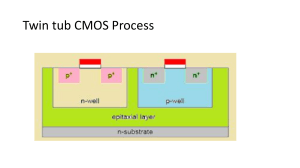
MIDDLE EAST TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY NORTHERN CYPRUS CAMPUS ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING PROGRAM Syllabus for: EEE 312 Electronics II (3-2) 4, Spring 2024-2025 Instructor’s Name Office Phone Dr. Bilal Ahmad Course Schedule: Lab Schedule: SZ-45 2955 e-mail bahmad@metu.edu.tr Wednesday 10:40 – 12:30 & Thursday 11:40 – 12:30 Lab assistants will do the scheduling. (TA Mr. Shame and Mr. Zeeshan) Instructor Office Office hours: Thursday 10:40 – 11:30 Main Text: Jaeger & Blalock, “Microelectronic Circuit Design”, McGraw-Hill Int. Ed. Auxiliary Text: DeMassa & Ciccone, “Digital Integrated Circuits”, Wiley. Rabaey, Chandrakasan, Nikolic, “Digital Integrated Circuits”, Pearson. Weste & Harris, “Integrated Circuit Design: A Crcts and Sytms Pers.”, Pearson. Sedra & Smith, “Microelectronic Circuits”, Oxford Univesity Press. Mano & Ciletti, “Digital Design”, Prentice Hall. Software: LTspice IV available for download at http://www.linear.com/designtools/software/ MATLAB/Simulink Catalog Content: Large signal transistor models. TTL, MOS and CMOS logic gates: Inverters, input and output circuits, NAND and NOR gates; static and dynamic analyses. Regenerative circuits: Astable, monostable, bistable multivibrators and Schmitt triggers. Introduction to VLSI. Static and dynamic memories: RAM, ROM, EPROM, EEPROM, etc. A/D and D/A converters. Course Objectives: Today’s electronic systems are mostly based on digital circuits, from cell phones to the most sophisticated computers. There has been a tremendous development in digital circuits over the past 3 decades, and there are a number of approaches for implementation of digital circuits. This course will give you a background on digital electronics. The course will cover various circuit families, including diode-transistor logic (DTL), transistor-transistor logic (TTL), emitter-coupled logic (ECL), NMOS, and CMOS logic. Design procedure and trade-offs in CMOS integrated circuits will also be investigated by analyzing some fundamental CMOS digital building blocks. Course Outline Introduction, Properties and Definitions of Digital ICs Pseudo-NMOS Logic; Diodes, Diode-Resistor-Logic (DRL); Introduction to CMOS; CMOS inverter BJTs; Bipolar Digital Circuits; Resistor-Transistor-Logic (RTL) CMOS Tri-state Buffer; Compound Gate Design; Diode-Transistor-Logic (DTL); Transistor-Transistor-Logic (TTL) CMOS Cascade Buffers; Pass Transistor Logic Transistor-Transistor-Logic (TTL); Emitter-Coupled Logic (ECL) Dynamic Gates; Regenerative Circuits; Schottky Transistor and STTL; Examples; Schmitt-Trigger; CMOS Sequential Building Blocks; Multivibrator Circuits; 555 Integrated Circuit (IC); MOSFETs; NMOS Digital Circuits 555 IC; CMOS ROM, SRAM & DRAM Memory Cells; Grading: Midterm 30% Final Exam 40% Lab 30% Policies/Comments: • Those who fail to get a satisfactory score from the laboratory portion will fail the class. This score will be 70.00%. • • • Those who fail to follow the rules of academic honesty will fail the class. All course work should be completed independently (including reports!). Attendance is highly recommended to do well in this class. You can discuss all course works with your study group or friend(s) but your submission must be your own, not a copy of someone else. If identical copies are found, all students who have submitted the identical copy will have zero for the related course works. Furthermore, any course work that is too much like the solution manual will also receive zero.