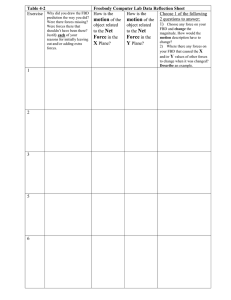
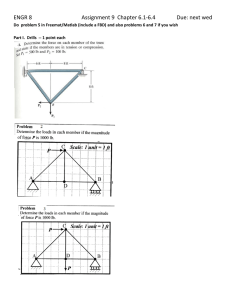
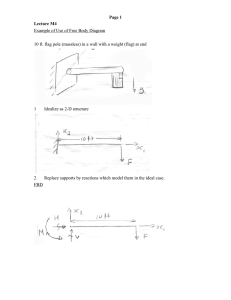
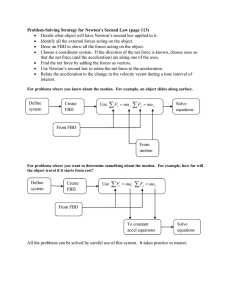
2025 Spring Solid Mechanics Problem Sets 2025 Spring Chapter 1 & 2 Please include FBD in your solution. 1. The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing at A and a smooth journal bearing at B. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at C. Please include FBD in your solution. 2. The pipe has a mass of 12 kg / m. If it is fixed to the wall at A, determine the resultant internal loading acting on the cross section at B. Please include FBD in your solution. 3. The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress distribution at the support varies as shown, determine the force P applied to the plate and the distance d to where it is applied. Please include FBD in your solution. 4. The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional area of 780 mm2. If the maximum average normal stress in any bar is not to exceed 140 MPa, determine the maximum magnitude P of the loads that can be applied to the truss. Please include FBD in your solution. 5. If the load P on the beam causes the end C to be displaced 10 mm downward, determine the normal strain in wires CE and BD. Please include FBD in your solution. 6. The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape shown by the dashed lines. Determine the average normal strain along diagonal BD, and the average shear strain at corner B relative to the x, y axes. 2025 Spring Chapter 3 Please include FBD in your solution. 1. Data taken from a stress–strain test for a ceramic are given in the table. The curve is linear between the origin and the first point. (a) Plot the diagram, and determine (b) the modulus of elasticity, (c) the modulus of resilience. Plus, determine approximately (e) the modulus of toughness. The rupture stress is σr = 373.8 MPa. Please include FBD in your solution. 2. The stress–strain diagram for a bone is shown, and can be described by the equation 𝜖 = 0.45(10-6) σ + 0.36(10-12) σ3, where σ is in kPa. Determine the yield strength assuming a 0.3% offset. Please include FBD in your solution. 3. The two bars are made of polystyrene, which has the stress–strain diagram shown. If the cross-sectional area of bar AB is 975 mm2 and BC is 2600 mm2, determine the largest force P that can be supported before any member ruptures. Assume that buckling does not occur. Please include FBD in your solution. 4. The plug has a diameter of 30 mm and fits within a rigid sleeve having an inner diameter of 32 mm. Both the plug and the sleeve are 50 mm long. Determine the axial pressure p that must be applied to the top of the plug to cause it to contact the sides of the sleeve. Also, how far must the plug be compressed downward in order to do this? The plug is made from a material for which E = 5 MPa, 𝜈 = 0.45. Please include FBD in your solution. 5. The lap joint is connected together using a 30 mm diameter bolt. If the bolt is made from a material having a shear stress–strain diagram that is approximated as shown, (a) determine the shear strain developed in the shear plane of the bolt when P = 340 kN. Plus, (b) determine the permanent shear strain in the shear plane of the bolt when the applied force P = 680 kN is removed. (a) Please include FBD in your solution. 5. The lap joint is connected together using a 30 mm diameter bolt. If the bolt is made from a material having a shear stress–strain diagram that is approximated as shown, (a) determine the shear strain developed in the shear plane of the bolt when P = 340 kN. Plus, (b) determine the permanent shear strain in the shear plane of the bolt when the applied force P = 680 kN is removed. (b) 2025 Spring Chapter 4 Please include FBD in your solution. 1. The assembly consists of three titanium (Ti-6A1-4V) rods and a rigid bar AC.The cross-sectional area of each rod is given in the figure. If a force of 30 kN is applied to the ring F, determine the angle of tilt of bar AC. Please include FBD in your solution. 2. The pipe is stuck in the ground so that when it is pulled upward the frictional force along its length varies linearly from zero at B to fmax (force/length) at C. Determine the initial force P required to pull the pipe out and the pipe’s elongation just before it starts to slip. The pipe has a length L, cross-sectional area A, and the material from which it is made has a modulus of elasticity E. Please include FBD in your solution. 3. The tapered member is fixed connected at its ends A and B and is subjected to a load P = 35kN at x = 750mm. Determine the reactions at the supports. The material is 50 mm thick and is made from 2014-T6 aluminum. Please include FBD in your solution. 4. The rigid bar is supported by the two short white spruce wooden posts and a spring. If each of the posts has an unloaded length of 1 m and a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2, and the spring has a stiffness of k = 2 MN/m and an unstretched length of 1.02 m, (a) determine the force in each post after the load is applied to the bar. Plus, (b) determine the vertical displacement of A and B after the load is applied to the bar. Please include FBD in your solution. 5. The AM1004-T61 magnesium alloy tube AB is capped with a rigid plate E. The gap between E and end C of the 6061-T6 aluminum alloy solid circular rod CD is 0.2 mm when the temperature is at 30°C. (a) Determine the normal stress developed in the tube and the rod if the temperature rises to 80°C. Plus, (b) determine the highest temperature to which it can be raised without causing yielding either in the tube or the rod. Neglect the thickness of the rigid cap. (a) Please include FBD in your solution. 5. The AM1004-T61 magnesium alloy tube AB is capped with a rigid plate E. The gap between E and end C of the 6061-T6 aluminum alloy solid circular rod CD is 0.2 mm when the temperature is at 30°C. (a) Determine the normal stress developed in the tube and the rod if the temperature rises to 80°C. Plus, (b) determine the highest temperature to which it can be raised without causing yielding either in the tube or the rod. Neglect the thickness of the rigid cap. (b)