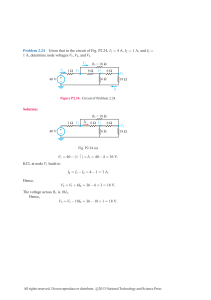
Series-Shunt Feedback Amplifiers * The closed loop gain of feedback amplifier is given by 𝑥𝑜 𝐴 𝐴𝑓 ≡ = 𝑥𝑠 1 + 𝐴𝛽 This suggests that Af can be determine by calculating A and β. This method is called feedback analysis. *Alternatively, the complete closed loop amplifier can be analyzed directly. But it will be evident after you gain feedback analysis experience that it provides faster and simpler way to analysis and design solutions. * Now we will consider each feedback topologies separately and explain the approach of tackling them. Also, their different properties will be considered. Voltage Amplifiers: Series-Shunt * The series-shunt feedback amplifier topology is depicted again in Fig. 1. Our goal is to decompose the given circuit to circuit A and Circuit β. Then, values of A and β will be determined by analyzing circuit A and Circuit β, respectively. Vs Basic amplifier Rs RL Rin Rif + Vo - Rof Rout 1 Feedback network 2 Fig. 1: Practical series-shunt feedback amplifier (Fig. 8.10(a)) * As you know any two port network can be represented by any one of the four different two port parameters namely, h-parameters, g-parameters, z-parameters and y-parameters. Rs Vs I1 1 Basic amplifier RL h12V2 + V2 - + Vo - h11 h21 I1 h22 2 Feedback network Fig. 2: Series –shunt amplifier with feedback network replaced by its h-parameters A circuit + Rs V1 h11 Vs - Vf + Basic R amplifier L h12 Vo + Vo - h22 + Vo - β circuit Fig. 3: Derivation of circuit A and circuit β for the series-shunt feedback amplifier * Now circuit A is the shaded amplifier with input Vi and output Vo. Note that it include the basic amplifier, Rs, R11, RL and R22. * What is left now is to calculate the gain A, R11, R22, and β. The rules of finding these parameters are summarized in Fig. 4. Via Rs R11 Ria Basic R amplifier 22 RL + Voa - Roa Circuit-A (a) 1 Feedback network 2 1 Feedback network 2 R22 R11 (b) + Vf - (c) I1 1 Feedback network 2 Vt (d) Fig. 4: Rules for circuit-A and circuit-β of the series shunt topology * To calculate the of circuit A, used the develop circuit A and apply a test voltage Via and determine its response voltage Voa as shown in Fig. 4(a). The gain A is defined as 𝐴 ≡ 𝑉𝑜𝑎 . You should remember that the input to circuit A is voltage and measured output is 𝑉 𝑖𝑎 voltage as the name of the topology is voltage mixing voltage sampling. * To calculate R11 of the feedback network, short circuit port-2 and determine R11 as seen from port-1. (Fig. 4 (b)). * To find R22, open circuit port-1 and calculate R22 as seen from port-2 (Fig. 4(c)) * To obtain β, open circuit port-1 as we are measuring feedback voltage signal. Apply a test voltage at port-2 and find its open circuit response at port-1 