Russia and China: Post
advertisement

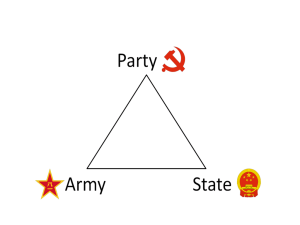
Russia and China: PostCommunism Themes • Globalization: liberalization (Washington Consensus) – End corporatism in Mexico – Implementation Four Modernizations China (Deng) – Immigration + global culture • “Red Oxen” in Mongolia – Neo-Mercantilism: import substitution + export-driven growth – Anti-globalization • Democratization: post-communism – – – – “Color revolutions”: Ukraine, Lebanon Nigeria, Mexico “no representation w/o taxation” Islamo-Fascism + Putinism Communism • • • • • • • Soviet Union • China General Secretary • Central Committee – Secretariat (General Secretary; Hu Politburo (Political Bureau) Jintao, 2002) Central Committee (ran Party – Politburo + Standing Committee (24 / + gov’t in between 9) Congresses) – Central Military Commission (chair: Hu, ’04; PLA 3rd “branch” of gov’t) Party Congress (every 5 years; • National People’s Congress but none ’39-’52) [every 5 years; “one party two Party cell (any org. w/3+ factions”: Shanghai clique (rich, Communists urban) and populist coalition (rural, Party ran the state; Party Communist Youth League); extra-legal complementary, expertise, unity achieved through patronage] • President of the PRC (1982 Constitution; Hu, ‘03) • State Council (top People’s Government; Premier: Wen Jiabao) • Party bound by PRC Constitution, “rule of law” China • USSR + Imperial China structure – Bureaucratic admin., centralized control (but increasing devolution; Hong Kong, Macau) • “Mass Line”: “from the masses, to the masses”; peasants as revolutionary (contra Marx + Lenin); investigate conditions, listen to ideas, raise consciousness • “Democratic centralism”: members subordinate to org.; minority to majority; lower to higher; gov’t to Party; all to Central Committee – No private/indiv. interest, “people’s democratic dictatorship” no organized opposition (non-CCP parties controlled by CCP; “vanguard of the proletariat”); Party represents objective history (Marxism/Maoism) • “Harmony”: “harmonizing” (e.g. websites) = censorship; Falun Gong; Tibet; Xianjiang province Democratization in China • Deng’s 4 Modernizations; esp. Special Economic Zones • Household responsibility system; Township and Village Enterprises (TVE) “industrial clusters” • Key: Industries allowed to exceed quotas, buy and sell, reinvest • 1989: Tiananmen Square protests crackdown purge • 2002: SARS • 2008: Tibet vs. earthquake; economic slowdown (crucial: trade off collapsing) Communist Party Membership Routes • • • • • Russia • Cost-benefit: Purges vs. Nomenklatura (list + class) Young Pioneers Komonsol (Young Communist • League) Communist Party membership – 1986: 10% of pop. • • • China Power = connections (Deng Xiaoping post-”resignation”); Party networks; jobs – BUT: ideology, desire to travel overseas Young Pioneers Communist Youth League – Shut down in Cultural Revolution, replaced by Red Guards Requires nomination existing member, testing/assessment + probation period 70+ million members (largest party in world) – Only 17% of members are women and 78% are over 35 years old, though efforts are under way to broaden its membership and attract more young people Democratization in Russia • M. Gorbachev • Perestroika (1987): political + economic “restructuring”: multi-candidate (not party) elections, called Party Conference; Law on State Enterprise: output based on demand, private ownership certain sectors • Glasnost: “openness;” get around apparatchiks (agent of the apparatus) • Secession crisis 1991 coup, Yeltsin gains power 26 December USSR dissolves Commonwealth Independent States • 1993: Yeltsin’s “shock therapy” crisis bombards legis new structure (Federal Assembly) + increased Pres power via referendum on Constitution – How democratic was Yeltsin? Many of Putin’s actions expansion Yeltsin