washington, DC
Kept most of Kennedy’s team, although he distrusted
them (“the Harvards”)
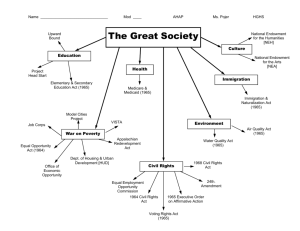
THE LBJ PRESIDENCY
War
•
•
•
•
•
on Poverty and the “Great Society”
Aid to Education
Medical Care for poor and elderly
Immigration Reform
Voting Rights Act of 1964 (24th Amendment)
Vietnam and the “Gulf of Tonkin Resolution”
Civil Rights
Israel and the start of the unending problem
Vietnam and the “Tet Offensive”
The Counter Culture Movement (3 P’s)
1964 – Civil Rights bill passed after lengthy
Southern filibuster
Banned racial discrimination in most private facilities
open to the public
Strengthened federal government’s power to end
segregation in schools and other public places
Created federal Equal Employment Opportunity
Commission (EEOC) to eliminate discrimination
Included Title VII ending gender discrimination
Backed up in 1965 with Affirmative Action executive
order to pvt. Contractors getting federal contracts
The
Great Society
Billion-dollar “War on Poverty”
Economic & welfare measures based on New
Deal
1962 – The Other America
• By Michael Harrington
• 20% of the population (40% of the black
population) lived in poverty
• Moved public to support Great Society proposals
1964 Presidential Race – LBJ vs. Goldwater
Goldwater attacked federal income tax, Social
Security, Tennessee Valley Authority, civil rights laws,
nuclear test-ban treaty, and especially the Great
Society
Republican slogan - “In Your Heart You Know He’s
Right”
• Democratic reply – “In Your Guts You Know He’s
Nuts”
• August 1964 – Gulf of Tonkin incident changes
LBJ
Johnson won a landslide with 61% of the vote
LBJ and the Voting Rights Act
Mississippi had largest black population
• Only 5% of those eligible were registered to vote
Ways to keep blacks from voting
• Poll tax, literacy test, intimidation
• 24th amendment (ratified February 1964) outlawed
poll tax in federal elections
Freedom Summer (1964)
• Blacks join white students in massive voterregistration drive in Mississippi
White
attacks during Freedom Summer
June 1964 – 1 black and 2 white civil rights
workers from North disappeared in Mississippi
• Badly beaten bodies found buried
• FBI arrested 21 whites (including a sheriff)
White juries refused to convict
Newspapers rally against the actions of
“Southern Justice”
Photographs
of Civil Rights
Workers after
They
Disappeared
in Mississippi
Early 1965 – King resumed voter-registration in Selma,
Alabama
Blacks 50% of the population but only 1% of
registered voters
State troopers used gas and whips to stop a peaceful
march from Selma to Montgomery
Police Actions Captured on Television
President Johnson makes stirring speech on national
television after events in Selma
Nation “must overcome the crippling legacy of bigotry
and injustice…And we shall overcome.”
