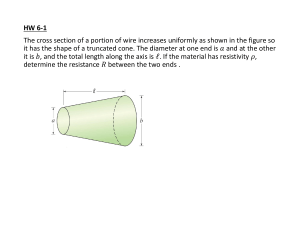
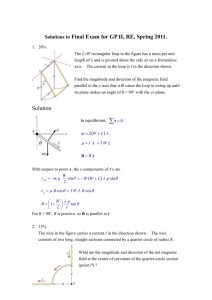
Azadi APS & C, Sargodha. PHYSICS Retest HSSC–II SECTION – A (Marks 17) Time allowed: 25 Minutes Section – A is compulsory. All parts of this section are to be answered on this page and handed over to the Centre Superintendent. Deleting/overwriting is not allowed. Do not use lead pencil. Q.1 Fill the relevant bubble for each part. Each part carries one mark. (1) Two charges q1 and q2 are placed in vacuum at a distance d and force between themis F. If a medium of relative permittivity 4 is introduced between them then new force will be: F F A. ⃝ B. ⃝ 4 2 C. (2) (3) (4) 2F ⃝ D. 4F Three capacitors of 4F each are connected in such a way that net capacitance oftheir combination is 6F. It is possible if: A. All the three in series B. All the three in parallel C. Two in series and one in parallel D. Two in parallel and one in series Slope of I-V graph of a resistor is numerically equal to: A. C. Conductivity Resistance ⃝ ⃝ B. D. Conductance Resistivity Which one of the following is correct for an open circuit? A. B. Vt = 0 Vt < E ⃝ C. (5) (6) Vt = E ⃝ D. Vt = E – Ir ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ Magnetic flux will be maximum when: A. Magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane area ⃝ B. Magnetic field lies parallel to the plane area ⃝ C. Area is held at an angle of 45o ⃝ D. Magnetic flux density is perpendicular to area vector of the surface ⃝ A proton is moving along the axis of a solenoid carrying a current. The magneticforce on proton will be: A. Radially inward ⃝ B. Radially outward ⃝ C. Zero ⃝ D. Parallel to axis of solenoid ⃝ (7) A steady current is passing through a coil, magnitude of self- induced emf in it,will be: A. zero ⃝ B. maximum ⃝ I I C. =L ⃝ D. = L ⃝ t t (8) At high frequency in a capacitive circuit, the current will be: (9) Large Small A. B. ⃝ Zero Infinite C. D. ⃝ The peak value of A.C source is 20 A, its rms value will be: A. 14.1 A B. 10 A ⃝ C. 20 A D. 28.2 A ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ (10) The materials in which disordered structure of liquid is frozen are: A. Amorphous B. Crystalline ⃝ C. Polycrystalline D. Quartz ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ (11) The temperature below which the resistivity of a superconductor falls to zero iscalled: A. Absolute temperature ⃝ B. Curie temperature ⃝ C. Limiting temperature ⃝ D. Critical temperature ⃝ (12) In a pure inductance circuit the current: A. Lags the voltage by 90° B. Leads the voltage by 90° C. Both have same values D. Lags the voltage by pie/4° ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ Unit of electric field intensity is: A. V/m B. NC C. None D. Both a and c ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ (13) (14) (15) (16) (17) Unit of Resistivity is: A. Ohm/meter meter/Ohm C. Tesla is the unit of: A. magnetic flux B. electric flux C. magnetic field D. Both a and c ⃝ ⃝ B. D. Ohm-meter Ohm ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ Henry is a unit equal to ________: A. J/A2 B. A2/J C. A/ Wb D. Both b and c ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ EKG is used to diagnose: A. heart condition B. lung condition C. liver condition D. Both b and c ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ ⃝ Time allowed: 2.35 hours Total Marks: 68 Note: Answer all parts from Section ‘B’ and all questions from Section ‘C’ on the E-sheet. Write your answers on the allotted/given spaces. SECTION – B (Marks 42) Q.2 Attempt all parts from the following. All parts carry equal marks. i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. x. xi. (14×3=42) Define electron volt (eV). Derive its relation 1000J? OR A unit volume metal rod having an energy density of 0.4kJ undergoes a stain of 4x10-4N/m2. What will be its Young’s modulus? Compare the effects of temperature increase on thermistor and copper wire resistivity. OR Differentiate ‘curie temperature’ and ‘critical temperature’ along with an example. A galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter and a voltmeter by connecting resistance with it. What are the basic differences in their construction from a galvanometer? OR Define stiffness & Ductility. A rectangular coil of 100 turns and area 500 x 10 -4 m2 carrying 2 A current is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 10T. Find the maximum torque applied on the coil. OR A 2cm diameter ring is moved from the uniform magnetic field of 10T in 0.1s. What is the magnitude of induced emf in the ring if the normal ring is parallel to the magnetic field at all times? Define the mutual inductance of two coils. Write its formula. Also, define its SI unit. OR What is hysteresis loss? Why are induction heaters more efficient than conventional gas heaters? OR How does stator help rotor to rotate in AC motor? What is power dissipation value in capacitor and inductor in AC circuits?Elaborate your answer OR A 220V, 50Hz A.C. supply is applied to series combination of a 2.5Ω, 6mH inductor and a 6.5μF capacitor. Calculate (i) the reactance of the inductor (ii) the reactance of the capacitor (iii) the impedance of the circuit. What are brittle and ductile materials? Draw a stress-strain curve to differentiatebetween brittle and ductile materials. OR What will be the capacitance of the capacitor if the source of 400Hz frequency has a max emf of 20V & current of 1.8A? What will the length of the wire be if the force of 10N is applied across the area of the wire is 2x10-6 m2 & Young’s modulus is 2x1011 m2 causing an increase in the length of the wire is 2x105 m? OR Differentiate hard and soft magnetic materials? What will be distance b/w two charges of 2nC & 4nC if both possess P.E of 1.028x10 -6J OR For a common base configuration of n.p.n transistor, collector current is greaterthan base current. Why? What is meant by permittivity & permeability? OR At what distance from a charge of 2 micro C if it produce an E.F of 1.8N/C? xii. xiii. xiv. On what principle seismometer work? OR What is a choke, describe its function. A metallic wire has a resistance of 19m(ohm), a length L equal to 30cm, and a diameter d equal to 1mm. what will be its resistivity OR What enables a floating bullet train to achieve a speed of 600 km/hour, how? Mention the properties of ferromagnetic materials. OR Find the current in each loop of the circuit given below: SECTION – C (Marks 26) Note: Attempt all questions. Marks of each question are given within brackets. Q.3 Q.4 Q.5 (26) Define electric potential energy and potential due to point charge. Find an expression for electric potential energy at a distance from a charge. (1+3+3) OR State and explain the Hysteresis loop. What is a Potentiometer? Derive its formula to calculate the unknown power supply. (1+2+4) OR State Ampere’s law. Derive the formula for the magnetic field inside the current-carrying solenoid using this law. (1+1+1+4) Describe AC terminologies with a graph. (6) OR Explain the Mechanical properties of solids in detail. Q.6 Explain the principle of AC generator through graph & also drive mathematical expression of A.C. of calculation emf at any instant of the time. (1+2+3) OR What are the R.L.C series circuit’s inductive reactance, capacitive reactance, and current of the 50 Hz frequency of AC source of 240Vrms having 50-ohm resistor, 0.20 H inductor & 150 micro F capacitor? (2+2+2)