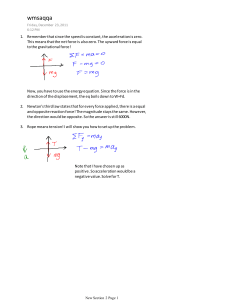
Forces worksheet 1. What effects does force have on an object? 2. What is the unit of a force? 3. What is the difference between a balanced force and an unbalanced force? 4. A box is pulled along a wooden floor with a force of 300N. An initial resistive force acts in the opposite direction to the box with a magnitude of 135N. 4.1. What is the name of the resistive force 4.2. Draw a force diagram to show these two forces acting on the block. Label the arrows with the size of the force. 4.3. What is the effect of the forces on the motion of the box? 4.4. The box is then pulled with the same force of 300N but this time on a carpet. Explain what will happen to the resistive force on the box. 5. Dennis goes skydiving. He falls for two minutes before the parachute is opened. Just before the parachute is pulled Dennis is traveling at a constant speed. Dennis has a weight of 750N. 5.1. What is the name of the resistive force acting against Dennis? 5.2. What is the magnitude of this force? Dennis pulls the cord to release the parachute. This produces a resistive force of 4000N. 5.3. Explain why there is a big increase in the resistive force. 5.4. How does Dennis’s Speed change when he opens the parachute? 5.5. Sketch and label a graph to show Dennis’s motion. 6. Net force and acceleration (F = ma) 6.1. How much force is needed to accelerate a 66kg skier at 2m.s-2? 6.2. What is the acceleration of a 50kg object pushed with a force of 500N? 6.3. A bowling ball rolled with a force of 15N accelerates at a rate of 3m.s -2. A second ball rolled with the same force accelerates at 4m.s-2. What is the mass of the two balls? 6.4. A 5 kg block is pulled across a table by a horizontal force of 40 N with a frictional force of 8 N opposing the motion. Calculate the acceleration of the object. 6.5. If a 60 kg person on a 15 kg sled is pushed with a force of 300 N, what will be person’s acceleration? 6.6. A student is pushing a 50Kg cart, with a force of 600N. Another student measures the speed of the cart, and finds that the cart is only accelerating at 3m.s-2. How much friction must be acting on the cart? 6.7. An object of mass 30 kg is falling in air and experiences a force due to air resistance of 50N 6.7.1. Determine the net force acting on the object 6.7.2. Calculate the acceleration of the object. 7. Gravity 7.1. Define the term gravitational force 7.2. Tabulate two difference between mass and weight 7.3. Weight is a vector quantity. What does this mean? 7.4. What force works in equilibrium with weight 7.5. Using the formula Fg = mg calculate the following (g = 9.8m.s-2 on Earth) 7.5.1. A bowling ball has a mass of 7.37kg. What is its weight? 7.5.2. A box has a weight of 75N, what is its mass? 7.5.3. A 80kg man has a weight of 336.4N on Mars. Calculate the gravitational field strength on Mars 7.5.4. A man has a weight of 800N on Earth. 7.5.4.1. What happens to the astronauts mass on the moon? 7.5.4.2. Calculate his weight on the moon if the moon has a gravitational field strength on 1.63m.s-2 7.5.4.3. The astronaut travels to Mars where her weight becomes 266N. Calculate the gravitational field strength on the surface of Mars. 8. Matilda and Ravi carried out an experiment with springs. They put different masses on the spring and measured the length of the spring each time. The table shows some of their results. Mass ( ) Weight / force ( ) Length of spring ( ) Extension ( ) 0 0 10 0 20 2 14 4 40 4 18 8 60 22 80 26 100 30 8.1. 8.2. 8.3. 8.4. 8.5. 8.6. Fill in the missing units in the table Fill in the missing weights in the table Fill in the missing extensions in the table Draw a graph of the weight vs extension of the spring. Calculate the k-constant of the spring using your graph Provide a conclusion for this experiment