A Civil Rights Marcher Attempts to Ward Off
the Attack of State Troopers
A Civil Rights
Marcher Suffering
from Exposure to
Tear Gas, Holds
an Unconscious
Woman in Selma,
Alabama
1965
The Rise of the African American Vote,
1940-1976
Black Power
Passage of Voting Rights Act of 1965 marked
end of an era in civil rights movement:
Pre-1965 – movement focused on nonviolent
protest in South
Post-1965 – movement marked by militant
confrontation, led by radical and sometimes
violent spokespersons, and often aimed not at
interracial cooperation but at black separatism
• Moderate Martin Luther King, Jr. attacked by new
generation of younger black leaders
• Malcolm X becomes the symbol of the new strategy
Black Power Key Events
– 1965
Newark and Detroit – 1967
Malcolm X (killed Feb. 1965)
Black Panthers
MLK (killed April, 1968)
Watts
Watts Rioting - 1965
Watts Riots - 1965
Rioting at Newark, NJ, 1967
Black Power
Malcolm X
Joined Nation of Islam while in prison
Pushed for black separatism, attacking “blue-eyed
white devils”
Broke with Nation of Islam in 1964 and travelled to
Mecca, where he saw white Muslims
• Softened his attacks on whites
February 1965 – killed by 3 Nation of Islam
members while speaking in New York City
Malcolm X
Killed 1965
Black
Panther Party
Black
Power
Assassination of MLK. April 1968
Destruction Caused by Chicago Riots
After Dr. King's Assassination
LBJ AND VIETNAM
1965 – escalation begins
End of 1965 – 184K US troops there
Early
1968 – 500,000 troops and $30
billion annually sunk into Vietnam
By
South Vietnam is spectator as war is
Americanized
World
opinion will turn against America
U.S. Combat Troops in Vietnam
US Battle Deaths in Vietnam
Vietnamese Civilians Escaping an Accidental
Napalm Bombing of Their Village
Domestic protests over Vietnam Increase
1965 – campus “teach-ins”
Protests increased as war got worse and
draft reached more young men
• “Hell no, we won’t go!”
Resisters burned draft cards - go to Canada
News showed US troops burning hunts
and civilians burned with napalm
News showed pictures of dying U.S. troops
• “Hey, hey, LBJ, how many kids did you
kill today?”
1968 – Vietnam was longest and
most unpopular war in US history
Early
Government failed to explain rationale
for war to public
Johnson claimed he could see “the
light at the end of the tunnel”
• Most Americans did not believe him
January 1968 – Tet Offensive
Communist offensive over entire country
• Eventually defeated by US forces – the Tet
offensive was a military defeat for the Viet
Cong but bad public relations for USA.
Public turned against the war
• Military leaders requested 200,000 more
troops (staggering amount to public)
A South Vietnamese Officer Kills a Bound Viet
Cong Suspect During the Tet Offensive
March 31, 1968 – Johnson surprise T.V. talk
Announced he would freeze US troop
levels and scale back the bombing
Also announces that “I shall not seek, and I
will not accept the nomination of my party
for another term as your president.”
Orders that bombing raids over North stop
Johnson’s Speech Announcing He Would
Not Run Again For President 3/31/68
of 1968 – Democrats fight for
nomination
Summer
V.P. Hubert Humphrey carrying on LBJ
policies
Senator McCarthy and Senator Kennedy
fought for “dove” vote, with Kennedy
gaining momentum
June 5, 1968 – Kennedy wins in California
primary but is then killed
August Dem. Convention turns into a “zoo”
Robert Kennedy Immediately After the
Shooting
Police and Demonstrators Fighting Outside 1968
Democratic National Convention
Results of election: 1968
Nixon won a close race against Humphrey
Democrats kept both houses of Congress
Nixon had won no mandate to do anything
Wallace received almost 10 million votes
• Largest 3rd party vote in US history
“I knew from the
start if I left a
woman I really
loved -- the
Great Society -in order to fight
that bitch of a
war in Vietnam
then I would
lose everything
at home.”
Lyndon Johnson
THE COUNTER CULTURE MOVEMENT
“Trust
no one over 30”
Roots in Beatnik generation of 1950s
Can be attributed to the 3 P’s
Population (young)
Prosperity (economics of war)
Protest Movement
1964
– Free Speech Movement
University of California at Berkeley
Students objected to ban on political
debate in campus space
Used sit-ins to protest university
Spreads to campuses across the country
Vietnam “radicalized” the middle class
Free Speech Rally at UC Berkeley, 1964
A Love-In
Demonstration 1967
1960s
sexual revolution
• 1960 – birth control pill introduced
• Increased experimentation with sex
Gay rights
• 1969 – attack by off-duty police at
Stonewall Inn in N.Y. energized gays
Drug use leads to organized drug gangs and
urban decay of the 1970s
Protest movement of the 1960s would lead to
violence of the “radicals” in the 1970s