Adjective Clauses present
advertisement

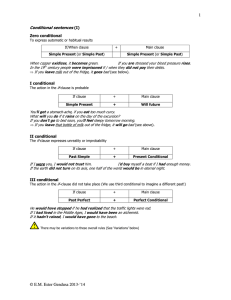
1. Masayu martika sari 2. Dhea riski 3. Meri puspita sari 4. Navisa novaria 5. Rizky wulandari XII IPA 1 Differences between two stories on pages 44-45 The Pied Piper of Hamelin Hansel and Gretel The children in the story and the pied piper of a sudden disappeared. The children in the story of Hansel and Gretel to be removed by his parents. In the story of the pied piper, the parents and especially the mother very concerned about their children. In the story of Hansel and Gretel's stepmother they want to eliminate them, not worrying about them. The Pied Piper of Hamelin happen in Hansel and Gretel happen in a great a town. forest. The Pied Piper tell us about the rich citizens. Hansel and Gretel tell us about the poor wood cutter. Similarities between two stories on pages 4445 The Pied Piper of Hamelin Hansel and Gretel Tells the story of about children Tells the story of about children Solve a problem Solve a problem The stories are narrative text. They have same purpose The stories are narrative text. They have same purpose The stories used past tense. The stories used past tense. Adjective Clauses • Adjective clauses adalah dependent clause yang memiliki subjek dan predikat yang tidak berdiri sendiri dalam kalimat. Adjective clauses ini berfungsi seperti halnya adjectives yang menerangkan nouns (kata benda) atau pronouns (kata ganti). Adjective clause tidak merubah arti dasar dari sebuah kalimat. • Posisi adjective clause selalu mengikuti noun atau pronoun yang diterangkannya. Di dalam kalimat, noun atau pronoun itu berfungsi sebagai subject atau object. • Adjective clause is kumpulan kata yang sederhana dengan subjek dan kata kerja yang menyediakan penjelasan. Klausanya dimulai dari kata ganti seperti who, whom, which dan that yang berfungsi menjembatani hubungan •Independent Clause adalah kalimat lengkap. Independent clause mengandung subject utama dan kata kerja dari suatu kalimat. Independent clause juga disebut sebagai main clause (induk kalimat). •Dependent Clause adalah kalimat yang tidak lengkap dan tidak dapat berdiri sendiri.Dependent clause (anak kalimat) harus dihubungkan dengan Independent clause (induk kalimat). Relative pronoun (who, which, that) can be subject if don’t have subject. Relative Pronoun +/- S+V Independent Clause + Adjective Clause Who Whom Adjective clause Whose Which That Adjective clauses used subordinate conjunctions: “where,when, and why” 1) Adjective Clause used “where” Where is used in adjective clause to change place (country, city, room, house, etc). Example: 1. –The church is old. -My grandparents married. => The church where my grandparents were married is old. 2. -Yogyakarta is a city. -I was born. => Yogyakarta is a city where I was born. 2. Adjective Clause used “when” When is used in adjective clause to change a noun from time (year, day, date, etc). Example: 1. -I’ll never forget the day. -I hold your hand. => I’ll never forget the day when I hold your hand. 2. - She don’t remember that time. - She fell into the swimming pool. => She don’t remember the time when she fell into the swimming pool. 3. Adjective Clause used “why” Why is used in adjective clause to adapt the reason about something that people have to do. Example: I don’t remember the reason why I went there. Thank’s