Neutralization Reactions: Definition, Examples, and Applications
advertisement

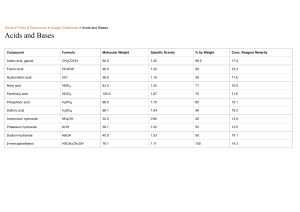
Neutralization Definition Neutralization is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form salt and water. The reaction typically involves the combination of hydrogen ions (H+) from the acid and hydroxide ions (OH-) from the base to form water (H2O). General Equation Acid + Base => Salt + Water Examples of Neutralization Reactions 1. Hydrochloric Acid + Sodium Hydroxide HCl + NaOH => NaCl + H2O 2. Sulfuric Acid + Potassium Hydroxide H2SO4 + 2KOH => K2SO4 + 2H2O 3. Nitric Acid + Calcium Hydroxide 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 => Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O Applications of Neutralization 1. Medicine - Antacids (like magnesium hydroxide) neutralize excess stomach acid. 2. Agriculture - Lime (Ca(OH)2) is added to acidic soil to neutralize acidity. 3. Water Treatment - Acids and bases are used to neutralize wastewater before disposal. 4. Personal Care - Toothpaste neutralizes acid in the mouth to prevent cavities.