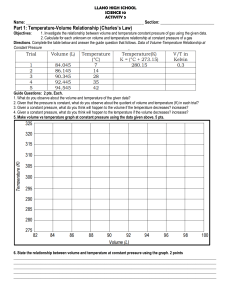
Subject: science 10 Grade Level: Grade 10 Objective: 1. Analyze the relationship between volume and temperature at the constant pressure of a gas. 2. Perform an experiment on the relationship between volume and temperature at the constant pressure of a gas. 3. Recognize the practical application of Charles Law in everyday scenarios. Learning within the curriculum: 1. The topic of gas laws in chemistry, particularly the Ideal Gas Law, relates to the current lesson as it encompasses the behavior of gases under various conditions, expanding on the concept of volume and temperature. Understanding the Ideal Gas Law helps students see how Charles Law fits into a broader context of gas behavior. 2. The study of thermal expansion of materials also connects to the objective, as it illustrates how temperature changes can affect the volume of solids and liquids, thereby reinforcing the concepts learned from Charles Law about gases. Learning across the curriculum: 1. In mathematics, the topic of linear equations can be integrated, as students can represent the relationship between volume and temperature as a linear graph, further emphasizing the analytical skills required to interpret data. This connection helps students visualize the relationship quantitatively. 2. In physics, the concept of kinetic molecular theory can be examined, which explains how temperature affects the motion of gas particles and correlates to volume changes, thus deepening students’ understanding of molecular behavior in relation to Charles Law. Elicit: Teaching Strategy: Cooperative Learning Instructional Materials: Whiteboard and markers Anecdote 1: "When I was a child, I remember my mother cooking rice and how she would always tell me to keep the lid on the pot. She explained that if we kept it covered, the steam would increase the temperature inside, causing the rice to expand and cook perfectly. This is similar to how gases behave with temperature changes." Anecdote 2: "I once visited a local bakery where I saw bread rising in the oven. The baker explained that as the temperature increased, the air inside the dough expanded, making the bread fluffier. This is a great example of how heat affects volume in gases." Engage: Teaching Strategy: Interactive Learning Instructional Materials: Balloons and warm water Energizer 1: "Hot Air Balloon Activity" - Students will blow up balloons and then place them in warm water. They will observe how the balloons expand as the temperature of the air inside increases, linking this to the concept of Charles Law. Energizer 2: "Temperature Walk" - Students will take a short walk outside (or in the classroom) to feel the difference in temperature, discussing verbally how they think temperature can affect different materials, including gases. This requires no materials and can be done in any setting. Explore: Activities Activity 1: "Charles Law Experiment" Teaching Strategy: Inquiry-Based Learning Materials: Balloons, measuring tape, thermometer, water Significance: This experiment allows students to observe the direct relationship between volume and temperature in a controlled setting. Instructions: 1. Fill a balloon with air and measure its circumference. 2. Place the balloon in warm water and measure the temperature. 3. After 10 minutes, measure the balloon's circumference again. Rubrics: - Accurate measurements: 5 pts. - Clear observations and explanations: 5 pts. - Participation and teamwork: 5 pts. Assessment Questions: 1. What measurements did you take? 2. How did the balloon's volume change with temperature? 3. What conclusion can you draw about the relationship between volume and temperature? Activity 2: "Graphing Charles Law" Teaching Strategy: Constructivist Learning Materials: Graph paper, markers Significance: This activity helps students visualize the relationship between volume and temperature through graphing, reinforcing their analytical skills. Instructions: 1. Record the temperatures and corresponding volumes from the previous experiment. 2. Plot the data on graph paper, with temperature on the x-axis and volume on the yaxis. 3. Draw a line of best fit and analyze the graph. Rubrics: - Correctly plotted points: 5 pts. - Clear line of best fit: 5 pts. - Analysis of the graph: 5 pts. Assessment Questions: 1. What does the graph indicate about the relationship between temperature and volume? 2. How does the line of best fit help you understand the data? 3. What predictions can you make based on your graph? Explain: Activity 1 - The objective of analyzing the relationship between volume and temperature at constant pressure helps students understand how gases expand when heated, following Charles Law. Activity 2 - Recognizing practical applications of Charles Law in everyday scenarios allows students to see the relevance of scientific principles in real life, such as in cooking or weather phenomena. Activity 3 - Understanding that gas behavior can be predicted through mathematical relationships deepens students' comprehension of science as a way of explaining the natural world. Elaborate: Teaching Strategy: Project-Based Learning 1. Task: Students will create a presentation on how Charles Law applies to a realworld scenario, such as weather balloons or hot air balloons. 2. Task: Students will conduct a home experiment observing how the volume of a gas changes with temperature (e.g., heating a sealed plastic bottle). Discussion: After the presentations, students will discuss the findings, sharing their experiences and insights on how gas laws govern practical situations in their lives. Evaluate: Teaching Strategy: Formative Assessment Questions: 1. Describe how you would explain Charles Law to someone who has never heard of it. 2. What factors must be kept constant when observing the relationship between volume and temperature? 3. Can you think of a situation where Charles Law is applied in daily life? For Higher Order Thinking Skills: Questions: 1. How would the behavior of gases change if the pressure were not constant? 2. Can you hypothesize what would happen to the volume of a gas if the temperature were drastically increased? 3. How does understanding Charles Law help us predict weather patterns? Answers: 1. If pressure is not constant, the relationship between volume and temperature may not hold true, leading to unpredictable gas behavior. 2. If the temperature were drastically increased, the volume of the gas would likely expand significantly, as predicted by Charles Law. 3. Understanding Charles Law allows meteorologists to predict how air pressure and temperature changes can affect weather systems, leading to more accurate forecasts. Extend: Teaching Strategy: Contextualized Learning Instructional Materials: Videos or articles on gas laws Usecase 1: Students can observe and report on how temperature affects the behavior of gases in different climates, such as comparing data from tropical and temperate regions. This will help them apply their understanding of gas laws in various environmental contexts. Usecase 2: Students can analyze how gas laws impact engineering designs, such as in the construction of pressure vessels or in automotive engineering, linking scientific principles to real-world applications in technology and design. Assignment: 1. Write a short essay on a practical application of Charles Law in your daily life or in a field of interest (e.g., cooking, weather, or engineering). Use specific examples to illustrate your understanding of the concept.