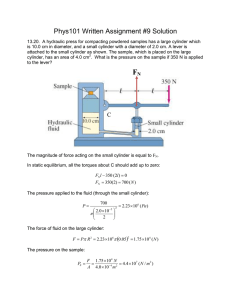
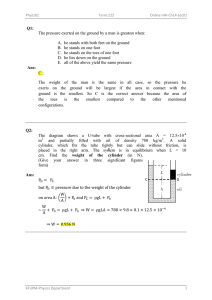
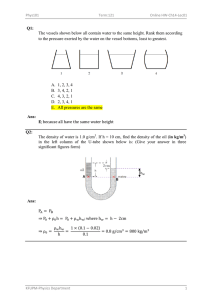
German University in Cairo Physics Department PHYS 101 Winter 2020 Dr. Amr Aboshousha Dr. Nermeen Serag Sheet 10: Elasticity and Fluid Mechanics Part B: Fluid Mechanics P1. Water and then oil (Which don’t mix) are poured into a U- shaped tube, open at both ends. They come to equilibrium as shown in the figure, What is the density of the oil? [Hint: Pressure at points a and b are equal. Why?]. 𝑃𝑎 = 𝑃𝑏 (𝜌𝑔𝐻)𝑜𝑖𝑙 + 𝑃𝑜 = (𝜌𝑔(𝐻 − ℎ))𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 + 𝑃𝑜 𝐻 = 27.2𝑐𝑚 ; ℎ = 8.62𝑐𝑚 𝜌𝑜𝑖𝑙 = 𝜌𝑜𝑖𝑙 = (𝜌𝑔(𝐻 − ℎ))𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 (𝑔𝐻)𝑜𝑖𝑙 1000(0.27 − 8.62) = 683.82𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 0.272 P2. (I) The maximum gauge pressure in a hydraulic lift is 17.0atm. What is the largest- size vehicle (kg) it can lift if the diameter of the output line is 22.5cm?. 𝑃𝑔 = 17𝑎𝑡𝑚 𝑟= 0.225 2 1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 1.013 × 105 𝑁/𝑚2 = 0.113𝑚 𝑃= 𝐹 𝑚𝑔 = 𝐴 𝜋 𝑟2 𝑃𝜋 𝑟 2 𝑚= 𝑔 17 × 1.013 × 105 𝜋 0.1132 𝑚= = 7049.2𝑘𝑔 9.8 1 PHYS101 Winter 20 (II) The gauge pressure in each of the four tires of an automobile is 240kPa. If each tire has a “footprint” of 220𝑐𝑚2 , estimate the mass of the car. 𝑃𝑔 = 240 × 103 𝑝𝑎 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑡𝑖𝑟𝑒 𝐴 = 220 × 10−4 𝑚2 𝑃= 𝐹𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑡𝑖𝑟𝑒 𝑚𝑔 = 𝐴 𝐴 𝑚 𝑃𝐴 = 4 𝑔 3 𝑚 240 × 10 × 220 × 10−4 = 4 9.8 𝑚 = 538.775 × 4 = 2155.1𝑘𝑔 P3. A hydraulic press for compacting powdered samples has a large cylinder which is 10.0 cm in diameter, and a small cylinder with a diameter of 2.0 cm as shown in the Figure. A lever is attached to the small cylinder as shown. The sample, which is placed on the large cylinder, has an area of 4.0 𝑐𝑚2.What is the pressure on the sample if F = 350 N is applied to the lever? (𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑙𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 𝑐𝑦𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟)𝑅 = 0.05𝑚 𝐴𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 = 4 × 10−4 𝑚2 Psample = ? (𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑐𝑦𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟)𝑟 = 0.01𝑚 at point C Σ 𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑞𝑢𝑒 = 0 𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑐𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑘𝑤𝑖𝑠𝑒 = 𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑘𝑤𝑖𝑠𝑒 350 × 2𝑙 = 𝑓 × 𝑙 𝑓 = 2 × 350 = 700𝑁 For the hydraulic Piston: 𝐹 𝑓 = 𝐴 𝑎 𝐴 𝜋𝑅 2 𝑅2 F=𝑓 =𝑓 2 =𝑓 2 𝑎 𝜋𝑟 𝑟 F = 700 × 0.052 = 17500𝑁 0.012 2 PHYS101 Winter 20 Psample = 𝑃𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 = 𝐹 𝐴𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 17500 = 43.75 × 106 𝑁/𝑚2 4 × 10−4 P4. A 15-cm radius air duct is used to replenish the air of a room 8.2 × 5 × 3.5 𝑚 every 12 min. How fast does the air flow in the duct? . 𝑟 = 0.15 𝑚 𝑉 = 8.2 × 5 × 3.5 𝑚3 𝑡 = 12 × 60 = 720 𝑠𝑒𝑐 𝑣 =? 𝑄 = 𝐴𝑣 𝑉 = 𝐴𝑣 𝑡 8.2 × 5 × 3.5 = 𝜋 × 0.152 𝑣 12 × 60 8.2 × 5 × 3.5 𝑣= = 2.82 𝑚/𝑠 12 × 60 × 𝜋 × 0.152 P5. How fast does water flow from a hole at the bottom of a very wide 5.3m deep storage tank filled with water? Ignore viscosity. ℎ = 5.3𝑚 𝑣 =? 𝑣 = √2𝑔ℎ 𝑣 = √2 × 9.8 × 5.3 𝑣 = 10.2 𝑚/𝑠 3 PHYS101 Winter 20 P6. Suppose the top surface of the vessel in the figure is subjected to an external gauge pressure 𝑃2 (a) Derive a formula for the speed 𝑦1 , at which the liquid flows from the opening at the bottom into atmospheric pressure, 𝑃0 . Assume the velocity of the liquid surface 𝑉2, is approximately zero. b) If 𝑃2 = 0.85 atm and 𝑦2 − 𝑦1 = 2.4 m, determine 𝑣1 for water. ℎ2 − ℎ1 = 2.4𝑚 𝑣2 = 0 𝑃2 = 0.85 × 1.013 × 105 𝑝𝑎 𝜌𝑤 = 1000𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 Using Bernoulli’s Equation 1 1 𝑃1 + 𝜌𝑔ℎ1 + 𝜌𝑣12 = 𝑃2 + 𝜌𝑔ℎ2 + 𝜌𝑣22 2 2 1 𝑃0 + 𝜌𝑣12 = 𝑃2 + 𝑃0 + 𝜌𝑔(ℎ2 − ℎ1 ) 2 2(𝑃2 + 𝜌𝑔(ℎ2 − ℎ1 )) 𝑣= √ 𝜌 𝑣= √ 2(0.85 × 1.013 × 105 + 1000 × 9.8 × 2.4) = 14.81𝑚/𝑠 1000 4 PHYS101 Winter 20