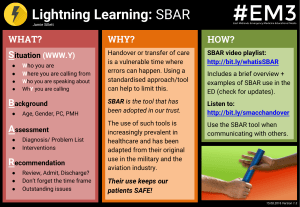
Table of Contents: 1. Continuity of Care 2. Quality Improvement 3. Conflict Resolution 4. NCLEX Practice Questions Management Principles 1. Continuity of Care Documentation Documentation is the written record of client care that supports: y Effective communication y Legal accountability y Team collaboration y Quality improvement y Billing and reimbursement When documenting, nurses must: Document in a timely manner to avoid delays in care. Do not delay documentation until the end of the shift. y Maintain client confidentiality. y Do not share client records with individuals not directly involved in care (see LEGAL CHEAT SHEET for more information on confidentiality). y Follow facility policy and best practices for documentation (TABLE 1). y Use only facility-approved terminology; avoid acronyms. y Example: Do not use trailing zeros, or “Q.D.” or “Q.O.D.” Common errors in documentation: y Omission or incomplete charting: Failing to chart interventions or client responses (e.g., failing to document follow-up pain score after administering analgesics) y Charting in advance: Documenting care before it is provided is falsification y Bias: Using subjective statements (e.g., “client is difficult”) Documentation: Document care immediately after it is performed, not at the end of the shift. Record only objective and factual information, avoid opinions, and never chart care before providing it. TABLE 1. BEST PRACTICES FOR DOCUMENTATION Practice Examples Be specific. Respirations even and unlabored at 12/min. Client appears to be breathing comfortably. Record objective facts, not opinions. Client refused antibiotic, stating, “I won’t do anything you say until you give me pain medicine.” Client being uncooperative and demanding. Be accurate and thorough. VAD site is patent and intact without any redness, swelling, or drainage. VAD site assessment appears normal. When documenting nursing assessments, interventions, and teaching, include: Time performed, equipment used, and client response. Reporting and communication Effective communication is a high priority to prevent safety issues. Use SBAR format (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation/Readback) to provide a standardized, effective report (TABLE 2). y Handoff report: Communicating client information when care is transferred from one nurse to another (shift change, client transfer) SBAR: Use the SBAR format (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation/ Readback) to ensure reports are standardized and include all necessary information. © Bootcamp.com 5 Management of Care Continuity of care involves providing consistent, coordinated client care through effective teamwork and communication. 1. Continuity of Care, Continued TABLE 2. SBAR REPORT Step Example Situation: Reason for calling, caller’s name and title, and client name/identifier “This is Nurse Adams calling because Mr. Smith has dyspnea.” Background: Pertinent history (diagnosis, medications) “The client has asthma and is on oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula.” Assessment: Current VS and status “He has dyspnea and wheezing with an oxygen saturation of 88%.” Recommendation/ Readback: Recommended actions and readback of important information “I recommend immediate evaluation by the HCP and an order for an albuterol nebulizer.” Interprofessional collaboration: y Nurses must collaborate with the interdisciplinary team to meet the client’s holistic needs. y Assess the need for referrals to other disciplines (TABLE 3). Discharge planning and education: y Discharge planning and education begins upon admission. y Case managers support discharge needs and monitor expected client progress (critical pathways). TABLE 3. HEALTHCARE TEAM MEMBERS Role Examples of Referral Needs Pharmacist: Manages medication regimens and drug interactions y Assists with adjusting medications or doses based on client allergies or condition (renal failure) y Determines medication interactions Physical therapist/ physiotherapist: Assists with gross mobility (“legs”) and physical exercise y Performs strengthening exercises y Teaches clients to use mobility devices (walker) y Provides prosthetic training after amputation Occupational therapist: Assists with ADLs and with using adaptive equipment focused on fine motor skills (“hands”) y Recommends adaptive equipment for dressing (button hooks) and eating y Assists with improving hand coordination for writing Registered dietitian: Manages nutritional needs and dietary plans y Adjusts diets based on diagnoses (e.g., low sodium for hypertension) y Provides education and support for tube feedings Respiratory therapist: Provides pulmonary hygiene and respiratory interventions y Administers nebulizer treatments y Adjusts mechanical ventilator and oxygen settings Social worker: Addresses psychosocial needs and access to resources y Connects clients to support groups y Seeks out financial resources for clients unable to afford medication or equipment Management of Care y When completing a handoff report: y Conduct at the bedside if possible. Emphasize priorities of care (allergies, changes in condition, critical lab results). y Avoid unnecessary details. y Allow the receiving nurse to ask questions. y Document the date, time, and individuals involved in the handoff report. Referrals: Case managers coordinate discharge planning and evaluate client progress. Physical therapists focus on gross mobility and exercises (“legs”), while occupational therapists assist with adaptive tools and fine motor skills (“hands”). © Bootcamp.com 2 TABLE 3. HEALTHCARE TEAM MEMBERS, CONTINUED Role Examples of Referral Needs Case manager: Coordinates treatment, services, and discharge planning throughout care y Evaluates client progress compared to expected progress (critical pathways) y Coordinates discharge plans for clients (home health consult) Speech-language pathologist: Assists with speech, language, and swallowing disorders y Provides therapy for speech alterations (aphasia, dysphasia) y Teaches safe swallowing techniques for clients with dysphagia Chaplain/clergy: Provides spiritual and emotional support y Offers spiritual support (prayers, religious services) at the client’s request y Provides support for clients and families during palliative and end-of-life care 2. Quality Improvement Quality improvement (QI) enhances care delivery through process improvement initiatives: y Identifying safety issues: Monitor for trends and problems. y Root cause analysis (RCA): Investigate adverse events after they occur to identify the cause. y QI projects: Implement evidence-based changes to improve care (e.g., improving hand hygiene, reducing infection rates). y Risk management: Identify and address organizational risk factors to prevent adverse events. Nurses’ role in QI: Implement current EBP when providing care. y Example: Removing indwelling catheters as soon as possible to prevent infections y Participate in QI projects and activities to improve client care. Quality improvement: Nurses should participate in QI by implementing evidence-based practices and reporting unsafe work conditions. Identify and report potential safety issues in practice. Complete an incident report when an unexpected safety event occurs (wrong site surgery, fall, medication error). y Document an objective description including: y What you observed/incident details y Client response y Follow-up actions Do not document the existence of an incident report or include a copy of the report in the client’s health record. 3. Conflict Resolution Conflict occurs when differing opinions or priorities among team members cause tension. y Open and professional communication can reduce unnecessary conflict. y Effective conflict resolution ensures team cohesion and client safety. y Unresolved conflict is a barrier to effective client care; conflicts should be resolved promptly. y Different conflict resolution styles are used to address conflicts (TABLE 4). TABLE 4. CONFLICT RESOLUTION STYLES Response Examples Accommodation: Giving in to another’s desires while neglecting one’s own “Let’s do your plan even though it’s not what I wanted.” Avoidance: Ignoring or withdrawing from conflict “Let’s talk about this later when we’re both calmer.” Collaboration: Seeking a solution that satisfies both parties “Let’s work together to find a solution.” Competition: Pursuing one’s own goals at the expense of another “I think my approach is best, and I will stick with it.” Management of Care 1. Continuity of Care, Continued Incident reports: An incident report must be completed whenever an unexpected safety event occurs. Do not mention or include the incident report in the client’s health record. © Bootcamp.com 3 4. NCLEX Practice Questions 1. “Client reports severe nausea; antiemetic administered.” 2. “Client reports nausea after pain medication. Administered ondansetron 4 mg IVP.” 3. “Client states, ‘I feel nauseated after morphine.’ Administered ondansetron 4 mg IVP. Client reports decreased nausea.” 4. “Client appears nauseated after pain medication administration. Administered ondansetron 4 mg IVP. Will contact HCP if symptoms do not improve.” Hint: Only one option demonstrates specific and objective documentation. SBAR: Which is the best example of an appropriate SBAR report? 1. “Mr. Smith has dyspnea and needs oxygen immediately.” 2. “Mr. Smith has dyspnea and needs new orders. Can you assess the client?” 3. “Mr. Smith, who has COPD, has acute dyspnea and wheezing. I recommend supplemental oxygen.” 4. “Mr. Smith, who has COPD, has dyspnea. I administered nebulizer medications, and he is not improving.” Hint: Only one option includes all elements of an SBAR report. Consults: A nurse receives an order to decrease the medication dose for a client with renal failure. Which team member should the nurse contact? 1. Pharmacist 2. Social worker 3. Case manager 4. Registered dietitian Correct: 3. This option provides objective and specific information, including client quotes, medication name and dose, and client response. Incorrect: 1. Does not provide specific information (medication name and dose, client quote) or client response to intervention. 2. Does not provide specific information (client quote) or client response to intervention. 4. Provides subjective opinion instead of facts (e.g., client appears). Correct: 3. This option describes the situation, background, assessment findings, and care recommendations. Incorrect: 1 & 2. Do not provide background or assessment findings. 4. Does not provide assessment findings or care recommendations. Correct: 1. Pharmacists assist with determining safe medication dosing. Management of Care Documentation: Which is the best example of appropriate documentation? Incorrect: 2, 3, & 4. These health care team members do not assist with determining safe medication dosing. Hint: Only one team member provides guidance on medication dosing. © Bootcamp.com 4 Documentation should be _____ (objective or subjective?), factual, and performed immediately _____ (before or after?) care is provided. What are the elements of an SBAR report? Which health care team member should the nurse contact for care coordination and discharge planning? For assistance with gross mobility and exercise? For adaptive tools for fine motor skills? Name two ways nurses should participate in quality improvement. Whenever an unexpected safety event occurs, nurses should complete a(n) _____ report. Incident reports should be mentioned in the client’s health record (true or false?). Answers: 1. objective, after 2. Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation/Readback; SBAR provides a standardized format that ensures all necessary information is included in the report. 3. Case managers; Physical therapists; Occupational therapists 4. Implement evidence-based practices, report unsafe work conditions 5. incident; false Astle, B., Duggleby, W., Potter, P. A., Stockert, Perry, A. G., & Hall, A. M. (2024). Potter and Perry’s Canadian Fundamentals of Nursing (7th ed.). Elsevier. Callahan, B., Hand, M., & Steele, N. (Eds.). (2023). Nursing: A concept-based approach to learning (4th ed., Vol 2). Pearson. Berman, A. B., Snyder, S. J., & Frandsen, G. (2021). Kozier & Erb’s fundamentals of nursing: Concepts, process, and practice (11th ed.). Pearson. Huston, C. J. (2024). Leadership roles and management functions in nursing: Theory and application (11th ed.). Wolters Kluwer. Potter, P. A., Perry, A. G., Stockert, P. A., & Hall, A. M. (Eds.). (2023). Fundamentals of nursing (11th ed.). Elsevier. Waddell, J. I. & Walton, N. A. (2020). Yoder-Wise’s leading and managing in Canadian nursing (2nd ed.). Elsevier. © Bootcamp.com 5 Management of Care References: