Uploaded by
eleanorejroberts
Benzoin Condensation: Reaction, Mechanism, and Spectroscopy Analysis
advertisement

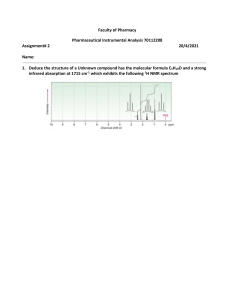
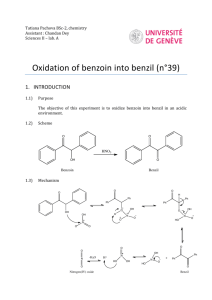
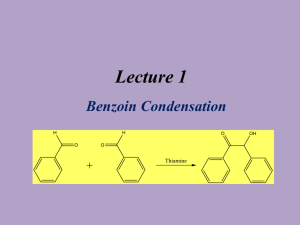
Benzoin Condensation Presented by Ellie Roberts Reaction Overview - Two cyclic aldehydes reacted with a cyanide ion to form benzoin NaCN CH3OH Spectra Mass Spectroscopy Molecular weight of benzoin: = 212.24 g/mol 13 C NMR Ketone or aldehyde: δ 198.9 Alkenes: δ 139.0, 133.9, 133.4, 129.1, 128.7, 128.6, 127.7 Alcohol, ether, or ester: δ 76.1 IR Alcohol (3403.27 cm-1) Conjugated ketone (1678.14 cm-1) Aromatic alkene (1594.60 cm-1) 1 H NMR Differences in the literature: - The c, d, and e protons were grouped 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.93–5.54 (m, 2H), 7.52–7.40 (m, 1H), 7.38–7.23 (m, 7H), 5.95 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H), 4.55 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H). Masaki Hayashi; Masatoshi Shibuya; and Yoshiharu Iwabuchi; The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2012, 77 (6), 3005-3009. Mechanism The mechanism is split into four main steps 1) 2) 3) 4) Formation of a cyanohydrin Nucleophile formation New C-C bond formation via nucleophilic attack Formation of benzoin via leaving group dissociation Formation of a cyanohydrin 1 Nucleophile Formation 2 Formation of new C-C bond 3 Formation of benzoin 4