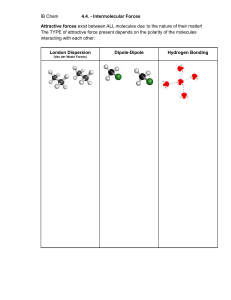
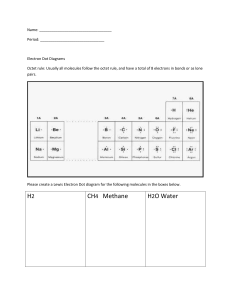
Senior High School Grade 11 – Physical Science 3RD GRADING EXAMINATION Name: _____________________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________________________ Score: _________________ Date: __________________ Test I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Read the following questions carefully and write the letter of your answer on the space provided before each item. 1.Which of the following is NOT an evidence of star formation? a. hydrogen b. helium c. infrared Radiation d. rocks 2. Which of the following is the sign that a protostar will transform into the next stage? a. When the it starts to spin faster b. When it starts to glow c. When Hydrogen nuclear fusion begins d. When it increases temperature igniting the Hydrogen 3. In this process there’s a buildup of a VERY heavy isotope, then as beta-decays occur, you march up in atomic number and produce heavy product. a. S Process c. Nuclear Fission b. R-Process d. Proton-Proton Reaction 4. Process that can produce elements up to #83 - Bismuth. a. Nuclear Fission b. R-Process c. S Process d. S Process 5. What do you call the relative ability of a bonded atom to attract shared electron pairs? a. Electron affinity b. Electronegativity c. Ionization energy d. Metallic property 6. From the given Lewis structure of NH3, how many nonbonding pair/s of electron are around the central atom? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 7. Which of the following IMFAs is considered as the weakest? a. H-bonding b. Ion-dipole c. Dipole-dipole d. London forces 8. The boiling point of water is greater than dihydrogen sulfide because of ______. a. Dipole-dipole bond b. H-bonding c. London dispersion d. Ion-dipole 9. Which of the following substances is miscible in hexane (C6H14)? a. Acetone (C3H6O) b. Vinegar (CH3COOH) c. Chloroform (CHCl3) d. Methanol (CH3OH) 10. Distillation separates two _______ by using different _____________. a. liquids, boiling points b. solids, particle size c. liquids, particle size d. gases, densities 11. Why are dispersion forces high in molecules with great number of electrons? a. The electron distribution of big molecules is easily polarized. b. The nucleus in the molecules has greater effective shielding effect. c. The electrons move freely around the nucleus resulting to greater energy. d. The electrons in the molecules can easily jump from one orbital to another. 12. What Intermolecular forces are present in CH4? a. London Dispersion force b. H-bonding c. Ion-dipole d. dipole-dipole 13. How does dipole-dipole interaction happen? a. Polar molecules shift electron density that gives rise to neutral substances. b. The electron distribution in the polar molecules is distorted that results to (-) and (+) poles. c. Polarization of big nonpolar molecules brings about the formation of permanent (+) and (-) charges. d. The (-) and (+) ends of one polar molecule align themselves to the (+)and (-) ends of another polar molecule and attract each other. 14. H-bonding forms when the substances involved are polar and have molecules with a. H-atoms attached to O, N, F. b. C-atoms attached to O, N, F. c. central atoms with O, N, F as attached atoms. d. unshared pair of electrons in the central atom. 15. The properties of matter seen in the macroscopic level influenced by intermolecular forces. a. bulk b. ionic c. covalent d. individual 16. The vapour pressure on top of the mountain is low so what will happen to the cooking time of an egg up there? a. The cooking time will be longer since the temperature of the water is higher. b. The cooking time will be shorter since the temperature of the water is higher. c. The cooking time will be longer since the temperature of the water is lower. d. The cooking time will be shorter since the temperature of the water is lower. 17. Which biomolecular group carries and passes on the hereditary information of the organism? