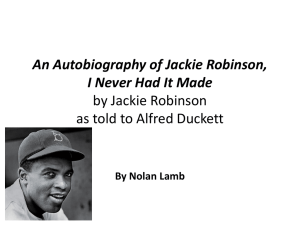Sports During the Civil Rights Movement
advertisement

Sports During the Civil Rights Movement Joe Hollinger Role Of Sports During the Movement During a time when the television had not yet become a staple in the American household, sports were one of the only forms of entertainment. Sports are unique in the sense that they captivate nearly the entire country and the athletes are real “characters” meaning they are the same person that they portray on the field. African Americans who broke the color barriers of their respective sports became nationally known heroes The sports world becomes a dynamic atmosphere in which citizens are able to invest their time, thoughts, and emotions. At the time sports were ruled by the idea of white supremacy. Sports have a huge impact on society, once civil rights activists recognized this, they were able to use sports as a platform to advocate social change and equality in the entire country. Muhammad Ali Muhammad Ali who was known as “The Greatest” had a large impact on not only sports during the movement but on politics and society as well. In 1967, he was stripped of his heavyweight championship title because he refused to fight in the Vietnam War. His reasoning for this was because no Viet-Cong had ever called him slurs due to his race, so therefore he would not fight them as he had no problem with them. Despite a torrent of racist opposition, Ali held his ground. Three years later, the United States Supreme Court ruled in his favor and Ali boxed again. Willie Mays Born on May 6, 1931, Willie Howard Mays Jr. grew up in Fairfield, Alabama, near notoriously racist Birmingham. In addition to learning the game of baseball Willie was taught to avoid conflict with Southern whites. At nineteen, Mays was signed by the New York Giants, and in 1950 he was the only black player with the Trenton Giants. Mays was often perceived by his critics as a gifted athlete who failed to use his privileged position to address civil rights issues at hand. Mays being a very quite person claimed he did advance the race, letting his play on the field do the talking. Earl Lloyd Lloyd, who on Halloween 1950 became the first black player in the NBA by taking the court for the Washington Capitols. Earl Lloyd grew up in Alexandria, Virginia, which was extremely segregated and then went on to attend an all-black college. A 6'6" power forward, he attended West Virginia State College where he was nicknamed “Moonfixer” for his height. In 1948 and 1949, he helped to lead the school’s basketball team to consecutive black college basketball tournament championships. The NCAA and NIT tournaments were still segregated at the time. It was only after he started playing pro basketball that he had a real conversation with a white man. Lloyd and the other early black players in the NBA endured many hardships including racial taunts from fans and being unable to stay in certain hotels or eat in many restaurants on the road. “Bleacher Report” Jackie Robinson Before entering the Major Leagues, Jackie Robinson competing in the Minor Leagues for the 1946 season. Even in the minor leagues Jackie's career was controversial. His team was threatened by police to cancel games if he was not taken off of the team. Many training facilities that the team used wouldn't allow him to train there either. When the Dodgers were finally allowed to let Jackie play on March 17th, 1946, he became the first black man to play in the Minor Leagues and also the first to play against a Major League team. During that season, Jackie earned the league's Most Valuable Player. Just a few days before the 1947 season, Jackie Robinson was called up to play for the Brooklyn Dodgers Major League Baseball team. On April ,1947 Jackie became the first black player to break the Major League Baseball color barrier. This is Jackie Robinson's most notable accomplishment Despite Jackie making this accomplishment, many of his teammates still did not like the idea of playing against him. A temporary ending was put to this after manager Leo Durocher stated, "I do not care if the guy is yellow or black, or if he has stripes like a zebra. I'm the manager of this team, and I say he plays”. This stopped the abuse he received from his teammates but not from his oppenents who, threatened to hit him during the games. However the commisioner noted that any player that partakes in rough play would be fined. Jackie continued his success throughout his career, although he still had to deal with the pressures and criticism that came with breaking the baseball color barrier. Jackie was one of the pioneer baseball players of his time, truly revolutionizing baseball and welcoming colored players into Major League Baseball. Jackie Robinson Cont. Jackie Robinson can be considered one of the pioneers for sports figures during the civil rights movement. Jackie was the chairman of the NAACP "Fight for Freedom" campaign, in which he traveled around the country giving speeches and lectures. In 1958, Robinson was elected into the board of directors of the NAACP. However, some members of the NAACP said that he was too "militant" in his approach to racial segregation and exclusion in the South. Jackie criticized the NAACP for not being strong enough in the South where he believed it needed help the most. Some activists during the time thought that Robinson was outspoken, and Malcolm X alienated him. There are many pieces of evidence that Jackie was a big part in the Civil Rights Movement. – – – – Robinson wrote letters and telegrams to Presidents Eisenhower, Kennedy, Johnson, and VicePresident Nixon. In his first letter, which was send to President Eisenhower, he states that he once heard the President say that the blacks must wait. He tells the President that they cannot wait to gain the free rights of men that all men were granted 150 years ago. In his second letter to President Kennedy, Robinson openly says that Kennedy will be a great President, but he will openly criticize him if Civil Rights are not on his agenda to come. These letters show that Jackie Robinson is a strong supporter of equality during the time and that he wasn’t afraid to stand up to anyone at the time. Video ttp://www.biography.com/people/jackierobinson-9460813/videos/jackie-robinsonjackie-mlk-2183106679 How the athletes impacted the civil rights movement Each athlete helped break the color barriers in each of their respective sports. They proved to the entire world that they could overcome their adversities faced and become some of the greatest. Most of the athletes who broke color barriers became involved in the movement such as Jackie Robinson writinggletters o the presidents and being involved in the NAACP. Breaking the color barriers in sports during the civil rights movement was a huge turning point due to the fact that sports represented such a role in the Nation. These athletes were all looked up to as heroes because they were not afraid to stand up against white supremacy to do what they love. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gtJg4BGI8_k Bibliography Briley, Ron. "Project MUSE - Willie Mays: The Life, the Legend (review)." Project MUSE - Willie Mays: The Life, the Legend (review). N.p., 2011. Web. 01 Dec. 2013. "Feature African-American Athletes." PBS. PBS, n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2013. "Jackie Robinson: A Man Who Changed Sports Forever - Home." Changed Sports Forever. N.p., n.d. Web. 01 Dec. 2013. "Jackie Robinson - Jackie & MLK | TV-14." Bio.com. A&E Networks Television, n.d. Web. 01 Dec. 2013. Merlino, Doug. "NBA." Bleacher Report. N.p., 15 Apr. 2011. Web. 01 Dec. 2013. "Rev. Al Sharpton Says Sports Helped the Civil Rights Movement." YouTube. YouTube, 01 Feb. 2012. Web. 01 Dec. 2013. <http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gtJg4BGI8_k> Willie Mays. Digital image. Academy of Achievement. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 Dec. 2013. <http://www.achievement.org/autodoc/page/may0gal-1>. Wilson, Greg. Muhammed Ali. Digital image. Greg Wilson. N.p., 17 Jan. 2012. Web. 1 Dec. 2013. <http://www.gregwilson.co.uk/2012/01/ali-at-three-score-and-ten/>. Jackie Robinson: A Man Who