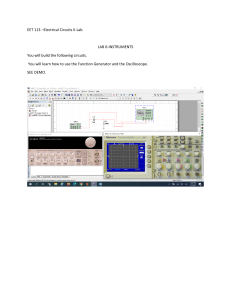
The Oscilloscope An oscilloscope is a laboratory instrument commonly used to display and analyze the fast waveforms of electronic signals which are fast voltage changes that cannot be monitored and measured with a multimeter. In effect, the device draws a graph of the instantaneous signal voltage as a function of time. History The oscilloscope was invented by a French physicist André Blondel in 1893. His device was able to register the values of electrical quantities such as alternative current intensity. An ink pendulum attached to a coil recorded the information on a moving paper tape. The first oscilloscopes had a very small bandwidth, between 10 and 19 kHz. After many years of development, a lot has changed since the invention of the first oscilloscope, it is made up of a lot of parts and systems that work in conjunction that allows it measure electronic signals, here are some; Display CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) Acting as the heart of traditional analog oscilloscopes, the CRT generates electron beams to create visual displays of waveforms. Grid Layouts Modern displays often feature customizable grid layouts, divided into divisions or "boxes." These grids assist engineers in measuring and comparing signals by providing a reference framework. The one used in the students’ experiment featured 10x8 grids. The vertical System Serves as a critical control mechanism for the display and analysis of waveforms. It allows to alter the vertical aspects of the signal. Vertical controls Usually a knob positioned at the front panel that has vertical oriented arrows, it is used to adjust the amplitude representation on the screen that allows the students to zoom in or zoom of the waveform to focus on details and obtaining overviews. Scaling Based on the used instrument, it is in the shape of a dial, it is used for adjusting the vertical size of the waveform. It allows the users to change the volts-per-division (VOLTS/DIV) setting that allows for compressing or stretching of the waveform vertically. Allows for a detailed or broader perspective of the waveform. Positioning Allows for the movement of the waveform up or down the screen. It is utilized when comparing multiple waveforms or focusing on a certain detail of the wave without changing the scaling. Channel Selection Modern oscilloscopes now come with multiple channels allowing for simultaneous observation of several signals. The divisions in the front panel allows the user to adjust them individually and gives ease in comparing signals, relationships or isolation of specific behaviors. Bandwidth Considerations Refers to the range of frequencies that the oscilloscope can measure, it is important to know that the bandwidth of an oscilloscope should be higher than the frequency to ensure accurate measurements as it impacts the ability to analyze high frequency components and transient behaviors within the signal. Effects of a the used components to the oscilloscope REF Understanding Oscilloscope Parts and Function: A Comprehensive Guide - Used Keysight Equipment What is oscilloscope? | Definition from TechTarget