Types of Pumps: Reciprocating, Rotary, Centrifugal & More
advertisement

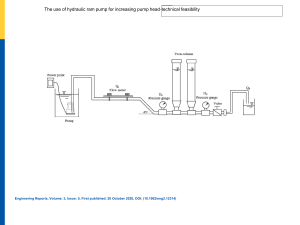
Types of Pumps and Their Key Components 1. Reciprocating Pump o Category: Positive displacement o Main Parts: Cylinder, piston or plunger, valves, crankshaft, and connecting rod o Description: Operates through a back-and-forth motion, transferring liquid in fixed volumes. It delivers high pressure but at a relatively low flow rate. 2. Rotary Pump o Category: Positive displacement o Main Parts: Rotors, casing, inlet and outlet ports o Description: Uses rotating elements to move fluids continuously. It is self-priming and maintains a steady flow. 3. Centrifugal Pump o Category: Dynamic o Main Parts: Impeller, volute casing, shaft, and bearings o Description: Relies on centrifugal force to transport liquid. Best suited for high-flow applications with low-viscosity fluids. 4. Progressive Cavity Pump o Category: Positive displacement o Main Parts: Rotor (single helix), stator (double helix), suction and discharge ports o Description: Moves fluids in a smooth, continuous manner with minimal pulsation. Ideal for handling thick and shear-sensitive substances. 5. Gear Pump o Category: Positive displacement o Main Parts: Gears (internal or external), casing, inlet and outlet ports o Description: Utilizes meshing gears to transport liquid. Commonly used for high-viscosity fluids, providing a constant output. 6. Screw Pump o Category: Positive displacement o Main Parts: Interlocking screws, casing, inlet and outlet ports o Description: Ensures a smooth and non-pulsating flow. Wellsuited for lubricating fluids and high-pressure applications. 7. Diaphragm Pump o Category: Positive displacement o Main Parts: Flexible diaphragm, check valves, air chamber (for air-operated models) o Description: Uses diaphragm movement to transfer fluids, making it ideal for handling corrosive, abrasive, and viscous materials. 8. Submersible Pump o Category: Dynamic (typically centrifugal) o Main Parts: Sealed motor, impellers, and casing o Description: Designed to operate fully submerged in liquid. Often used for deep wells, sewage systems, and drainage applications. Accessories 9. Bourdon-Type Pressure Gauge o Main Parts: C-shaped or coiled tube, pointer, dial, and mechanical linkage o Description: Measures fluid pressure by detecting the deformation of a Bourdon tube. Commonly used for highpressure systems. 10. Compound Pressure Gauge o Main Parts: Bourdon tube, dial, pointer, and mechanical linkage o Description: Capable of measuring both vacuum and positive pressure within a system. Frequently used in HVAC, refrigeration, and vacuum applications.