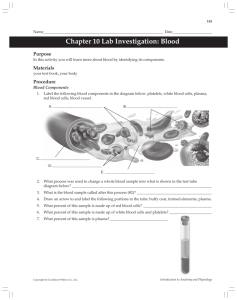
Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative Approach By Michael McKinley, Valerie O'Loughlin and Theresa Bidle 1.A patient on dialysis has a low RBC count. What hormone, secreted by the kidney, can be assumed to be deficient? Explain your answer – what is the function of the chosen hormone? The hormone, Erythropoietin (EPO), is deficient. EPO is the hormone because it helps make red blood cells, in other words, it stimulates production and helps maintain RBCs. (Mckinley 709). Source:MCKINLEY, MICHAEL.Anatomy and Physiology an Integrative Approach. MCGRAW-HILL US HIGHER ED, 2021. 2.An elderly man has been receiving weekly injections of vitamin B12 ever since he nearly had all of his stomach removed 6 months previously. Why is he receiving the vitamin injections? What would be the result (condition) if he refuses the injections? He is receiving the vitamin B12 injections because his body is not able to absorb it, and his body is not secreting glycoprotein to protect the vitamin B12. The result condition would be pernicious anemia (Mckinley 715). Source:MCKINLEY, MICHAEL.Anatomy and Physiology an Integrative Approach. MCGRAW-HILL US HIGHER ED, 2021. 3.John, a novice smoker is trying to impress his buddies by smoking two packs a day – inhaling every drag. What do you think will happen to his reticulocyte count? Explain your reasoning. (2 points) The reticulocyte count will increase because smoking causes blood to receive less oxygen. The lower oxygen levels will send signals to the body saying hemoglobin levels are low (Mckinley 60). This will result in an increase hemoglobin production and reticulocytes. 4.Mrs. Carlyle’s sister has had two miscarriages before seeking medical help with her third pregnancy. Blood typing shows that she, like her sister, is Rh negative; her husband is Rh positive. What course of treatment will be followed? The course of treatment that would be followed is giving her special immunoglobulins (ex. RhoGAM). The immunoglobulins will stop the mother from making anti-D antibodies (Dantibodies destroy fetal erythrocytes). This is crucial so that the newborn does not get HDN or hyperbilirubinemia (Mckinley 721). Source: MCKINLEY, MICHAEL.Anatomy and Physiology an Integrative Approach. MCGRAW-HILL US HIGHER ED, 202 1 A bone marrow biopsy of Mr. Bongalonga, a man on a long-term drug therapy, shows an abnormally high percentage of nonhematopoietic connective tissue. What condition does this indicate? If the symptoms are critical, what short-term and longterm treatments are indicated? Will infusion of whole blood or packed red cells be more likely? This is indicative of aplastic anemia, as is shows abnormally high percentages of nonhematopoietic connective tissue, which is a big symptom. Short-term effects may require a blood transfusion, but if his condition worsens, he's going to need a bone marrow transplant. Also, the blood should be packed with RBCs because the patient is hardly making any. A woman comes to the clinic complaining of fatigue, shortness of breath, and chills. Blood tests show anemia, and a bleeding ulcer is diagnosed. What type of anemia is this? The symptoms that the woman is displaying definietly make it iron-deficiency anemia. It's more common in women, and the lack of iron in the diet or slow/prolonged bleeding depletes iron reserves that are needed for producing hemoglobin. A patient is diagnosed with bone marrow cancer and has a hematocrit of 70 percent. What is this condition called? They have a condition called polycythemia vera, which is a condition that results from bone marrow cancer. Polycythemia may result in being out of breath. A middle-aged college professor from Boston is in the Swiss Alps studying astronomy. He arrived two days ago and plans to stay the entire year. However, he notices that he is short of breath when he walks up steps and that he tires easily with any physical activity. His symptoms gradually disappear; after two months, he has a complete physical exam and is told that his erythrocyte count is higher than normal. Attempt to explain this finding. Will his RBC count remain at this higher-than-normal level? Why or why not? He has secondary polycythemia, which can result from bone marrow cancer, or can just happen due to the increase in altitude. What happens is that excessive numbers of RBCs is increased blood viscosity, which causes it to flow sluggishly in the body and impairs circulation. His RBC count should decrease once he leaves the Alps. Why is someone more likely to bleed to death when an artery is cleanly severed than when it is crushed and torn? A person is more likely to bleed to death when an artery is cleanly severed, because there isn't any more artery left, so there's lots of open space and nowhere for the clotting process to begin. Think of it like a garden hose - if it's cleanly severed, lots of water flows through, but if it's mangled, the water has a harder time getting through. 