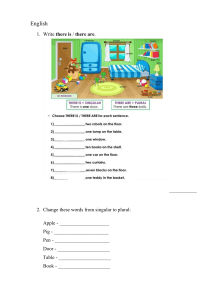
CONCORD Notes on Concord Concord refers to the agreement between different parts of a sentence. The primary types of concord are as follows: 1. Subject-Verb Concord: The subject and the verb must agree in number (singular or plural). o Example: The teacher speaks. (Singular subject "teacher" with singular verb "speaks") o Example: The teachers speak. (Plural subject "teachers" with plural verb "speak") 2. Noun-Pronoun Concord: Pronouns must agree with the nouns they replace in terms of number, gender, and person. o Example: The boy lost his book. (Singular noun "boy" with singular pronoun "his") o Example: The girls lost their books. (Plural noun "girls" with plural pronoun "their") 3. Concord with Collective Nouns: Collective nouns like team, family, audience, committee can take either singular or plural verbs, depending on whether the group is viewed as a unit or as individuals. o Example: The team is winning. (Singular: viewing the team as a unit) o Example: The team are arguing among themselves. (Plural: viewing the members as individuals) 4. Concord with Indefinite Pronouns: Some indefinite pronouns like everyone, someone, each, and nobody take singular verbs, while others like few, many, both, and several take plural verbs. o Example: Everyone is excited. (Singular) o Example: Few are attending the event. (Plural) 5. Concord with Correlative Conjunctions: When using pairs like either...or, neither...nor, both...and, the subject closest to the verb determines the verb form. o Example: Either the teacher or the students are responsible. (Plural subject "students") Page 1 of 4 Example: Neither the teacher nor the student is responsible. (Singular subject "student") 6. Concord with 'None': The word "none" can take either singular or plural verbs, depending on whether it refers to a singular or plural noun. o Example: None of the cake is left. (Singular) o Example: None of the apples are ripe. (Plural) 7. Concord in Phrasal Subjects: Compound subjects formed by using and, or, etc., determine whether the verb is singular or plural. o Example: Peanut butter and jelly is my favourite snack. (Singular subject) o Example: Peanut butter and jam are available in different flavours. (Plural subject) 8. Concord in Complex Sentences: In sentences with multiple clauses, the subject and verb in the main clause and any dependent clauses must agree. o Example: The book that she borrowed is on the table. (Singular subject "book") o Example: The books that she borrowed are on the table. (Plural subject "books") 9. Concord with "There" + "Be" Sentences: In sentences starting with there is or there are, the verb must agree with the noun that follows. o Example: There is a book on the table. (Singular) o Example: There are books on the table. (Plural) 10.Concord with More than One: The phrase more than one usually takes singular agreement. o Example: More than one student has arrived late. 11.Concord in Conditional Sentences: In conditional sentences, subjectverb agreement follows the usual rules for the subject and verb in both the if-clause and the main clause. o Example: If she is ready, we can leave. (Singular) o Example: If they are ready, we can leave. (Plural) o Page 2 of 4 Exercise: Fill in the Blanks 1. Neither the teacher nor the students _____ present in the class yesterday. (was / were) 2. The dog and the cat _____ hungry. (is / are) 3. Each of the teachers _____ preparing for the lesson. (is / are) 4. The committee _____ made their decision. (has / have) 5. Neither the bread nor the cakes _____ fresh. (is / are) 6. The family _____ visiting their relatives this weekend. (is / are) 7. Everyone in the class _____ completed their assignments. (has / have) 8. The team _____ practising for the tournament. (is / are) 9. The children in the group _____ happy with the surprise. (was / were) 10. Neither of the options _____ suitable. (is / are) 11. Both of the reports _____ accurate. (is / are) 12. More than one book _____ missing. (was / were) 13. The woman with the two dogs _____ walking down the street. (is / are) 14. The students and the teacher _____ excited for the event. (is / are) 15. None of the cake _____ left. (is / are) 16. Neither the teacher nor the student _____ responsible for the delay. (was / were) 17. Neither the students nor the teacher _____ heard the announcement. (has / have) 18. The books on the shelf _____ covered in dust. (is / are) 19. Each of the boys _____ bringing their own lunch tomorrow. (is / are) 20. The manager, along with his assistants, _____ in charge of the meeting. (is / are) 21. The audience _____ clapping for the performance. (was / were) 22. More than one student _____ called to the principal's office. (was / were) 23. Neither of the teachers _____ available today. (is / are) 24. If she _____ available, we can go to the concert. (is / are) 25. If they _____ here, we could begin the meeting. (were / was) 26. The children and their parents _____ excited for the holiday. (is / are) 27. Neither the soup nor the sandwich _____ fresh. (was / were) 28. Neither of the paintings _____ original. (is / are) 29. Both the teacher and the students _____ ready for the presentation. (is / are) 30. Everyone in the room _____ a chance to speak. (has / have) 31. The committee _____ scheduled the meeting for tomorrow. (has / have) 32. The police _____ investigating the case. (is / are) 33. The book that I borrowed _____ on the table. (is / are) 34. More than one person _____ interested in the job. (was / were) 35. The dog, along with its puppies, _____ playing outside. (is / are) 36. There _____ a new film in the cinema. (is / are) 37. Neither the students nor the teacher _____ happy with the decision. (was / were) 38. There _____ many opportunities for advancement. (is / are) 39. The jury _____ deliberating on the verdict. (is / are) 40. Neither the company nor its employees _____ aware of the policy changes. (was / were) Page 3 of 4 Memo (Answers): 1. were 2. are 3. is 4. has 5. are 6. is 7. has 8. is 9. were 10. is 11. are 12. were 13. is 14. are 15. is 16. was 17. has 18. are 19. is 20. is 21. was 22. were 23. are 24. is 25. were 26. are 27. was 28. is 29. are 30. has 31. has 32. are 33. is 34. was 35. is 36. is 37. were 38. are 39. is 40. were Page 4 of 4