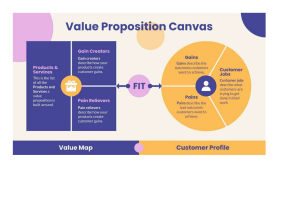
BUSINESS PLAN - document that describes the various external and internal elements involved in starting a business or in expanding an existing venture - Blueprint for business - Will change over time as it develops - Useful for forecasting or raising additional capital for expansion - Can include straggles to transfer ownership or dissolution USERS USER OF BUSINESS PLAN VALUE • Serves as a roadmap. Entrepreneu • Identi es the resources. • Anticipate potential business r risks • Assess Character, Cash ow, Collateral, Equity Contribution Lender • Investor Allows investor to gauge whether projected returns are acceptable, as well as capability of the venture s management team ’ ’ fl fi fi fi fl WHY SOME FAIL: • Document looks unprofessional. • Executive summary is not coherent/ too long. • Unclear on its marketing/ production plan • Sales and nancial projections are unreasonably optimistic. • Inadequate description of the quali cations and experience of management team • Inadequate assessment of the potential threats MAJOR SECTIONS 1. Title Page •Business name and logo •Names of business owners 2. Executive Summary •summarizes the business •short enough for the readers to understand and conceptualize the entire concept of the business 3. SWOT Analysis •Compilation of the business's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats • help organizations develop a full awareness of all the factors involved in making a business decision. 4. Description of the business •Product and/ or services •Mission, Vision statement and core values •Location of the business 5. Operations Plan •Description of the company s operation (Input-Process-Output) •machinery and equipment needed and suppliers of raw materials •Flow of orders for goods and services •procedures in completing a transaction re ected in operations layout 6. Marketing Plan •Marketing Plan steps •comparisons of major competitors •marketing mix strategies (product, place, promotion, price) 7. Organizational Plan •Form of ownership •Principal shareholders, or partners •Organizational chart/ lines of authority •Background of the management team • Roles and responsibilities of the team 8. Financial Plan •Assumptions •COGS •OPEX •markup and selling price •income statement •sources and uses of funds •Break-even Analysis SWOT ANALYSIS - help organizations develop full awareness of all factors in making a business decision Strengths - factors the company hold expertise in - Basis for continued success Weaknesses - factors that preen meeting mission - Hamper growth and success Opportunities - the environment within which organization operated fi fi fl Threats - factors existing in external environment that jeopardize pro tability and reliability - Uncontrollable and are risks to stability or survival Internal factors Strengths (S) and weaknesses (W) - experience readily available to you • • • • • Financial resources (funding, sources of income and investment opportunities) Physical resources (location, facilities and equipment) Human resources (employees, volunteers and target audiences) Access to natural resources, trademarks, patents and copyrights Current processes (employee programs, department hierarchies and software systems) External factors - in uence and affect every company, organization and individual - opportunity (O) or threat (T) - External factors are typically things you or your company do not control, such as the following: • Market trends (new products, technology advancements and shifts in audience needs) • Economic trends (local, national and international nancial trends) • Funding (donations, legislature and other sources) • Demographics • Relationships with suppliers and partners • Political, environmental and economic regulations MARKETING PLAN - organizational function and a set process for creating, communicating, delivering value to customers, and managing customer relationships How customers decide when purchasing: 1. Recognizing a need or want - triggered by internal or external stimulus SEGMENTATION - divide market into groups of customers using segmentation practices - Identify and pro le distinct groups of buyers who prefer varying product and service mixes - examining demographic, psychographic, behavioral differences among buyers TARGETING - determine which customer group to focus marketing efforts on POSITIONING - create product positioning and marketing mix most likely to appeal to selected audience 2. Seeking or retrieving information - search for information to learn about the competing products and services and their features 3. Evaluating Choices - attributes important to buyers beliefs and attitudes - Some make rational approach others to marketing stimuli 4. Making A Purchase - what brand to buy, where to buy, how many, when and how to pay for it fi fi fi 5. Assessing the product or service - consumer assess his experience - Delighted skim some steps - satis ed seeks further information - dissatis ed:1. Exit 2. Voice MARKETING MIX 4 Ps 1. Product • Product Features (serving, size, number of pieces, color, temperature) • Styles/ Options Available • Brand Name • Quality of Materials or Components used • Product Bundling • Packaging • After-sales service/ warranties offered • 2. Price Cost-based Pricing Competitionbased Direct labor, raw materials, Variable Cost commission, Consider prices of packaging existing products cost or services in the market Fixed Utilities cost, (overhead rent cost) 3. Place - address of store - Advantage disadvantage - Number of distributor - Electronic channel use 4. Promotion - advertising, sale promotion, personal selling, public relation - Promotional strategy and budget PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE 1. Introduction - investment in advertise 2. Growth Value-based The value attached by customers to products or services - if product is successful - Growing demand, increase production, expansion in availability 3. Maturity - most pro table stage - Costs of producing and marketing decline 4. Decline - increased competition as others emulate success with enhancement or lower price - May lose market EFFECTIVE MARKETING AND TRENDS 1. Satisfying customers needs •Starts with the recognition and identi cation of customer needs, wants and expectations and continuously monitoring, updating any changes. •De nes who these customer targets are •Creates a program to satisfy these needs fi ’ ’ fi fi fi fi fi 2. Pro tably satisfying organization •Aims to achieve organizational goals of pro tability, growth, and sustainability. •Satisfying company stakeholders • 3. Superior to competition •Developing and maintain a competitive advantage •Remain relevant and sustainable making the organization distinctly ef cient in satisfying customer needs, thus locking customer s loyalty PRODUCT ORIENTATION VS MARKET ORIENTATION Company Missouri-Pacific Railroad Product Market We are a people-andWe run a railroad goods mover We make copying We improve office Xerox equipment productivity Standard Oil We sell gasoline We supply energy Columbia Pictures We make movies We entertain people