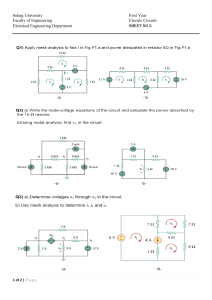
IS200MVRPH1A - Power Distribution Board worldofcontrols.com/IS200MVRPH1A SPECIFICATIONS Part Number: IS200MVRPH1A Manufacturer: General Electric Series: Mark VIe Function: Power Distribution Board Availability: In Stock Stab-on Connector: X1 Vertical Pin Header Connectors: Two 7-pin and one 9-pin Female Plugs: 2-position and 6-position Vertical Pin Male Multipin I/O Connector: One Repair: 3-5 Days Product type: PCB Manual: GEH-6721 Country of Manufacture: United States (USA) Functional Description IS200MVRPH1A is a power distribution board designed and developed by GE. It is a part of Mark VIe control system. The Mark VIe control was created to serve a wide range of control and protection applications, including steam and gas turbines, as well as power generation balance of plant equipment. The control system is fully programmable. Factory software automation tools maintain application software by selecting proven GE control and protection algorithms and integrating them with the I/O, sequencing, and displays for each application. There are several block libraries with general-purpose blocks, math blocks, macros (user blocks), and application-specific blocks. Changes to the application software can be made while the system is running and downloaded to the controller(s) without rebooting the main processors. In redundant control systems, the application software in each controller is identical and appears to maintenance personnel as a single program. IS200MVRPH1A Features The board incorporates several features and components. Here is an expanded explanation of its features: Transformer Component: The board consists of a single transformer component. This component is responsible for transforming electrical energy from one circuit to another. 1/6 Heat Sink: The board includes a heat sink, which helps dissipate heat generated by electronic components, ensuring proper temperature regulation and preventing overheating. High Voltage Capacitor: The board features a high voltage capacitor. Capacitors store and release electrical energy as needed and can handle higher voltage levels. X1 Stab-on Connector: The board is equipped with an X1 stab-on connector. This type of connector allows for secure and reliable electrical connections, typically used for power or signal transmission. Vertical Pin Header Connectors: The component has three vertical pin header connectors: two 7-pin connectors and one 9-pin connector. These connectors provide attachment points for other devices or components, enabling electrical connections. Vertical Pin Male Multipin I/O Connector: The board includes a vertical pin male multipin I/O connector. This connector enables input and output connections, allowing the board to interact with external devices or systems. Female Plugs: The board features two female plugs: one 2-position plug and one 6position plug. These plugs provide connectivity options for external devices or cables, enabling easy and secure connections. Manufacturer's Logo and Reference Designators: The board bears the manufacturer's logo, representing the company responsible for designing and producing the board. It also includes reference designators, which are alphanumeric codes or labels used to identify specific components or locations on the board, aiding in troubleshooting and assembly processes. Characteristics The PDM (Power Distribution Module) system possesses several notable characteristics. Here is an expanded explanation of these characteristics: Core Distribution System: The PDM system is divided into two major categories, with the first being the core distribution system. The core distribution system consists of essential components that are responsible for managing and distributing power within a cabinet or a series of cabinets. These core pieces have the capability to connect to a PPDA (Power Distribution Accessory) I/O pack, enabling system feedback and monitoring of power-related data. Branch Circuit Elements: The second major category of the PDM system comprises the branch circuit elements. The branch circuit elements function to distribute the power output generated by the core distribution system to individual circuits within the cabinets. 2/6 Unlike the core components, the branch circuits do not contribute to the PPDA system feedback. Instead, they have their own set of feedback mechanisms or monitoring systems in place. Selective Utilization: It is important to note that not all of the PDM's core components and branch circuits are expected to be utilized in every system. The specific configuration and utilization of the PDM system may vary based on the specific requirements and power distribution needs of a given application or installation. System PDM Features The Mark VIe control is intended to run on a flexible, modular array of power sources. In many redundant combinations, the power distribution modules (PDM) support 115/230 V ac, 24 and 125 V dc power sources. The applied power is converted to 28 V dc to power the I/O packs. The controllers can run on 28 V dc, direct ac, or direct 24 V dc battery power. The PDM system is divided into two major categories: the core distribution system and the branch circuit elements. The core pieces all have the capability of connecting to a PPDA I/O pack for system feedback. They manage the primary power for a cabinet or series of cabinets. The branch circuit elements distribute the core output to individual circuits in the cabinets. They do not contribute to the PPDA system feedback. Branch circuits have their own set of feedback mechanisms. It is not expected that all of the PDM's core components and branch circuits will be used on every system. The power distribution capabilities of the Mark VIe system are designed to accommodate a versatile range of power sources, offering flexibility to adapt to various industrial setups. These power sources can be configured in different combinations, including 24 V DC, 125 V DC, and 120/240 V AC sources, based on the specific requirements of the application. The Mark VIe power distribution hardware is carefully configured to suit the needs of the system and the equipment it controls. Depending on the installation and available power sources, the hardware may be tailored to utilize the necessary power inputs while disregarding unused ones. This ensures efficient utilization of the available resources while meeting the demands of the system. One of the vital functions of the power distribution hardware is the conversion of input power to a standardized 28 V DC. This 28 V DC supply serves as the primary source of power for operating the control electronics within the Mark VIe system. By converting the diverse input power into a uniform 28 V DC output, the system achieves a consistent and stable power supply, promoting smooth and reliable operation. 