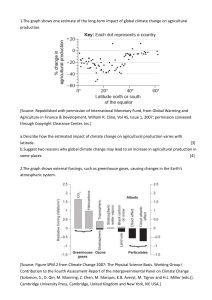
Before 2023, CO2 concentration below 300 ppmv; In 2023: 400 ppmv 1. energy consumption greatly increase after 1950 2. fossil fuel is still the main source of greenhouse gas Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Scientific concerns about global warming grew during 1980s • In 1988, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) established IPCC to investigate and report on scientific evidence on climate change and possible international responses to climate change • IPCC‘s first assessment report (in 1990) fed into the drafting of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in 1991. 166 nations signed at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro in 1992 and came to force in 1994. • An objective of stabilizing the climate to prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system in a timeframe that allow natural systems to adapt without major damage to food systems and economic development. Kyoto Protocol • In the 1997 Conference of Parties (COP) meeting in Kyoto, Japan, delegates agreed on Kyoto Protocol • The protocol required Annex I countries to reduce emissions but exempted other countries. • The participants agreed to reduce their CO2 and other GHG emissions to a level 7% below the 1990 total, with the agreement to take force during 2008–2012 Copenhagen Summit • Establish a replacement for the Kyoto Protocol • Failed its key goal of establishing binding emissions limits after 2012. • Adopted a target temperature limit for climate policy • Countries recognized “the scientific view that the increase in global temperature should be below 2 degrees Celsius.” Paris Agreement: adopted 12 Dec 2015 at COP21, came into force 4 Nov 2016; ratified 179/197; with Nationally Determined Contributions— country determine how to meet the emission target; increase global average temp below 2ºC & pursue efforts to limit temp increase to 1.5ºC California • Ambitious Emissions Targets: California has set rigorous greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction goals (e.g., aiming for carbon neutrality by 2045) • Clean Vehicle Policies: California leads nation in zero emission vehicle (ZEV) adoption with incentives and mandates to transition car manufacturers toward EV production. • Renewable Energy: Renewables Portfolio Standard (RPS) requires utilities to derive 60% of electricity from renewables by 2030, aiming for 100% carbon-free power by 2045. tribal sovereignty. • Regulatory Stance: State officials often push back on federal regulations aimed at reducing methane leaks or emissions from oil and gas operation European Union • The EU has generally been a global frontrunner in setting binding climate targets and implementing legislation to curb greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. • Key initiatives include the European Green Deal, targeting climate neutrality by 2050, and a series of interim targets (e.g. reducing net emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.) •The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) is one of the world’s largest carbon markets and a central policy tool Bodily subsystems: immune systems-->the person-->fam social groups-->society-->species-->biospecies South America • Many South American nations, including Brazil, Chile, Colombia have submitted NDCs under Paris Agreement. • Efforts include protecting and managing natural carbon sinks (Amazon rainforest), transitioning to renewable energies, and implementing adaptation strategies for agriculture • Challenges include balancing economic development and deforestation pressures, as well as political and economic instability in some regions. Middle East • Oil-producing countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, have begun diversifying their economies with varying degrees of commitment to renewables, green hydrogen, and other low-carbon strategies (e.g., Saudi Green Initiative, UAE’s Net Zero by 2050 pledge). •Many Middle Eastern countries face water scarcity and extreme heat, driving adaptation measures. However, dependence on fossil fuel exports remains a significant challenge for deep decarbonization 1. Everything is connected to everything else. Systems Think embraces Loop Structure Thinking Event oriented thinking: everything is explained by casua chains of events. Root causes are the events starting the chains of cause and effects, Systems thinking: systems behavior emerges from struct of feedback loops. Root causes are not individual nodes b forces emerging from particular feedback loops 2. The whole is greater than the sum of the parts The most critical feature is the interconnections or relationships, between the elements Elements involved in wildfires: forest, drought, bark beet wildfire, climate change, lightening, human activities Drought: • Drought conditions reduce the water availability for tre stressing them and weakening their immune systems. • A stressed tree is less able to produce sap, which acts a natural defence against bark beetles. Bark Beetles & Forest Health: • In a healthy forest, trees can usually defend themselves from these beetles by producing sap to push them out. • However, in times of drought, trees may not have enou sap to fend off the beetles, leading to higher infestation r and widespread tree mortality, particularly in conifer fore • Combination of drought stress and bark beetle infestat can lead to large-scale tree mortality. When many trees d creates fuels for wildfire Climate Change: • Climate change exacerbates all of these interactions. • Increased temperatures and altered precipitation patter can make droughts more frequent and severe • Create conditions that allow bark beetles to spread eas 1. Faster development 2. Extended range 3. Easier surviv cold seasons 3.Systems are dynamic and their behavior is emergent Prescribed fires are used to reduce the accumulation of ris 1. Reducing Fuel Loads: preventing the buildup of large amounts of flammable material, which fuel more intense f 2. Creating Firebreaks: areas where fuel has already been removed or burned, making it harder for a wildfire to sprea 3. Reducing Tree Density: create more space between tre making it more difficult for fires to spread rapidly. 