as shown in Fig. 4(d). Example 1: Consider the inverting amplifier shown in Fig. 5. The op amp is replaced by a simple model of finite input resistance Rid, finite open loop gain μ and non-zero output resistance ro. Use feedback analysis to determine the closed loop gain= Vo/Vs. Rs Rid Vs + V1 - ro Vo μV1 RL Rin Rif R1 Rout R2 Rof Fig. 5: Non-inverting amplifier with op amp model (Fig. 8.12 a) Solution: 1. Label the two terminal of the feedback network consisting of R1 and R2 as port-1 at vand port-2 at Vo and as shown in Fig. 6(a) Rs Rid Vs Rif + V1 - ro Vo μV1 RL Rin R1 1 R2 2 Rout Fig. 6(a): Same as Fig. 5 but with labels 2. Find R11. Use the rule and short port-2 to get R11=R1||R2. 3. Find R22. Use the rule and open port-1 to get R22= R1+R1. 4. Slide back R11 in series with Rid and R22 in parallel with the load RL. 5. This way you form circuit-A as shown in Fig. 6(b). Rof Via + Rs Via Rid - + V1 - ro μV1 Voa RL (R2+ R1) Roa Ria (R1 || R2) OR Via Ria + Rs Via Rid - + V1 - ro μV1 Voa RL (R2+ R1) Roa (R1 || R2) (b) Fig. 6(b): Circuit-A Apply a test voltage Via and determine Voa as follows: By VDR (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑉𝑜 = 𝜇𝑉 𝑟𝑜 + (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 1 Also, by VDR 𝑅𝑖𝑑 𝑉1 = 𝑉 𝑅𝑖𝑑 + 𝑅𝑠 + (𝑅1 ∥ 𝑅2 ) 𝑖𝑎 Substituting (2) in (1) results in: (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 𝑉𝑜𝑎 = 𝜇 𝑉 𝑟𝑜 + (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 + 𝑅𝑠 + (𝑅1 ∥ 𝑅2 ) 𝑖𝑎 𝑉𝑜𝑎 (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 ⇒ ≡𝐴=𝜇 𝑉𝑖𝑎 𝑟𝑜 + (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 + 𝑅𝑠 + (𝑅1 ∥ 𝑅2 ) 6. To find β, open circuit port-1 and apply test voltage Vt. Find the open circuit feedback voltage Vf from the circuit shown in Fig. 6 (c) as follows: By VDR 𝑉𝑓 𝑅1 𝛽≡ = 𝑉𝑡 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 Note that both A and β are positive such that their multiplication will be positive. Hence the feedback is negative. + Vf - R1 R2 + Vt - Vt Fig. 6(c): Circuit-β 7. Use the closed loop gain formula: 𝑉𝑜 𝐴 𝐴𝑓 ≡ = = 𝑉𝑠 1 + 𝐴𝛽 (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 𝑟𝑜 + (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 + 𝑅𝑠 + (𝑅1 ∥ 𝑅2 ) (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 𝑅1 1+𝜇 𝑅 𝑟𝑜 + (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 + 𝑅𝑠 + (𝑅1 ∥ 𝑅2 ) 1 + 𝑅2 𝜇 Example 2: Assume the op amp used to realize the circuit of Fig. 5 has open loop gain of 104 , input resistance of 1MΩ and output resistance of 0.1kΩ. Also assume Rs=1kΩ, RL=10kΩ, R2=9kΩ and R1=1kΩ. Find A, β, and the non-inverting amplifier gain. Solution: (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 𝐴=𝜇 𝑟𝑜 + (𝑅1 + 𝑅2 ) ∥ 𝑅𝐿 𝑅𝑖𝑑 + 𝑅𝑠 + (𝑅1 ∥ 𝑅2 ) Use the value of resistor in