2 Explain how fetal hemoglobin, HbF, enhances oxygen transfer across the placenta from the mother to the fetus. Fetal hemoglobin is better than normal hemoglobin because it has a greater potential to pick up oxygen than normal hemoglobin. It's needed for development. Examination Questions and Answers in Basic Anatomy and Physiology 1. To which of the following would the term “white cell” NOT be applied? A. erythrocyte B. leucocyte C. lymphocyte D. monocyte Answer is A: An erythrocyte is a red blood cell 2. In the haemostasis process, what forms as a result of the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways? A. fibrin B. thrombin C. a platelet plug D. prothrombinase Answer is D: The extrinsic and intrinsic pathways form “prothrombinase” (also called prothrombin activator) from factor X. 3. The blood group known as the ABO system is based on the presence of what proteins on blood cells? A. antibodies B. antigens C. agglutinins D. immunoglobulins Answer is B: Antigens are on the membrane of the rbc. The other three terms all describe the same thing, antibodies that are circulating in the plasma. 4. What is found in blood serum that is also in blood plasma? A. blood cells B. platelets C. plasma proteins D. clotting factors Answer is C: Plasma proteins (except fibrinogen) are in plasma and in serum. Serum = plasma minus the clotting factors. Blood cells and platelets are not in plasma. 5. What is the term “formed elements” used to mean in a description of blood? A. white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets B. blood plasma C. blood serum D. the clotting factors in blood Answer is A: Formed elements are the non-liquid or solute parts of the blood. 6. 7. What type of blood may a patient with blood type “B+” be infused with? Any blood that is 3 A. positive for rhesus antigen D B. negative for rhesus antigen D C. negative for antigen B D. negative for antigen A Answer is D: A patient that is B+ may receive B+, B−, O+ or O− blood because those types do not have antigen A in the plasma. 8. What is the first process that occurs after a blood vessel is damaged? A. coagulation B. platelet plug formation C. vasoconstriction D. haemolysis Answer is C: Almost immediately (within 2 secs) after a blood vessel is cut the vessel walls contract in a spasm to slow the flow of blood (vessel diameter decreases). 9. Which blood cells are involved in protecting the body from pathogens and foreign cells? A. erythrocytes B. leucocytes C. platelets D. haemoglobin Answer is B: Leucocytes (white blood cells) include NK (natural killer), T & B lymphocytes & macrophages & microphages. 10. Which individuals can receive any type of blood and are considered universal recipients? A. A+ B. O− C. AB+ D. B− Answer is C: People with AB+ blood do not have agglutinins (antibodies) against A, B, or D in their plasma. Hence can receive any blood without causing the rbc in the donated blood to clump. 11. Which is the most abundant plasma protein? A. alpha- and beta- globulins B. albumin C. mitochondria D. haemoglobin Answer is B: About 58 % of plasma proteins are albumins. Haemoglobin is a protein but it is contained within the rbc. 12. Which characteristic of blood refers to the concentration of solutes? A. salinity B. pH C. osmolality D. viscosity Answer is C: Osmolality is the number of osmoles (osmol) of solute per kilogram of solvent. (osmolarity (with an “r”) is defined as the number of osmoles of solute per litre of solution). 13. Which type of white blood cell is responsible for engulfing pathogens during phagocytosis? A. thrombocyte B. neutrophil C. erythrocyte D. basophil Answer is B: Neutrophils are microphages – phagocytes of bacteria. Thrombocytes and erythrocytes are not wbc. 4 14. What does “Rhesus positive” refer to? A. The presence of antigen D on the surface of red blood cells B. The final factor involved in blood clotting C. The presence of the rhesus antibody/agglutinin in the blood D. A deficiency of Factor VIII that results in haemophilia Answer is A: Rh factor, Rh positive and Rh negative refer to the D antigen only. If the antigen is present on your rbc, you are called Rh-positive (you have the Rh factor). 