4. Promoting Fire-Resilient Landscapes: help promote m fire-resilient landscape by encouraging the growth of fire resistant plants and trees. Healthy, fire-resilient landscape less likely to burn at high intensity Higher the resilience, lower the vulnerability Interconnected negative feedback loops -> system resilien Planck feedback: relation between radiative energy and te • Higher temp, emit more energy by radiation Atmosphere, ocean, land warm up, radiation strengthens a help avoid accumulation of energy Higher GDP, higher CO2 emission North Dakota • Fracking Boom: The Bakken Formation made North Dakota a major U.S. oil producer. Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) operations expanded rapidly. • Pipeline Infrastructure: The state supports pipelines such as the Dakota Access Pipeline to transport shale oil, despite legal challenges and protests related to environmental risks and China • China is the world’s largest emitter; but it plans to peak CO₂ emissions before 2030 & achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. • Investments in renewable energy (solar and wind) are significant, and China leads the world in total installed renewable capacity (10 x in 10 yr) • Policy measures include national carbon trading scheme, though challenges in transparency, enforcement, and balancing economic growth with climate goals Troposphere is most important layer of atmosphere, whe weather systems exist and 70% of mass of the atmosphe System is an interconnected set of elements, organized in a way that achieves sth (a distinct function or purpose) and produces its own pattern of behaviour over time. Systems can be ‘nested’ within other systems. We are all made of, part of, and surrounded by systems. • Global warming potential: amount of warming one ton of gas would create relative to one ton of CO2 over a 100-year scale CO2: 1 (74.4%) CH4: 27-30 (17.3%) N2O: 273 (6.2%) F gas: 1000-10000 (2.1%) • Desert Climate: the Mojave Desert (e.g. Palm Springs) have arid, desert climate, extremely hot summers and cold winters Due to rain shadow effect Agriculture • Agriculture, forestry & other land use (AFOLU): ¼% of GH Bottom to top & equator to pole drive temperature gradients • Warm air rise and cold sink, so have convection in the tropics Electromagnetic spectrum • increasing frequencies/decreasing energy: radio waves-> microwaves -> infrared -> visible light -> UV -> X rays -> gamma rays Energy Budget: global energy flow diagram for Earth system Unit: W/m² Oceanic process influence • carbon cycle (photosynthesis of phytoplankton: bacteria, protists, most are single cell plants) e.g. cyanobacteria, dinoflagellates, green algae • weather (set bottom boundary condition) •climate change (absorb >90% of the heat) California Climate • Mediterranean Climate: Most of coastal California (LA and San Francisco) Hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters • Mountain Climate Sierra Nevada, cold, snowy winter and mild to warm summer Santa Ana wind: high wind speed, warm temp, low humidity Climate prediction is hard: scenario + physics uncertainty Climate scientists compute climate: 1. Need to know the governing equations first, if possible 2. Atmosphere and oceans are divided to small grid cells (discretization) 3. They need to use approximations for small scale processes (parameterization) 4. Societal impacts need to be computed to help with policymaking (integrated assessment model) e.g. climate impacts, socioeconomic development, energy & land use, emissions, climate change Solar and terrestrial radiation • Earth emit radiation at longer wavelength (5-25 um) • Sun emits radiation at wavelength less than 2 um Cause of greenhouse effect: Atmosphere is transparent to solar radiation. Terrestrial radiation is absorbed and remit in its upward passage through atmosphere Why greenhouse gas has greenhouse effects? • Oxygen and nitrogen absorb energy with tightly packed wavelengths of around 200 nanometres or less • CO2 absorb energy at 2000-15000um, overlap with infrared’s Greenhouse gas concentration • CO2, CH4 (methane), N2O, Fluorinated gas/synthetic greenhouse gas/ F-gas (HFCs, PFCs, SF6, NF3) CO2 • Enter atmosphere through burning fossil fuels, solid waste, trees, biological material, chemical reaction (produce cement) • Removed from atmosphere when is absorbed by plants as part of biological carbon cycle Other use of fossil fuels • cement and steel industry generate greenhouse gas Making things (cement, steel, plastic): 31% Plugging in (electricity): 27% Growing things (plants, animals): 19% Transport (plane, truck, cargo ship): 16% Maintaining temp (heating, warming, refrigeration): 7% Cement • CO2 is emitted as a by-product of clinker production, which CaCo3 