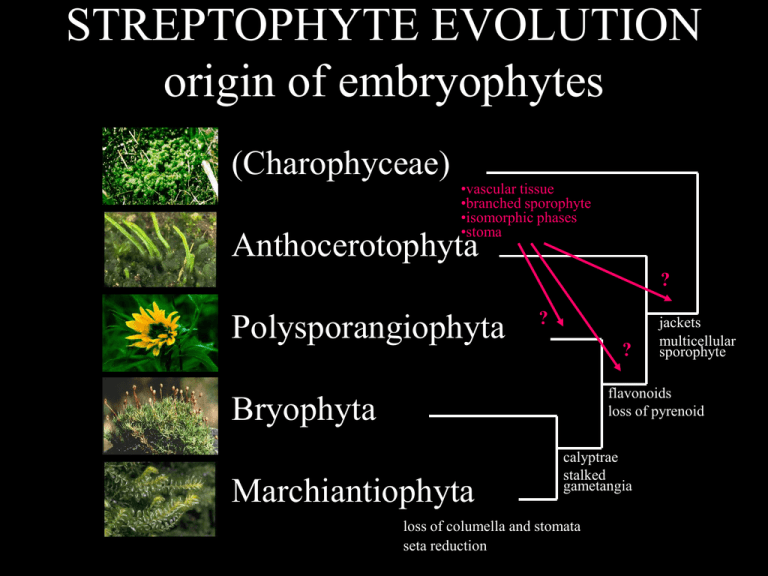
STREPTOPHYTE EVOLUTION
origin of embryophytes
(Charophyceae)
•vascular tissue
•branched sporophyte
•isomorphic phases
•stoma
Anthocerotophyta
?
Polysporangiophyta
?
?
jackets
multicellular
sporophyte
flavonoids
loss of pyrenoid
Bryophyta
Marchiantiophyta
calyptrae
stalked
gametangia
loss of columella and stomata
seta reduction
Classification and Differentiation
of Anthocerotophyta
• thalloid without internal differentiation
• smooth rhizoids, cells with pyrenoid (only
in algae)
• sex organs embedded
• sporophyte without seta, with stomates and
columella, grows indeterminately, split
longitudinally in two valves
• multicellular elaters
Anthoceros
Classification of Bryophyta
• Class Sphagnopsida
• Class Andreaeopsida
• Class Polytrichopsida
• Class Bryopsida
Sphagnum
Andreaea
Dawsonia
Hypnodendron
Differentiation of mosses
• gametophyte: stem & leaves
• sporophyte: single sporangium
(capsule) on persistent stalk
(seta) and elaborate structure for
spore release (peristome)
• calyptra: part of the
gametophore covering the
sporangium
Differentiation of mosses, the
gametophyte
•
•
•
•
filamentous protonema
multicellular rhizoids
apical cell
unistratose leaves, helically
arranged
• leaf cells often elongated
• vascular tissue in stem and
leaves
Differentiation of mosses, the
sporophyte
• more or less persistent seta
• stomates in theca (capsule wall)
• operculum and peristome
usually present
• no elaters among the spores
• calyptra often elevated by
growing sporophyte
Classification of
Marchantiophyta
• Class Marchantiopsida
• Class Jungermanniopsida
– Subclass Metzgeriidae
– Subclass Jungermanniidae
Conocephalum
Asterella
Pallaviciniaceae
Jungermannia
Differentiation of liverworts
• sporophytes matures completely
within the confines of
gametophore, lacks stomates and
columella
• thalloid structure in both the
marchantioid and some of the
jungermannioid taxa
Differentiation of liverworts, the
gametophyte
• no extensive protonema,
unicellular rhizoids
• gametophores either thalloid or
leafy, with leaves in two or three
rows
• leaves often complicate lobed
• leaf cells usually isodiametric,
often with trigones and oil bodies
Differentiation of liverworts, the
sporophyte
• no peristome, operculum, or
stomates
• no columella, but elaters among
the spores
• seta elongates after maturation of
sporangium, and is ephemeral
• calyptra stays at the base of
sporophyte