15. What are red blood cells primarily composed of? A. alpha- and beta- globulins B. albumin C. mitochondria D. haemoglobin Answer is D: About one third of the mass of a rbc is haemoglobin. Choices A & B are plasma proteins and are not in rbc. 6. Which is the LEAST common type of white blood cell? A. lymphocyte B. basophil C. thrombocyte D. neutrophil Answer is B: Less than 1 % of wbc are basophils. Neutrophils are the most common. Thrombocytes are not wbc, or even cells. 17. In the process of haemostasis, which phase involves the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways? A. the platelet phase B. the clot lysis phase C. the vascular phase D. the coagulation phase Answer is D: The clotting (coagulation phase) has these two pathways. 18. In haemostasis, which molecule polymerises to become the insoluble blood clot? A. factor X B. thrombin C. fibrin D. plasmin Answer is C: Fibrin is a monomer that polymerises to form a “soft clot”, then crosslinking between fibrin produces a stable, web-like “hard clot”. 19. Which enzyme converts fibrinogen to fibrin? A. serotonin B. thrombin C. renin D. secretin Answer is B: Thrombin is the enzyme. It is not present until prothrombinase converts prothrombin to thrombin. 20. 21. What can be said about a person who has the “A” antigen on their red blood cells? A. their blood contains anti-B agglutinins B. their blood contains anti-A agglutinins C. their blood contains anti-A and anti-B agglutinins D. their blood contains neither anti-A nor anti-B agglutinins Answer is A: Their blood contains anti-B agglutinins. If you have the A antigen 5 on your rbc, you cannot have the anti-A agglutinin in your plasma or you would agglutinate your own blood. 22. Which one of the following is NOT a plasma protein? A. keratin B. albumin C. ferritin D. globulin Answer is A: Keratin is the protein that the stratum corneum of the skin, and that hair and nails are made of. 23. 24. Which statement about neutrophils is correct? A. they have no nucleus B. they contain haemoglobin C. they function as a body defence mechanism D. eosinophils are one type of neutrophil Answer is C: Neutrophils do have a nucleus but don’t have haemoglobin. Eosinophils are a type of wbc as are neutrophils but they are not the same. 25. What are red blood cells also known as? A. erythrocytes B. thrombocytes C. monocytes D. eosinophils Answer is A: rbc = erythrocytes (erythroid means red) 26 27. A person’s blood group is determined by: A. the agglutinogens circulating in their plasma B. the antigens on the surface of their red blood cells C. the antibodies on the surface of their red blood cells D. the agglutinins circulating in their plasma Answer is B: Antigens are on the surface of rbc. Antibodies (=agglutinins) circulate in the blood stream and react with (agglutinate) their appropriate antigen. 28. If a blood sample is taken for DNA testing, which of the following would be examined? A. leucocytes B. erythrocytes C. thrombocytes D. plasma proteins 6 Answer is A: Only leucocytes (wbc) possess a nucleus from which DNA may be sampled. Erythrocytes are anucleate. 29. What is the major task of red blood cells? A. to transport carbon dioxide B. to ensure haemostasis C. to provide immunity D. to transport oxygen Answer is D: Red blood cells contain much haemoglobin which binds to oxygen to it transport to the tissues. 30. Careful blood matching is performed prior to transfusing blood in order to avoid which scenario? يتم إجراء مطابقة دقيقة للدم قبل نقل الدم من أجل تجنب أي سيناريو؟ A. newborn haemolytic disease B. the recipient’s antigens attacking the red blood cells in the transfusion C. the recipient’s antibodies attacking the red blood cells in the transfusion D. the antigens on the recipient’s red blood cells reacting with the antibodies in the transfused blood Answer is C: If the recipient’s antibodies attack the donated rbc, agglutination will occur. The reverse (choice D) is not a problem. 