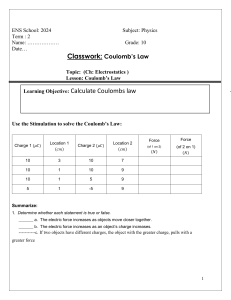
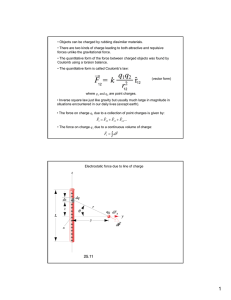
ELECTROSTATICS is the branch of physics that deals with the study of electric charges at rest. It encompasses: a basic property of matter that describes the amount of electrical energy that an object possesses. can be positive or negative. objects with different charges will experience an attractive or repulsive force. THE COULOMB (C) The unit of electric charge is the Coulomb (C). One Coulomb of charge is defined as the amount of charge that passes through a conductor when a current of one Ampere flows for one second. 6.24 × 10^18 electrons. THE LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF CHARGE behavior and interactions of static electric charges; the distribution of charge on conductors and insulators; and production and discharge of static electricity WHAT IS AN ELECTRIC CHARGE COULOMB’S LAW electric charge is a conserved quantity, meaning that it can neither be created nor destroyed, only transferred from one object to another. These forces can be described using a fundamental principle in electrostatics called the Coulomb’s Law. states that the force of interaction between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of their electric charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. 𝑭= 𝒌 𝒒𝟏 𝒒𝟐 𝒅𝟐 where: F = force of interaction (attraction/repulsion) k = constant of proportionality known as Coulomb's constant q1 and q2 = the magnitudes of the charges of the two objects d = distance between the objects CONSTANT OF PROPORTIONALITY, K used to relate the magnitude of the electric force between two charged objects to their charges and the distance between them. has a value of 𝟗. 𝟎𝟎 × 𝟏𝟎𝟗 𝑵𝒎𝟐 𝑪𝟐 . DISASTER a serious disruption of the functioning of a community or a society involving widespread human, material, economic, or environmental losses and impacts which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources. Disaster are often described as the result of the combination of: 1. Exposure to hazard 2. Conditions of vulnerability that are present 3. Insufficient capacity or measures to reduce or cope with the potential negative consequences. RISK The possibility that something bad or unpleasant, such as an injury or a loss, will happen.