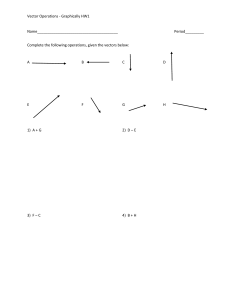
Vectors in 2D Grade 11 Physical Sciences Vectors acting at an angle 3 Ways of describing the direction of vectors 1. Bearings 2. Compass readings 3. X- and y-axes 1. Bearings • With bearings, we use the North as a reference line (taken as 0°). • We then measure an angle clockwise from the reference line to the vector in question. • For example: • Vector A in the diagram on the left has a bearing of 30° • Vector B has a bearing of 120° 2. Compass readings • With compass readings, we use the 4 cardinal points i.e. North, South, East and West or a combination of these e.g. NE (North East) or even combine these with angles. • If the Cardinal points are used with angles, we measure the angle from the nearest cardinal point. • For example: • Vector A is 60o East of North or N 60° E • Vector B is 20o west of South or S 20° W 3. x- and y-axis • In this method, we measure the angle with respect to the negative or positive axis and above or below. • For example: • Vector A is 30° above the positive x-axis • Vector B is 45° below the positive x-axis.