31. Which cell in the list below is the MOST common white blood cell? A. basophils B. lymphocytes C. monocytes D. neutrophils Answer is D: Neutrophils (also called polymorphonuclear leucocytes) constitute between 50 and 70 % of wbc. 32. What substance is the product of the second step in the blood clotting process? A. thrombin B. prothrombin C. prothrombin activator D. fibrin Answer is A: The second step is the formation of thrombin from prothrombin (first step is formation of prothrombinase (=prothrombin activator)). 33. A person whose blood group is “B positive” has which of the following? A. the rhesus D antigen and the B antigen on their rbc, and the anti-A agglutinin. B. the rhesus D antigen and the B antigen on their rbc, and the anti-B agglutinin. C. the rhesus D antigen and the A antigen on their rbc, and the anti-B agglutinin D. no rhesus D antigen and the B antigen on their rbc, and the anti-A agglutinin Answer is A: “B+”, means having the B antigen on rbc and being positive (i.e. having) the D antigen on the rbc as well. 7 34. The role of platelets in blood clotting includes all of the following EXCEPT one. Which one? A. to form a plug in the hole of the damaged blood vessel B. to convert prothrombin to thrombin C. to release chemicals to attract other platelets D. to adhere to exposed collagen fibres in damaged blood vessels Answer is B: Prothombinase is the enzyme that converts prothrombin to thrombin (it does not come from platelets). 35. If someone’s ABO blood group is “type A”, this means that A. they have the type A antigen on their red blood cells B. their blood contains anti-A agglutinins C. they can receive blood from a type B donor D. they may donate blood to a type B recipient Answer is A: Type A means having the A antigen on the rbc (and having anti-B agglutinins in the plasma). 36. Which statement below about vitamin K is true? A. It is water soluble. B. It is essential for prothrombin production by the liver. C. It is part of the “extrinsic pathway” of formation of prothrombin activator. D. It destroys fibrin so allowing a clot to gradually dissolve. Answer is B: Vit K is needed for the liver to produce prothrombin (inactive thrombin). Plasmin destroys fibrin. 37. What is the function of the plasma proteins in blood? A. to transport oxygen. B. to regulate electrolyte balance C. to exert osmotic pressure and so help maintain blood volume. D. to function as a non-specific body defence mechanism. Answer is C: Plasma proteins exist in the plasma but not in the interstitial fluid. Hence their osmotic influence draws water into the blood. Haemoglobin which is not a “plasma protein” transports oxygen. 38. The term “formed elements” used in relation to the blood include which of thefollowing? A. fibrinogen. B. white blood cells. C. electrolytes. D. plasma proteins. Answer is B: White blood cells are one of the formed elements (that is, substances that are not dissolved in plasma) 39. Which blood cell fits the following description: multi-lobed nucleus,inconspicuous cytoplasmic granules, most common type of blood cell except for red blood cells? A. neutrophil 8 B. eosinophil C. basophil D. lymphocyte Answer is A: Neutrophils are the most common wbc and have a large multilobed nucleus. 40. What constitutes blood plasma? A. whole blood without the formed elements. B. blood without the red blood cells. C. whole blood without blood cells and clotting factors. D. blood minus blood cells and proteins. Answer is A: Plasma is blood without the “formed elements”, that is, cells. Choice C refers to serum. 41. Which of the following statements about a person with blood group “A” is true? They have the: A. A antigen on their red blood cells. B. anti-A antibodies in their plasma. C. anti-A agglutinogen on their red blood cells. D. A antibody on their red blood cells. Answer is A: Blood group A is named for having the A antigen on the rbc. 42. Which of the following statements concerning intracellular and extracellular fluids is FALSE? A. The concentration of sodium is higher in extracellular fluid than in intracellular fluid. B. The concentration of potassium is lower in extracellular fluid than in intracellular fluid. C. Blood plasma is an example of intracellular fluid. D. The volume of intracellular fluid is greater than that of extracellular fluid. Answer is C: Blood plasma is external to cells hence is an extracellular fluid. 43. Which of the following is not a type of white blood cell? A. leucocyte B. eosinophil C. erythrocyte D. neutrophil Answer is C: Erythrocytes are red blood cells. 