3/6 Furthermore, the Mark VIe system efficiently distributes the remaining power to fulfill specific requirements, such as powering various Input/Output (I/O) signals. This distribution process ensures that the appropriate power is allocated to the relevant components, enabling seamless communication and functionality within the system. Core Distribution In the realm of Power Distribution Modules (PDM), the core distribution circuit stands as a pivotal component responsible for the primary management of power within a cabinet or a series of interconnected cabinets. It serves as the central hub for controlling and regulating the power flow to various critical components and devices within a system. Here, we delve into the intricate workings and features of the core distribution circuit. Power Sources and Input: At the heart of the core distribution circuit lies a corresponding module or board that acts as the recipient of power from one or more sources. This input typically comprises alternating current (AC) power, which forms the basis for the subsequent power distribution process. The core distribution circuit is equipped to accept power from multiple AC sources, ensuring redundancy and reliability. Control Electronics and Terminal Boards: One of the primary functions of the core distribution circuit is to provide power to the control electronics within the system. To achieve this, power is meticulously distributed to terminal boards, which serve as intermediaries between the core circuit and the various electronic components. These terminal boards play a critical role in routing power to the right destinations, ensuring the smooth operation of control systems and devices. Bulk Power Supplies: Integral to the core distribution circuit are the bulk power supplies. These specialized power supplies are fundamental components within the core PDM system. Their primary function is to convert the incoming AC power into a stable and standardized 28-volt direct current (DC) power output. This output is vital for powering a wide array of electronic components and devices, guaranteeing their proper functionality. Monitoring and Distribution: Within the core distribution circuit, one or more 28-volt output boards are strategically positioned. These boards serve as vigilant overseers of the 28-volt power distribution process. They monitor the power levels and ensure that the precise amount of power required by each component is delivered efficiently. This meticulous monitoring and distribution process minimize power wastage and enhance the overall energy efficiency of the system. Interconnectivity and Feedback: The core distribution circuit can also be interconnected with other core boards within the system. This interconnection is often facilitated by the use of ribbon cables, which link various core boards to the one housing the Power and Data Acquisition (PPDA) Input/Output (I/O) pack. This interconnected setup allows for seamless communication and coordination between different components, further optimizing system performance. 4/6 Complete Monitoring and System Feedback: One remarkable feature that sets the core distribution circuit apart from traditional power distribution methods is its capacity for comprehensive monitoring and system feedback. Unlike conventional systems, which may lack real-time insights into power utilization, the core PDM system continuously monitors power levels, ensuring that each component receives the necessary supply. This proactive approach to power management not only enhances system reliability but also facilitates informed decision-making regarding maintenance and upgrades. Branch Circuits Branch circuits play a crucial role in the overall power distribution within the cabinets. These circuits are responsible for dividing the power output from the Power Distribution Module (PDM) core into individual alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) circuits. The purpose of these branch circuits is to facilitate the efficient and controlled distribution of power to various components and subsystems within the system. It is important to note that branch circuits are not directly connected to PPDA Input/Output (I/O) pack, as their primary function is to provide power distribution rather than system feedback. Their main focus is on efficiently distributing power, ensuring that each component or subsystem receives the necessary power supply for its operation. One of the key aspects of branch circuits is the ability to provide power status feedback signals to the control system. This feedback allows the control system to monitor and assess the power status of individual elements or devices connected to the branch circuits. By receiving these feedback signals, the control system can detect any power-related issues or anomalies, enabling timely intervention or troubleshooting. In most cases, branch circuit elements are typically single circuit boards that handle specific power distribution functions. These circuit boards are dedicated to individual circuits within the system, ensuring precise control and management of power distribution. By utilizing dedicated circuit boards, the system can effectively allocate power to different components or subsystems, optimizing the overall performance and reliability. WOC is happy to assist you with any of your GE requirements. Please contact us by phone or email for pricing and availability on any parts and repairs. FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What is IS200MVRPH1A? It is a power distribution board designed and developed by GE. What type of connectors does the component have? The component has three vertical pin header connectors: two 7-pin and one 9-pin. 5/6 What kind of male connector is on the board? The board has one vertical pin male multipin I/O connector. What type of female plugs does the board include? The board includes two female plugs, one 2-position and one 6-position. What is the Mark VIe control system? The Mark VIe control system is a fully programmable system created by GE to serve a wide range of control and protection applications, including steam and gas turbines, as well as power generation balance of plant equipment. Can changes be made to the application software while the system is running? Yes, changes to the application software can be made while the system is running and downloaded to the controller(s) without rebooting the main processors. What is the function of the branch circuit elements in the PDM system? The branch circuit elements distribute the core output to individual circuits in the cabinets. They do not contribute to the PPDA system feedback. 6/6