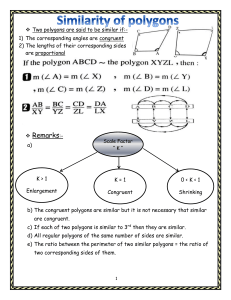
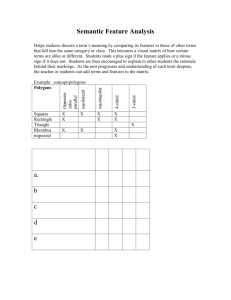
Properties of Polygons This section describes and compares the properties of regular and irregular polygons. Introduction to Polygons A polygon is a closed twodimensional shape with straight sides. Polygons can have any number of sides, and each side must intersect with exactly two other sides. Regular Polygons A regular polygon is a polygon with all sides and angles congruent. Examples of regular polygons include equilateral triangles, squares, and regular hexagons. Regular Polygons A regular polygon is a polygon in which all sides are of equal length and all angles are of equal measure. Examples of regular polygons include triangles, squares, pentagons, hexagons, and so on. Regular polygons have many interesting properties, such as: • • • • All interior angles are equal • All exterior angles are equal The sum of the interior angles is equal to (n-2) times 180 degrees, where n is the number of sides The measure of each interior angle is given by (n-2) times 180 degrees divided by n The measure of each exterior angle is given by 360 degrees divided by n Irregular Polygons Irregular polygons are polygons that do not have congruent sides or angles. They can have any number of sides and angles, and their sides can be of different lengths. Unlike regular polygons, irregular polygons cannot be classified by a single formula for calculating their perimeter or area. Instead, the perimeter and area must be calculated by adding up the lengths of the sides or using more complex formulas. Angles in Polygons Interior Angles The sum of the interior angles in a polygon can be calculated using the formula (n-2) x 180, where n is the number of sides in the polygon. For example, a triangle has 3 sides, so the sum of its interior angles is (3-2) x 180 = 180 degrees. A hexagon has 6 sides, so the sum of its interior angles is (6-2) x 180 = 720 degrees. Exterior Angles The exterior angle of a polygon is the angle formed by a side of the polygon and the extension of an adjacent side. The sum of the exterior angles in a polygon is always 360 degrees. For example, a regular pentagon has 5 sides , so each exterior angle measures 72 degrees (360 / 5). Perimeter of Polygons Regular Polygons The perimeter of a regular polygon can be found by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides. Irregular Polygons The perimeter of an irregular polygon can be found by adding the lengths of all its sides. Area of Polygons Regular Polygons The area of a regular polygon can be calculated using the formula A = (1/2) x ap, where a is the apothem (distance from the center to the midpoint of a side) and p is the perimeter. Irregular Polygons The area of an irregular polygon can be calculated by dividing it into smaller regular polygons and then summing their areas. Congruent Polygons Congruent polygons are polygons that have the same shape and size. To show that two polygons are congruent, we use the symbol ≅ . For example, if polygon ABCD is congruent to polygon ABCDEFGH, EFGH we write: ≅ In order for two polygons to be congruent, all corresponding sides and angles must be equal. This means that if we know the measures of the sides and angles of one polygon, we can use that information to find the measures of the sides and angles of a congruent polygon. Similar Polygons Similar polygons are polygons that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. This means that the corresponding angles of similar polygons are congruent, and the corresponding sides are proportional. Proportions of Sides To determine whether two polygons are similar, we need to compare the ratios of their corresponding sides. If the ratios are equal, then the polygons are similar. Applications Similar polygons are used in many real-world applications, such as map-making, architecture, and engineering. For example, architects use similar polygons to design buildings that have the same shape but different sizes. Engineers use similar polygons to design structures such as bridges and towers that are strong and stable. Applications of Polygons • Architecture: Polygons are widely used in architectural designs to create unique • and aesthetically pleasing structures. Examples include the Sydney Opera House and the Guggenheim Museum Bilbao. • Engineering: The properties of polygons are important in engineering applications • such as designing bridges, tunnels, and dams. Engineers use polygons to determine the strength and stability of these structures. Art and Design: Polygons are used in graphic design and digital art to create intricate patterns and shapes. They are also used in 3D modeling and animation to create realistic objects and environments. Geography: Polygons are used in geography to represent land masses and bodies of water on maps. They are also used to calculate the area and perimeter of these regions.