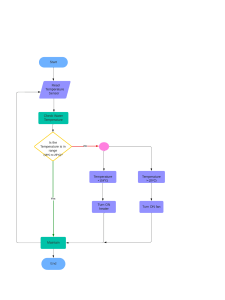
13. Expert Systems a) What is an expert system? An expert system is a computer program that uses artificial intelligence to simulate the decisionmaking ability of a human expert. b) State 3 features of an expert system. Uses a knowledge base of facts and rules. Has an inference engine to draw conclusions. Provides explanations or advice to users. c) State the processes that take place in an expert system. Knowledge acquisition: Gathering and entering expert knowledge into the system. Inference: The system uses the inference engine to process data and rules. Explanation: The system explains its reasoning or provides advice to the user. 14. Monitored and Controlled Washing Machine a) Name the devices X and Y. Device X: Sensor (temperature sensor) Device Y: Actuator (relay or switch) b) State the functions of the devices X and Y. X (Sensor): Measures the temperature of the water in the washing machine. Y (Actuator): Controls the heater based on signals from the microprocessor. c) State the processes that take place in this system. The sensor (X) measures the water temperature. The sensor sends the temperature reading to the microprocessor. The microprocessor compares the measured temperature with the desired value. If the temperature is too low, the microprocessor signals the actuator (Y) to switch on the heater. Once the required temperature is reached, the microprocessor signals the actuator to switch off the heater. 16. Simulation in Housing Projects a) Identify 3 things to be input in the simulation model. The cost of materials. The design of the housing structure. The number of workers needed. b) The program produces a report. Give 1 item that can be included in the report. The total estimated cost of the project. c) What are benefits of using simulation in this situation? Reduces costs by identifying the best design before building. Helps predict possible problems. Saves time by testing different scenarios quickly. 17. Algorithm for Larger Number 1. Input A 2. Input B 3. If A > B then Output A 4. Else Output B 18. Robot Feedback a) What type of feedback is this? Open-loop feedback. b) Name and explain the other feedback that could have been used. Closed-loop feedback: The robot checks if the car was assembled correctly and makes adjustments if needed. 19. Car Allowance Calculation Pseudocode: Input engine_size Input distance If engine_size < 1500 then allowance = distance * 80 Else allowance = (distance * 80) + (distance * 15) Output allowance This code calculates the allowance based on engine size and distance travelled. For engines less than 1500 CC, the allowance is 80 thebe per kilometre. For engines greater than 1500 CC, there is an additional 15 thebe per kilometre. ⁂