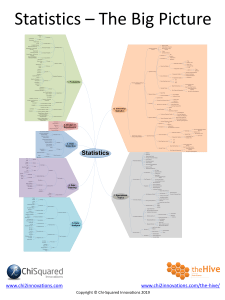
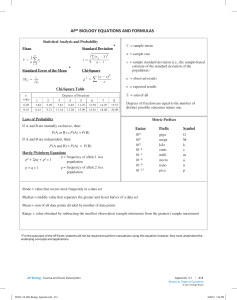
Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function Name ________________________ Period _________ Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function Guided Reading Activities Chapter Content: The Structural Organization of Animals Complete the following questions as you read the twenty-first chapter content—The Structural ­Organization of Animals: 1. Place the following levels of biological organization into the proper order from smallest to largest. Tissues, cells, organ systems, organs, organism. Cellular level: Muscle cell Tissue level: Cardiac muscle Organ level: Heart Organ system level: Circulatory system Organism level: Multiple organ systems functioning together A) B) C) D) E) Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 157 157 5/15/18 3:09 PM Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function 2. One of the most fundamental relationships in biology is between and . 3. No other cell in your body has the structure of a neuron. Based on your knowledge of form and function, what can you infer from this? 4. Use the answers to question 2 to answer this. Anatomy is to . 5. Which of these levels of organization include the other? Cell…organ 6. A 7. List the four animal tissue types. as physiology is to is a group of cells with similar structures and functions. A) B) C) D) 8. Which of the following is a type of connective tissue? A) Blood B) Skeletal muscle C) Epithelium D) Nervous tissue 158 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 158 5/15/18 3:09 PM Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function 9. Briefly explain why the small intestine pictured here is considered an organ. Small intestine (cut open) Epithelial tissue Connective tissue (containing blood and lymph vessels) Smooth muscle tissue (two layers) Connective tissue Epithelial tissue Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 159 159 5/15/18 3:09 PM Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function 10. List three organ systems and their primary functions. Chapter Content: Exchanges with the External Environment Complete the following questions as you read the twenty-first chapter content—Exchanges with the External Environment: 1. The continuous exchange of chemicals and energy with your surroundings is referred to as a(n) . 2. What is a major adaptation that complex animals, such as humans, have evolved to maximize exchange with the external environment? 3. Briefly explain why the hydra does not need a digestive, respiratory, and urinary system. Mouth Gastrovascular cavity Exchange Exchange 160 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 160 5/15/18 3:09 PM Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function Chapter Content: Regulating the Internal Environment Complete the following questions as you read the twenty-first chapter content—Regulating the ­Internal Environment: 1. True or false: The human body’s internal environment is constantly fluctuating in response to fluctuating conditions outside. If false, make it a correct statement. 2. Homeostasis literally translates to “steady state.” Explain why this is an accurate term for what it describes. 3. is the mechanism that controls homeostasis. 4. Complete the following table regarding negative and positive feedback mechanisms. Negative feedback Positive feedback Description Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 161 161 5/15/18 3:09 PM Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function 5. You develop a fever of 103oF. According to the figure, what point of thermoregulation has the fever altered? Skin Sweat gland Response: 1. Blood vessels dilate 2. Sweat is produced Control center in brain activates cooling mechanisms Stimulus: Body temperature is above set point Body temperature drops Set point: Body temperature near 37°C (98.6°F) Stimulus: Body temperature is below set point Body temperature rises Skin 162 Response: 1. Blood vessels constrict 2. Person shivers 3. Metabolic rate increases Control center in brain activates warming mechanisms Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 162 5/15/18 3:09 PM Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function 6. What are the three largest components of human urine? 0.1% Uric acid 0.15% Creatinine 0.25% Potassium 0.25% Phosphate 0.25% Sulfate 0.5% Sodium 1% Chloride 3.5% Urea 94% Water 7. List three adaptations that different animals have for thermoregulation. Major Theme Connection: 1. Positive feedback loops are the opposite of negative feedback loops. In a positive feedback loop, any change in the original variable triggers mechanisms that actually push the variable further in the direction of the change. Imagine that body temperature was regulated in this way. Briefly explain what would happen. Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 163 163 5/15/18 3:09 PM Chapter 21: Unifying Concepts of Animal Structure and Function Common Thread Connection: What was the oxygen consumption for a Burmese python at 20 contractions per minute? O2 consumption (mL O2/hr) per kg 1. 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Contractions per minute 164 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. SIMO0333_06_ARG_SE_C21_PRF.indd 164 5/15/18 3:09 PM