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. nucleic acids d. proteins 18. Which is a good example of saturated fat? a. butter b. corn oil c. olive oil d. sunflower oil 19. Which nutrient group is used in the composition of waxes and responsible for insulation of some organisms? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. nucleic acids d. proteins 20. In which of the following groups are all polysaccharides? a. Sucrose, glucose and fructose b. Maltose, lactose and fructose c. Glycogen, sucrose and maltose d. Glycogen, cellulose and starch 21. Which of the following would NOT increase the rate of reaction? A. Increasing the temperature B. Adding catalyst C. Increasing the volume D. Increasing the concentrations 22. Suppose you dissolve Zinc (Zn) in Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and add more acid than usual. Then drop pieces of Zinc. What factor does NOT affect the rate of the reaction? A. Surface area of the Zinc B. Concentration of the reactant C. Temperature of the solution D. Amount of Hydrochloric acid 23. What conditions must be met in order for a chemical reaction to occur? A. Collision with proper orientation B. Sufficient activation energy C. Adding more reactant particles D. Both collision with proper orientation and sufficient energy 24. Why does a candle burn more rapidly when placed in an open jar than in air? What accounts for this reaction? A. Higher Oxygen Concentration B. Greater surface area of the jar C. Increasing the surrounding temperature D. Length of the candle 25. How does a catalyst work in speeding up a reaction? a. by lowering the activation energy or reaction. b. by giving them more energy. c. by making them more available. d. none of these. 26. Which factor/s help/s explain why so many collisions fail to produce products? Choose all that apply. a. Number of collisions c. Orientation b. Activation energy d. Energy released by reaction 27. How is catalyst different from a reactant? a. Adding more catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction. b. Adding more catalyst slows down the rate of reaction. c. The catalyst is not used up in the reaction. d. The catalyst increases the activation energy of the reaction. 28. Which of the following will lower the rate of reaction? a. Adding an enzyme to the reaction. b. Decreasing the temperature from 40oC to 10oC. c. Breaking a chunk of calcium up into smaller pieces. d. Increasing the amount of solute dissolved in solution. 29. It deals with the process that involves rearrangement of the molecular or ionic structure of a substance to form a new substance or product. a. chemical equilibrium c. chemical reaction b. chemical symbol d. stoichiometry 30. They are the reactants that are not used up when the reaction is finished. a. Excess Reagents c. Limiting Reagents b. Solute d. Solution 31. In the equation Mg+HCl→MgCl2+H2, how many molecules of hydrogen do we need to make hydrogen balanced? a. 3 b. 6 c. 2 d. 7 32. Which of the following equation below is balanced? a. Al+3O2→2Al2O3 c. 4Al+3O2→Al2O3 b. 4Al+O2→2Al2O3 d. 4Al+3O2→2Al2O3 33. Energy that comes from sources that will run out or will not be replenished in our lifetimes—or even in many, many lifetimes. a. kinetic b. non-renewable c. potential d. renewable 34. Which of the following is being described by this phrase, “It can be converted in form, but not created nor destroyed.” a. atom b. energy c. force d. matter 35. This source of energy is less of an environmental hazard compared to fossil fuels. a. batteries b. biomass c. geothermal d. hydrothermal 36. Which is an advantage of solar energy? a. abundant b. amount of space c. expensive d. rare metals 37. It is a granulated powder that can be used in scrubbing stains. a. Sodium percarbonate b. Alcohol Ethoxylate c. Phenols d. Ammonia 38. Mixing chlorine bleach with ammonia or vinegar can release what kind of poisonous gas? a. carbon b. chloramines c. potassium d. sodium 39. This ingredient balanced the acidity or base of a certain product. What is this ingredient? a. dye b. fragrance c. pH adjuster d. solvents 40. What substance when added to a cleaning product makes it stable and safe for a longer period? a. enzymes b. foam enhancer c. pH adjuster d. preservative