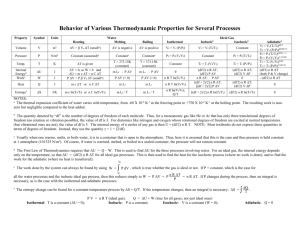
Thermodynamic Processes and Their Derivations Using First Principles Constant Volume Process (Isochoric Process) A constant volume process occurs when the volume remains unchanged during the process. From the First Law of Thermodynamics: dQ = dU + dW Since work done in a constant volume process is given by: dW = P dV = 0 Thus, the heat transfer in this process directly changes the internal energy: dQ = dU For an ideal gas, dU = m C_v dT where C_v is the specific heat at constant volume. Constant Pressure Process (Isobaric Process) In a constant pressure process, the pressure remains unchanged. From the First Law of Thermodynamics: dQ = dU + PdV For an ideal gas, dU = m C_v dT and using the ideal gas equation: dW = P dV = P (V_2 - V_1) Applying the relation between specific heats: dQ = m C_p dT where C_p is the specific heat at constant pressure. Polytropic Process A polytropic process follows the equation: PV^n = constant Differentiating both sides: P dV + V dP = 0 Applying the First Law: dQ = dU + dW Work done is given by: W = (P_2 V_2 - P_1 V_1) / (1 - n) For an ideal gas, dU = m C_v dT Heat transfer is then: Q = (C_p - C_v) / (1 - n) * (P_2 V_2 - P_1 V_1) Isothermal Process An isothermal process occurs at constant temperature, meaning dT = 0 and thus internal energy remains unchanged (dU = 0). Using the First Law: dQ = dW Work done is obtained from: W = ∫ P dV Using the ideal gas equation, P = (nRT) / V, we get: W = nRT ln(V_2 / V_1) Since dQ = dW, heat transfer is: Q = W = nRT ln(V_2 / V_1) Isothermal Process (Hyperbolic) For a hyperbolic process, the equation PV = C holds. The derivation remains the same as the isothermal process, leading to: W = P_1 V_1 ln(V_2 / V_1) Isentropic Process (Adiabatic and Reversible Process) For an isentropic process, entropy remains constant, and no heat transfer occurs (dQ = 0). Using the First Law: dU = -dW For an ideal gas: dU = m C_v dT and work done is: W = (P_2 V_2 - P_1 V_1) / (1 - γ) where γ = C_p / C_v is the adiabatic index. Using PV^γ = constant, we derive: T_2 = T_1 * (V_1 / V_2)^(γ - 1) which connects temperature and volume for an isentropic process.