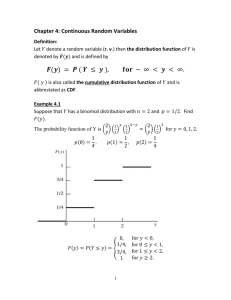
Spring 2025 - INDENG 172 Probability and Risk Analysis for Engineers IEOR UC Berkeley Daniel Pirutinsky, Runhan Xie, William Yan February 7, 2025 This is the 3rd homework for INDENG 172. It is released on Friday February 7th at 3pm PT and is due Friday February 14th at 11:59pm PT. Late submissions are not accepted. The total score is 66 points, including 1 point for correctly matching all questions to the corresponding pages. We expect justified answers, just the correct results without any explanation won’t be awarded full credit. Exercise 1 (10 points) Let E, F , and G be events in a sample space S. Show that PpE|F q “ PpE|F GqPpG|F q ` PpE|F Gc qPpGc |F q Exercise 2 (5 points ˆ 5 = 25 points) Consider a scenario where a fair coin is flipped 10 times. Define the random variable X as the number of heads observed in these 10 flips. (a) Write the Probability Mass Function (PMF): Write the PMF of the binomial distribution for this scenario. Clearly define all parameters. (b) Graph the PMF: Plot the PMF of X for n “ 10 and p “ 0.5. Label the x-axis (number of heads) and y-axis (probability). (c) Calculate the Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) at X “ 4: Compute P pX ď 4q. Show all steps in your calculation, using either the binomial formula or a statistical table. (d) Graph the CDF: Plot the CDF of X for n “ 10 and p “ 0.5. Highlight the area corresponding to P pX ď 4q. 1 (e) Interpret the CDF Value: What does the value of P pX ď 4q represent in the context of this problem? Exercise 3 (10 points) Three 6-faces dice are rolled. Find the probabilities attached to the possible values that X can take on, where X is the sum of three dice. Exercise 4 (10 points) Five balls, numbered 1,2,3,4, and 5, are placed in an urn. Two balls are randomly selected from the five, and their numbers noted. Find the probability distribution for the following: (a) The largest of the two sample numbers (b) The sum of the two sampled numbers Exercise 5 (10 points) Persons entering a blood bank are such that 1 in 3 have type O+ blood and 1 in 15 have type O- blood. Consider three randomly selected donors for the blood bank. Let X denote the number of donors with type O+ blood and Y denote the number with type O- blood. Find the probability distributions for X and Y . Also find the probability distribution for X ` Y , the number of donors who have type O blood. (Round the final answer to four decimal places.) 2