Kilo-ohms (10) ∥ 10 1000 𝐴 = 104 = 9785𝑉/𝑉 0.1 + (10) ∥ (10) 1000 + 1 + 0.9 𝑅1 1 𝛽= = = 0.1 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 1 + 9 The closed loop gain is given by: Af=Vo/Vs=A/(1+Aβ)=9785/(1+9785x0.1)=9.999 Which is very close to the ideal gain=10.0V/V. Effect of the series-shunt topology on the input and output resistance of the amplifier * Consider the series-shunt feedback amplifier with circuit-A replaced by its model as shown in Fig. 7. It is assumed that circuit-A has input resistance of Ria, voltage gain of A and output resistance of Roa. Ro I1 + Vi - Vs - Vf + Ri AVi β Vo + Vo - A circuit + Vo - β circuit Fig. 7: The series-shunt amplifier decomposed as circuit-A and circuit-β (Fig. 8.8 a) * Now we want to determine the input (Rif) and output resistance (Rof) of the feedback amplifier. * The input resistance can be obtained as follows: 𝑉𝑠 𝑉𝑠 𝑅𝑖𝑓 ≡ = 𝐼𝑖 𝑉𝑖 /𝑅𝑖 𝑉𝑠 𝑉𝑖 + 𝛽𝑉𝑜 𝑉𝑖 + 𝛽𝐴𝑉𝑖 = 𝑅𝑖 = 𝑅𝑖 = 𝑅𝑖 𝑉𝑖 𝑉𝑖 𝑉𝑖 ⇒ 𝑅𝑖𝑓 = 𝑅𝑖 (1 + 𝐴𝛽) This means the feedback increase the input resistance by the factor of (1+Aβ). Originally, the resistance is expected to increase as the feedback signal is mixed in series at the input port. * To find the output resistance, apply Thevenin theorem as follows: First, short circuit Vs, then apply voltage test at the output port as shown in Fig. 8. Ro - Vf + + Vi - Ri AVi β Vo + Vo - A circuit It Vt β circuit Fig. 8: Circuit to calculate Rof 𝑉𝑠 = 0 ⇒ 𝑉𝑖 = −𝛽𝑉𝑜 = −𝛽𝑉𝑡 By ohm’s law: 𝐼𝑡 = 𝑉𝑡 − 𝐴𝑉𝑖 𝑉𝑡 − (−𝐴𝛽𝑉𝑡 ) 1 + 𝐴𝛽 = = 𝑉𝑡 𝑅𝑜 𝑅𝑜 𝑅𝑜 𝑉𝑡 𝑅𝑜 = 𝐼𝑡 1 + 𝐴𝛽 This means the series-shunt feedback reduces the output resistance by the factor of (1+Aβ). This is logical connecting the feedback network in parallel with the basic amplifier reduces the output resistance. * In summary, to find the input and output resistance of feedback amplifier follow these steps: 1. Find the input and output resistance of circuit-A including Rs and RL. 𝑅𝑜𝑎 2. Use 𝑅𝑖𝑓 = 𝑅𝑖𝑎 (1 + 𝐴𝛽) and 𝑅𝑜𝑓 = 1+𝐴𝛽 which include Rs and RL effects. ⇒ 𝑅𝑜𝑓 ≡ 3. Find the actual input resistance Rin and output resistance Rout by excluding Rs and RL as follows: 1 𝑅𝑖𝑛 = 𝑅𝑖𝑓 − 𝑅𝑠 and 𝑅𝑜𝑢𝑡 = 1 1 − 𝑅𝑜𝑓 𝑅𝐿 Example 2: For the circuit of example 1, find the closed loop amplifier input resistance and output resistance. The input resistance can be calculated as follows: Using Fig. 6(b), 𝑅𝑖𝑎 = 𝑅𝑠 + 𝑅𝑖𝑑 + 𝑅1 ∥ 𝑅2 = (1 + 1000 + 0.9)𝑘𝛺 = 1001.9𝑘𝛺 ⇒ 𝑅𝑖𝑓 = 𝑅𝑖𝑎 (1 + 𝐴𝛽) = 1001.9𝑘(1 + 9785(0.091) ≈ 893.1𝑀𝛺 ⇒ 𝑅𝑖𝑛 = 𝑅𝑖𝑓 − 𝑅𝑠 = 893𝑀𝛺 − 1𝑘𝛺 ≈ 893𝑀𝛺 The output resistance can be determined as follows: Use Fig. 6(b) to find Roa. First, short the input Via. 𝑉𝑖𝑎 = 0 ⇒ 𝑉1 = 0 ⇒ 𝑅𝑜𝑎 = 𝑟𝑜 ∥ 𝑅𝐿 ∥ (𝑅2 + 𝑅1 ) ≈ 98𝛺 𝑅𝑜𝑎 98 ⇒ 𝑅𝑜𝑓 = = = 0.11𝛺 1 + 𝐴𝛽 891.4 1 1 ⇒ 𝑅𝑜𝑢𝑡 = = ≈ 0.11𝛺 1 1 9.09 − 0.0001 𝑅𝑜𝑓 − 𝑅𝐿 Extremely small output resistance less than 1Ω!