Chapter 3
advertisement

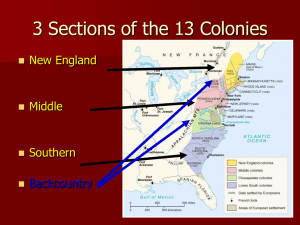
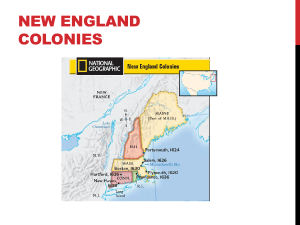
Chapter 3 Colonies Take Root Section 1: I Can Statement I can understand how the English set up their first colonies. Section 1: Bullet Points • Bullet Point #1: The English colony at Jamestown is founded in 1607. • Bullet Point #2: English Pilgrims seeking religious freedom settled the Plymouth Colony. England Seeks Colonies • England began to establish colonies in North America in the 1500s • Reasons for colonies: – New trade markets – Raw materials • First colony established in North Carolina; Roanoke Island Founding Jamestown • 1607 Virginia Company of London establishes a colony • Wanted to find gold and silver, or to trade with Indians for furs • King granted a charter • Charter: a document issued by a government that grants specific rights to a person or company • Virginia colony named Jamestown • Rough first year, many died • Problems: – Warm weather – Lazy colonists – Spent too much time looking for gold • John Smith: sent from London to lead Jamestown • Wrote new rules • #1 rule: “he who works not, eats not” • Hundreds of new colonists arrive • Women come to Jamestown • John Smith and men attack Indians to get food • John Smith goes back to England • Jamestown has a “starving time”, lack of food Jamestown Prospers • Virginia Company keeps sending new colonists • Virginia Company offers free land • New leaders sent to restore order in the colony • Found a new money maker: Tobacco House of Burgesses • Representative government: the form of government in which voters elect people to make laws for them • House of Burgesses= lawmaking body, that could pass and set laws and shared power with Virginia’s governor The Plymouth Colony • Separatists: English who wanted to separate from the Church of England, wanted religious freedom • Moved to the Netherlands and didn’t like it, wanted to go to Virginia • Pilgrim: person who takes a religious journey Mayflower Compact • • • • • Mayflower, Pilgrims ship Never reached Virginia Landed in Massachusetts Named colony Plymouth Mayflower compact: first document in which colonists claimed a right to govern themselves First Thanksgiving • Rough winter for the pilgrims • Not enough food, people dying due to disease and hunger • Got help from the Native Americans • Squanto: Indian who brought the pilgrims seeds of corn, beans and pumpkins and showed them how to plant them Section 2: I Can Statement I can understand how the religious beliefs and dissent influenced the New England Colonies. Section 2: Bullet Points • Bullet #1: Puritans seeking religious freedom settled the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1630. • Bullet #2: People unhappy with the Puritans’ religious intolerance founded Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Hampshire. Geography of New England • Made up of hills and low mountains • Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, Vermont and Maine • Farming is difficult • Winters: long and snowy • Summers: short and warm • Weather helps people live longer Puritans in Massachusetts Bay • Puritans: group that wanted reform of the Church of England • King Charles I didn’t treat the Puritans nicely • Puritans formed Massachusetts Bay Colony • John Winthrop: leader of the Puritans who was a respected landowner and lawyer Massachusetts Bay Colony • Boston: main city in the colony • Had an elected assembly, had to be a male and part of the Puritan church to vote • Didn’t believe in religious toleration (recognition that other people have the right to other opinions) New Colonies • Rodger Williams: minister of a church in Salem who believed the Puritans should split from the Church of England • Rhode Island founded by Williams, colony had no official religion Settling Connecticut • Thomas Hooker: minister who settled Connecticut • John Wheelright: forced to Massachusetts, settled New Hampshire Growth and Change • Town Meeting: an assembly of townspeople that decides local issues • Only men could be a part of town meetings • Gave people a place to speak their minds • Encouraged democratic ideas King Philip’s War • Indian population decreasing • Metacom: chief of the Wampanog, also know as King Philip, goal was to stop Puritan expansion • Uprising lasted a year, ended when Metacom was captured and killed • English colonies expanded after the war Section 