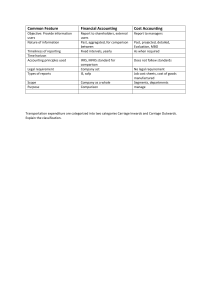
Income Statement and Statement of Financial Position Introduction to Accounting A Jacqueline Howell-Williams 2025 Objectives By the end of this lesson, you will be able: 1. Prepare a Trial Balance from a list of balances 2. To prepare a Vertical Income Statement (Trading and Profit and Loss A/c) and a Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) 3. Prepare accounts for Accruals and Prepayment Income Statement (Trading and Profit and Loss) & Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) Problem 1 Use the following information to prepare the Trial Balance, Trading and Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet for R. Mendez, 20 April 2021 $ $ Sales 18,600 Purchases 11,874 Opening Stock 2,368 Stock 30/09/19 2,946 Carriage Inwards 310 Carriage Outwards 200 Returns Inwards 205 Returns Outwards 322 Wages 3,862 Motor expense 664 Rent and Rates 304 Lighting and heating expenses 166 Office Expenses 216 Motor Vehicle Fixtures & Fittings 350 General Expenses Insurance 78 Equipment 5,000 Debtors 3,896 Cash in hand 82 Creditors 1,731 Cash at bank 400 Drawings 1,200 Capital 1,800 314 12,636 Trading and Profit and Loss Account Template Sales Less Returns Inwards Net Sales Less Cost of Goods Sold: Opening Stock Add Purchases Cos of Goods Available for Sale Less Returns Outwards Add Carriage Inwards Net Purchases Less Closing Stock Gross Profit Less Expenses Rent Paid Telephone Light/Electicity Wages Water/Rates Gas Traveling Net profit/loss xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx (xxx) xxx xxx xxx (xxx) xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx (xxx) xxx Add Revenues ( eg. Discount Received, Interest Received) to Gross Profit Trading and Profit and Loss Account Worked out R. Mendez Trading and Profi t and Loss Statement for the year ended 30th September 2019 Sales 18,600 Less Returns Inwards 205 Net Sales 18,395 Less Cost of Goods Sold: Opening Stock Add Purchases Less Returns Outwards Add Carriage Inwards Cos of Goods Available for Sale Less Closing Stock Gross Profit Less Expenses Rent and Rates Offi ce Expenses Wages Insurance General Expenses Motor Expense Carriage Outwards Lighting and heating expenses Net profit 2368 11,874 322 11,552 310 11,862 14,230 2946 304 216 3862 78 314 664 200 166 11,284 7,111 5804 1,307 Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) What is a Balance Sheet? • A Balance Sheet is a financial statement setting out the book values of assets, liabilities and capitals at a particular point in time. • It shows what the business owns and what it owes at a specific date. Components of the Balance Sheet ASSETS • Net Assets or Working Capital • Fixed Assets – are listed in the Current liabilities are deducted from balance sheet in the Order Of current assets. Permanency – the one that will last the longest will be recorded first. Eg: LESS Long- Term Liabilities: land, building, fixtures and fitting, bank loan, mortgage machinery, motor vehicle • Current Assets – These are listed FINANCED BY starting with the asset that is least • Capital likely to be turned into cash first and finish with cash itself. In the Order Of • Add Net profit Liquidity in ascending order. Eg. Stock, debtors, bank cash • Less Drawings Balance Sheet Template Vertical Format Balance Sheet as at day Month Year $ $ Fixed Asset Computer Equipment Fixtures and fi tti ngs Motor Vehicles Total Fixed Asset Current Assets Stock Debtor Bank Cash Less Liabilities Creditors xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx $ xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx Working Capital xxx xxx Financed by: Capital Add Net Profi t Less Drawings xxx xxx xxx (xxx) xxx Now we know the Net profit let us prepare the Statement of Financial Position R. Mendez Balance Sheet as at 30th September 