is calcinated and converted to Lime (CaO), main component of cement • Emitted during cement production by fossil fuel combustion • World use of cement lead to 8% of global CO2 emission • Concrete -> timber place pressure on beleaguered forest Steel • Emission from iron and steel: 7.2% • Melt iron at 1700C with oxygen and coke Transportation • Global transportation emission: 14% USA emission: 30% • Growth of transport GHG emission is in developing countries • Passenger vehicles are responsible for about half Buildings • Heating is essential in high latitude regions and seasons when solar is not reliable Strategy: electrify what we can, no natural gas water heater and furnace, develop clean fuels, improve building efficiency Efficiency strategy: Appliance-based efficiency (increase efficiency of space, water heating equipment) Design based efficiency (High performance window, insulation, sealants) Example: I-village (District cooling strategy, precast facade modules with thermal insulation, centralised hot water system with solar thermal, heat pump system,PV panel & BVPI system) Methane • Emitted during production & transport of coal, natural gas, oil • Result from livestock and agricultural practice, land use • By decay of organic waste in municipal solid waste landfill Ruminant livestock have microbes in rumen called methanogens., which produce methane then belched out Nitrous oxide Population growth • Norman Borlaug develop first semi-dwarf wheat, corn, ric • Yuan Longping develop first hybrid rice varieties Culprit in AFOLU • Major GHG are CH4, N2O, 28 and 265 times higher warm potential than CO2 • Population growth and when ppl is richer, they consume meat and dairy products • Enteric fermentation in ruminants produce methane, contribute to about 2 Gt CO2e • Animal manure contain nitrous oxide, methane, sulfur, ammonia, which is 2nd biggest emission Fertilizer • Contain nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium • Population will be 40-50% smaller without fertilizer • Plants cannot produce nitrogen but absorb anomia in so • Perihelion (Jan 3) Aphelion (July 4) • Each Jan, 6.8% more solar radiation than July, max diff: 23% • Cycle span about 100000 years Obliquity • Greater the Earth axial tilt angle, more extreme season • Larger tilt angle favour deglaciation: higher latitude has larger solar radiation than equator • Angle is slowly decreasing Precession • As earth rotate, it wobbles slightly upon its rotational axis, due to tidal forces by gravitational influence of Sun and Moon that cause Earth bulge at equator • Axial precession: direction of wobble relative to fixed position of stars • Season contrasts extreme in one hemisphere than other Eon: Hadean (4.54-4 bil), Archean (4-2.5 bil), Proterozoic (2.5 bil-541 mil), Phanerozoic (541 mil-present) Epoch: Quaternary period = Holocene + Pleistocene Anthropocene is also a potential new epoch Deforestation • 30% of AFOLU come from deforestation • Bc of carbon sink removal -> emission from plants and soil • Driven by animal farms and crop growing • Terrestrial sequestration of CO2 does not work Eon->Era->Period->Epoch Proxy data: preserved charactestics of environment that stand in for direct measurement Mass Fractionization Water with heavy isotope evaporate less readily and condense more readily. The colder, more vapour is removed by condensation, and the lighter the sample. O18 can measure past global ice volume. When climate cool and ice sheet grow, more precipitation in cold region is enriched in lighter isotopes (O18). Ocean is enriched in O18. Marine organisms incorporate oxygen from seawater in their shell. Higher O18 suggest larger global ice volume. • Puzzle like fit: coastline of South America and Africa • Fossil Distribution: identical fossils • Rock & Mountain Distribution: similar rock formation • Paleoclimate indicator: coal deposit and glacial striation in tropical or temperate regions • HK geology is formed by igneous rock from volcanic eruption Warmer past climate • High atmospheric CO2: volcanic activity and limited terrestrial vegetation cause higher greenhouse gas • Continental configuration: supercontinents influence oceanic and atmospheric circulation, major landmass near equator, cause more solar heating and reduce albedo • Limited polar ice caps: minimal polar ice Snowball Earth • Glaciers present near equator at low altitudes • Deposit produced by a glacier within 10 degrees of equator • Carbon 13 spikes in ocean sediments, photosynthetic life is surpassed • Banded iron deposit is anoxic Chemical weathering • Land mass is key in a process • Rain/snow fall on silicate rock, react and take Co2 out of atmosphere • Negative feedback: Hot climate, easier chemical weathering • During snowball earth, volcanic activity injects CO2 into atmosphere. When land and ocean covered by ice, no chemical weathering, Greenhouse effect is so strong that ice begins to melt. Melting proceeds rapidly. Milankovitch Cycle • Link between orbital cycle and glacial-interglacial period • How ice-albedo, CO2, ocean circulation affect orbital change • Unknown why glacial cycle shift from 41k to 100k ~ 1mil year • Assume changes in radiation at 65N latitude & in summer are most important • Cold summer (low tilt, North hemisphere summer at aphelion, moderate eccentricity) favor glaciation • Obliquity affect insolation in north latitude in summer Eccentricity • Pull of gravity from Jupiter & Saturn, vary from circle to elliptical. So, seasons have diff lengths.