44. Which of the following formed elements of the blood is important in the formation of clots? A. erythrocytes B. lymphocytes C. monocytes D. thrombocytes Answer is D: Thrombocytes (platelets) are attracted by chemicals released by damaged endothelial cells and in turn release substances which cause other platelets to aggregate to form a platelet plug to cover the hole. 9 45. With which blood types can a person with blood type B be safely transfused? A. A or AB B. B or O C. A or O D. B or AB Answer is B: A person with blood type B has anti-A agglutinins in their plasma so cannot receive cells with the A antigen on the rbc. Hence the blood types in choices A, C & D are not suitable. 46. Leucocytes may be correctly described as what? A. cells with nuclei that do not contain hemoglobin. B. cells without nuclei, that contain hemoglobin. C. white blood cells with granules in their cytoplasm. D. neutrophilic. Answer is A: All leucocytes have a nucleus and do not contain haemoglobin. 47. What are lymphocytes? Blood cells that: A. mature and proliferate in the bone marrow. B. contain haemoglobin. C. are involved in the body’s immune response. D. mature into macrophages. Answer is C: Lymphocytes (NK, T & B types) are part of the body’s specific defence mechanism. 48 49. Finish the sentence correctly. Plasma proteins: A. help maintain blood volume due to colloid osmotic pressure. B. are regarded as formed elements of the blood. C. are low molecular weight proteins. D. are part of the blood serum. Answer is A: Plasma proteins are responsible for colloid osmotic pressure. Serum does not include clotting factors – since fibrinogen is a clotting factor and a plasma protein, choice D is incorrect. 50. The colloid osmotic pressure of blood is due to which of the following? A. proteins in the blood B. proteins in the interstitial fluid C. sodium and chloride ions dissolved in blood D. the water component of the blood Answer is A: Plasma proteins (also called “colloids”) produce colloid osmotic pressure. There should be no proteins in the interstitial fluid. 51. Which one of the following terms refers to an abnormally low number of white blood cells? A. thrombocytosis 10 B. haemostasis C. leukopenia D. cytokinesis Answer is C: “Leuko-” refers to wbc; “-penia” refers to abnormally low, or lack of. 52. Which of the following three proteins are known as “plasma proteins”? A. albumin, globulin, haemoglobin B. insulin, glucagon, haemoglobin C. fibrin, globulin, albumin D. albumin, fibrinogen, globulin Answer is D: Haemoglobin is not a plasma protein. Fibrinogen, not fibrin exists in blood. 53. Which are the two most common types of white blood cells? A. neutrophils and lymphocytes B. erythrocytes and neutrophils C. neutrophils and eosinophils D. monocytes and lymphocytes Answer is A: 50–70 % of wbc are neutrophils and another 25 % are lymphocytes. 54. Blood plasma contains “plasma proteins”. Which of the following lists the plasma proteins? A. insulin, kaolin, bilirubin B. cholesterol, urea, glucagon 12 Cardiovascular System C. Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ D. albumins, fibrinogen, globulins Answer is D: None of the other choices list any plasma proteins. 55. What causes the blood’s osmotic pressure to be greater than the osmotic pressure of the surrounding interstitial fluid that is outside of the capillaries? A. there is a higher concentration of sodium and chloride ions in the blood than the interstitial fluid. B. there is a higher concentration of water in the blood than in the interstitial fluid. C. the plasma proteins in blood. D. the hydrostatic pressure produced by the heart’s contractions. Answer is C: Plasma proteins exist in blood but not in the interstitial fluid. 56. What does the term “neutrophil” refer to? A. An affinity for neutrons. B. An abnormally low number of cells. C. A type of white blood cell. D. An immature cell that will become a neutrocyte. Answer is C: Neutrophils are a white blood cell (whose nucleus stains with dyes of neutral pH). 11 57. One of the following cells does NOT occur in blood. Which one? A. erythrocytes B. basophils C. leucocytes D. osteocytes Answer is D: Osteocytes are bone cells. 58. What would a person with type A blood also have? A. antibody A B. antigen A C. agglutinin A D. agglutinogen B Answer is B: Type A blood means that the A antigen is on the red blood cells. They also have antibody B (= agglutinin B) in their plasma. An agglutinogen is an antigen that stimulates production of agglutinin, hence antigen A is also known as agglutinogen A. 12