2019 $ $ Fixed Asset Equipment Fixtures and fi tti ngs Motor Vehicles Total Fixed Asset Current Assets Stock Debtor Bank Cash Less Liabilities Creditors 5,000.00 350.00 1,800.00 2,946.00 3,896.00 400.00 82.00 $ 5,000.00 350.00 1,800.00 7,150.00 7,324.00 1,731.00 Working Capital 5,593.00 12,743.00 Financed by: Capital Add Net Profi t Less Drawings 12,636.00 1,307.00 13,943.00 1,200.00 12,743.00 Dr ($) Cr ($) Loan from P. Parkin 5,000 Captital Drawings 8,420 Cash at Bank 3,115 Cash in hand Debtors Creditors 295 12300 Stock 30 September 2007 23910 Motor Van 4,100 Office Equipment 6,250 Sales Purchases Returns Inwards Carriage Inwards Returns Outwards Carriage Outwards Motor Expenses Rent Telephone and internet charges Wages Insurance Office Expenses Sundry Expenses Total Stock at 30 September 2008 was J$27,475.00 25,955 9,370 130,900 92,100 550 215 309 1,630 2,970 405 12,810 492 1,377 284 171532 27,475 307 In Class Exercise Bins drew up the following trial balance as at September 2008. You are to draft trading and profit and loss accounts for the year to 30 September 2008 and a balance sheet as at that date. 171532 Trading and Profit and Loss Account Worked out Bins drew up the following trial balance as at September 2008. You are to draft trading and profit and loss accounts for the year to 30th September 2008 and a balance sheet as at that date. BINS Trading and Profit and Loss Statement for the year ended 30th September 2008 Sales 130,900.00 Less Returns Inwards 550.00 Net Sales Less Cost of Goods Sold: Opening Stock Add Purchases Less Returns Outwards Add Carriage Inwards Cost of Goods Available for Sale Less Closing Stock Gross Profit Less Expenses Carriage Outwards Offi ce Expenses Sundry Expense Insurance Wages Telephone and internet charges Motor Expenses Rent 92,100.00 307.00 91,793.00 215.00 Dr ($) 130,350.00 23,910.00 92,008.00 115,918.00 27,475.00 88,443.00 41,907.00 309.00 1,377.00 284.00 492.00 12,810.00 405.00 1,630.00 2,970.00 20,277.00 Net profit Cr ($) Loan from P. Parkin 5,000 Captital Drawings 25,955 8,420 Cash at Bank 3,115 Cash in hand 295 Debtors Creditors 12300 Stock 30 September 2007 23910 Motor Van 4,100 Office Equipment 6,250 Sales Purchases Returns Inwards Carriage Inwards Returns Outwards Carriage Outwards Motor Expenses Rent Telephone and internet charges Wages Insurance Office Expenses Sundry Expenses Total 9,370 130,900 92,100 550 215 309 1,630 2,970 405 12,810 492 1,377 284 171532 21,630.00 Stock at 30 September 2008 was J$27,475.00 27,475 307 171532 Recap The Income Statement The primary objective of any business is to make a profit. In order to determine the extent to which the objective of making a profit has been met, the firm prepares a statement called the Income Statement (Trading and Profit and Loss Account). This is done at the end of an accounting period, usually after one year. It involves the matching of income with expenses for the respective period. There are two aspects to the calculation of profits. 1. There is the calculation of profit earned from the sale of goods, or gross profit; 2. The profit earned from the operation of the business. The Income Statement has two main sections; the Trading Account and the Profit and Loss Account. Trading and Profit and Loss Account Worked out R. Mendez Trading and Profi t and Loss Statement for the year ended 30th September 2019 Sales 18,600 Less Returns Inwards 205 Net Sales 18,395 Less Cost of Goods Sold: Opening Stock Add Purchases Less Returns Outwards Add Carriage Inwards Cos of Goods Available for Sale Less Closing Stock Gross Profit Less Expenses Rent and Rates Offi ce Expenses Wages Insurance General Expenses Motor Expense Carriage Outwards Lighting and heating expenses Net profit 2368 11,874 322 11,552 310 11,862 14,230 2946 304 216 3862 78 314 664 200 166 11,284 7,111 5804 