3: I Can Statement I can understand how the diverse Middle Colonies developed and thrived. Section 3: Bullet Points • Bullet #1: After the English takeover, New Netherlands was renamed New York. • Bullet #2: Pennsylvania was founded in 1681 by a Quaker, William Penn. Geography of the Middle Colonies • New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey and Delaware • Climate was warm • Easier time farming, due to longer growing season New York and New Jersey • New York, began as Dutch colony • Known for fur trade • Taken over by the English • New Jersey • Split off from New York • Proprietary colony(colony created by a grant of land from a monarch to an individual or family) • Royal colony(colony controlled directly by the English King) Pennsylvania and Delaware • Quaker: religious group that believed that everyone had an inner light to God and that all people were equal in God’s eyes • William Penn: Quaker who settled Pennsylvania, provided religious freedom • Delaware: Swedish colony, then taken over by Dutch, then taken over by English, was part of Pennsylvania, then became its own colony Growth and Change • Farming increase • Manufacturing started The Backcountry • Backcountry: frontier region extending through several colonies from Pennsylvania to Georgia • Inhabited by Scot-Irish and Germans Section 4: I Can Statement I can understand the factors that influenced the development of the Southern colonies. Section 4: Bullet Points • Bullet Point #1: Maryland was founded as a colony where Catholics could worship freely. • Bullet Point #2: Large plantations marked the Tidewater region, and small farms dominated the backcountry. Geography of the Southern Colonies • Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia • Weather is warm and humid • Full of swampy areas and rolling hills • Long growing season • Main crops: tobacco and rice, spurred early development of slavery Virginia Grows • • • • Settlers keep coming despite high death rate Population grows, Indian numbers decrease More land taken over to farm on Problems with Indians Bacon’s Rebellion • Nathaniel Bacon: leader of the frontier settlers • Poor colonists wanted governor to take action against Indians • Governor hesitates, doesn’t want war • Bacon and his men attack and kill Indians, and attack Jamestown Religious Toleration in Maryland • Catholic colony formed, Maryland • Catholics and Protestants both lived here • Lord Baltimore: Cecil Calvert, took over Maryland when his dad died • Act of Toleration: gave all male Christians the right to vote and hold office Colonies in the Carolinas • North Carolina- developed slowly, grew tobacco and produced lumber • South Carolina, developed quickly, grew sugar and rice Georgia • Georgia started for 2 reasons: – Keep Spanish from expanding their colony – Wanted a colony where there would be protection for English debtors(people who owe money) • Slavery banned Change in the Southern Colonies • Two Distinct ways of life: • Tidewater Region: – Plantation: Large farm, grows cotton, sugar & rice – Divided white community • Backcountry: – Isolated farms – Poor and didn’t care about rank Section 5: I Can Statement I can understand how the Spanish established colonies on the borderlands. Section 5: Bullet Points • Bullet Point #1: Spain had large colonies in the Caribbean, Mexico, and South America. • Bullet Point #2: Spanish missions sought to convert Native Americans to Christianity. • Bullet Point #3: Spain established presidios and pueblos throughout the borderlands. Spanish Florida • St. Augustine: fort and first permanent European settlement in the US • Offered land to African Americans • Colony grew slowly • Had little control over the whole of Florida Settling the Spanish Borderlands • Borderlands: lands along a frontier, main job was to protect Mexico • Began in Florida and included Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Colorado, Utah, Nevada, and California Missions • Texas and Arizona: • Missions formed • Wanted Indians to be Christians • California: • Junipero Serra: missionary who helped colonize California • Presidios: military posts • Pueblos: civilian towns, centers of farming and trade Life in Spanish Missions • Indians farmed, built churches and learned a wide range of crafts • Worked 5-8 hours a day, 5-6 days a week • Indians had no control over their lives • Punished if they didn’t follow rules