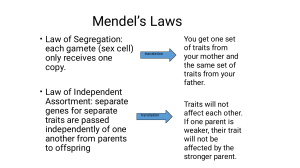
Genes and Variation What determines the phenotypes for a given trait? What is the difference between GENOTYPE and PHENOTYPE? Recall: GENOTYPE: Specific combination of alleles PHENOTYPE: Physical, physiological, and behavioral characteristics Genetics and the Evolutionar y Theory Natural selection acts on an organism’s characteristics, not on its alleles. Observe and record various traits among your classmates (or within your families) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ear lobe attachment (free or attached) Tongue rolling ability Hairline (widow's peak or straight) Eye color Height (approximate) These traits are determined by a single gene. SingleGene Traits They typically exhibit clear, distinct phenotypes (observable characteristics). Inheritance patterns often follow Mendelian genetics (dominant and recessive alleles). Ear lobe attachment: Example s of singlegene traits: •Free earlobes are often dominant, while attached earlobes are recessive. Tongue rolling: •The ability to roll the tongue is often a dominant trait. Widow's peak: •A widow's peak (a V-shaped hairline) is often a dominant trait. Eye color (in some simplified cases): •While eye color is complex, some simplified examples, like brown versus blue eyes, are often used to demonstrate single gene traits. Certain genetic disorders: •Cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia are examples of disorders caused by mutations in a single gene. These traits are influenced by multiple genes. Polygenic Traits They exhibit a wide range of phenotypes, often with continuous variation. Environmental factors can also play a significant role. Height: Example s of polygen ic traits: • Many genes contribute to a person's height, leading to a wide spectrum of heights within a population. Skin color: • Multiple genes determine the amount and type of melanin in the skin, resulting in a continuous range of skin tones. Eye color (complex versions): • While simple brown vs blue can be used to describe single gene traits, the vast amount of variation in eye color is due to multiple genes. Weight: • Numerous genes, along with environmental factors like diet and exercise, influence a person's weight. Intelligence: • Cognitive abilities are influenced by a complex interplay of many genes and environmental factors. Number of genes: Single-gene traits involve one gene; polygenic traits involve multiple genes. KEY DIFFERENCES : Phenotypic variation: Single-gene traits have distinct phenotypes; polygenic traits have continuous variation. Inheritance patterns: Single-gene traits often follow simple Mendelian patterns; polygenic traits have more complex inheritance patterns.