1,307 R. Mendez Balance Sheet as at 30th September 2019 $ $ Fixed Asset Equipment Fixtures and fi tti ngs Motor Vehicles Total Fixed Asset Current Assets Stock Debtor Bank Cash Less Liabilities Creditors 5,000.00 350.00 1,800.00 2,946.00 3,896.00 400.00 82.00 $ 5,000.00 350.00 1,800.00 7,150.00 7,324.00 1,731.00 Working Capital 5,593.00 12,743.00 Financed by: Capital Add Net Profi t Less Drawings 12,636.00 1,307.00 13,943.00 1,200.00 12,743.00 The Balance Sheet shows the firm’s financial position at the given date. It is comprised of the assets, liabilities and the owner’s equity, and maintains the equation of: The Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position) Assets = Liabilities + Capital/Owners Equity. Marshalling of the Assets Both the fixed and the current assets may be presented using one of two formats: Order of Permanence • Using this format, the assets are listed in the balance sheet starting with the most permanent, i.e. those which are hardest to be converted to cash, and leading to the most liquid, i.e. cash in hand. This is the conventional method that should be used. Order of Liquidity • In this approach, the assets are listed starting with the most liquid, leading to the most permanent, or the hardest to be converted to cash. Order Of Permanence Fixed Assets Land and Building Fixtures and Fittings Machinery and Equipment Motor Vehicle Current Assets Stock Debtors Accruals and Prepayment Accrued & Prepaid Expenses Accrual Principles: charge to the accounting year the amount of money DUE, not paid. • Accrued Expenses (Expense Owing) rule: add accruals • Prepaid Expenses (Paid in advance) rule: less prepayments. Question: how do you add to an expense A/C ? Place the figure on the Debit Side How do you less from an expense A/C? Place the figure on the Credit Side Accruals Accrued Expenses and Revenues Accrued/Outstanding Expenses Activity 1 In 2007, D. Stone’s telephone expense details were as follows: bank payments were made on April 2, $345, July 3, $420, October3, $375. A bill for $375 was still owing at the end of December. . 2007 April 2 July 3 Oct. 3 Dec 31 Telephone Expense A/C $ 2007 $ bank 345 Dec 31 Profit & Loss A/c 1,515 bank 420 bank 375 Accrued c/d 375 . 1515 1515 Jan 1 bal b/d 375 . . Activity 2 M. Williams insurance expense account for 2007 were as follows: February 9, bank $210, August 10 $420, November 18, $420, amount owing for December $210 Insurance Expense A/C . 2007 $ 2007 $ Feb. 9 bank 210 Dec 31 Profit & Loss 1,260 August 10 bank 420 Nov. 18 bank 420 Dec 31 Accrued c/d 210 _____ 1,260 1260 Jan 1 bal b/d 210 Rent Receivable A/C P. Thorpe collected from her tenants the following for 2019. April $400 cheque, July$400 cheque, October cash $400, at the end of the year $400 was owing. Rent Receivable A/C 2019 $ 2019 Dec 31 Profit and Los 1,600 April Bank July Bank Oct Cash 400 Dec Accrued c/d 1,600 Jan 1 accrued b/d 400 $ 400 . 400 400 1,600 Activity 3 N. Mitchell company’s book revealed the following: commission received April 30, bank $1,280, Sept. 2 bank $1,400, the amount that was owing at the end of December was $1,360. Prepare his commission receivable a/c. Commission Receivable A/C 2019 $ 2019 Dec 31 Profit and Loss 4,040 April 30 Bank Sept 2 Bank Dec 31 Accrued c/d 4,040 Jan 1 accrued b/d 1,360 $ 1,280 1,400 1,360 4,040 . Treatment in the Balance Sheet NB: add owings and show as one figure . Balance Sheet . Current Assets $ Stock X debtor X Accrued Revenue (400 + 1360) Bank X Cash X Current Liabilities trade creditors x Accrued Expense (375 + 210) Prepayment Expense and Revenue Prepayment/Prepaid/Paid in Advance These are payments made before they fall due or the due date Prepaid Expense V. Hamilton books revealed the following information: Rent paid by cheque as follows for 2017: Jan 2 $2000, March 31, $2000, July 7, $2000,Oct. 2, $2,000 and Dec.20 $2,000, included in these payment is $2,000 for Jan 2018. Rent Expense A/C 2017 $ 2017 Jan 2 bank 2,000 Dec 31 Prepaid c/d Mar.31 bank 2,000 Profit and Loss July 7 bank 2,000 Oct 2 bank 2,000 Dec 20 bank 2,000 10,000 Jan 1 prepaid b/d 2,000 $ . 2,000 8,000 10,000 Prepaid Expense The following was found in K. Crawford books for 2016. Rates paid as follows: March bank $4,000, July bank $4,000, Oct bank $4,000 and Dec. bank $4,000 $4, 000 was paid in advance. 2016 March bank July bank Oct bank Dec bank Jan 1 prepaid b/d Rates A/C $ 2016 4,000 Dec Prepaid c/d 4,000 Profit and Loss 4,000 4,000 16,000 4,000 $ 4,000 12,000 16,000 Prepaid Revenues - Example 1 In the books of K. Long, the following was noted. Rent Received from tenants for the year was: March cash $840, July, cash $840, Oct. Cash $840 and Dec, cash $840, included in this amount was $840 PREPAID by cash. Rent Received A/C 2016 Dec Prepaid c/d Profit & Loss $ 2016 840 March cash 2,520 July cash Oct cash Dec cash 3,360 Jan 1 prepaid b/d $ 840 840 840 840 3,360 840 Prepaid Revenues - Activity P. Presh an entrepreneur book revealed the following: 2019, commission received April 30, bank $4,500, Sept. 2 bank $4,500, Oct. 3. $4,500, Dec. 20,$4,500, he also received the amount for January 2020 $4,500. Prepare his commission receivable a/c. Commission Receivable A/C 2019 $ 2019 Dec 31 Prepaid c/d 4,500 April 30 Bank Profit & Loss 13,500 Sept 2 Bank Oct. 3 Bank Dec. 20 Bank 18,000 Jan. 1 Prepaid b/d $ . 4,500 4,500 4,500 4,500 18,000 4,500 Treatment in the Balance Sheet NB: add prepayments and show as one figure . Balance Sheet Current Assets $ Stock X debtor X Accrued Revenue X Prepaid Expense (200+4,000) Bank X Cash X Current Liabilities trade creditors x Accrued Expense x Prepaid Revenue (4,500+840) . Questions 1. If you are told that an expense account has a debit balance at the beginning of the year. What does this represent? Accruals or Prepayment Prepayment 2. If a revenue account has a debit balance at the beginning of the year what does this means? Accruals Draw up the trading and profit and loss account for J. Lester for the year ended 31 December 2010 and show the balance sheet extract. $ $ Sales 152,000 Rent and rates 3,790 Purchases 81,500 Bad debts Discount received 3,100 Discount allowed 1,650 Wages 21,470 Bank Charges Return Inwards 2,460 General Expenses Return Outwards 1,910 Commission received Equipment 60,000 Stock 1, Jan, 2010 570 Carriage outwards 510 Carriage inwards 360 230 2,490 820 21,600 a. Stock $27,540 b. Rent in arrears $320 c. Carriage outwards owing $70 d. Commission received owing $120 e. General expense prepaid $490 f. Discount received prepaid $100 J. Lester Trading and Profi t and Loss Statement for the year ended 31st December 2010 Sales 152,000.00 Less Returns Inwards 2,460.00 Net Sales Less Cost of Goods Sold: Opening Stock Add Purchases Less Returns Outwards Add Carriage Inwards 21,600.00 81,500.00 1,910.00 79,590.00 360.00 79,950.00 101,550.00 27,540.00 Cost of Goods Available for Sale Less Closing Stock Gross Profit Add Revenue Commission Received Add Accural Discount Received Less prepayment 820.00 120.00 3,100.00 100.00 3,000.00 3,940.00 79,470.00 Less Expenses Carriage Outwards Add : owings 570.00 70.00 Discount Allowed General Expenses Less Prepayment 2,490.00 490.00 2,000.00 Rent and Rates Add : owings 3,790.00 320.00 4,110.00 Net profit 74,010.00 75,530.00 940.00 Total Revenue Bad Debt Bank Charges Wages Total Expenses 149,540.00 640.00 1,650.00 570.00 230.00 21,470.00 30,670.00 48,800.00 Balance Sheet Extract Current Assets Stock $ 27,540 debtors prepaid expense 490 (general expense) accrued Revenue 120 (commission Received) Current Liabilities Creditors Accrued expenses Prepaid Revenue 390 (carriage out. & rent and rates) 100 (discount received)